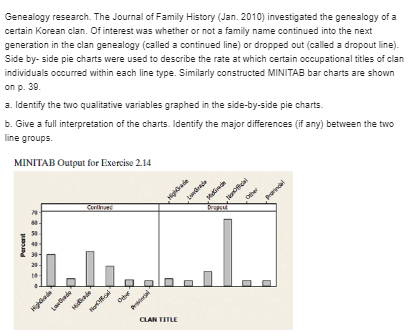
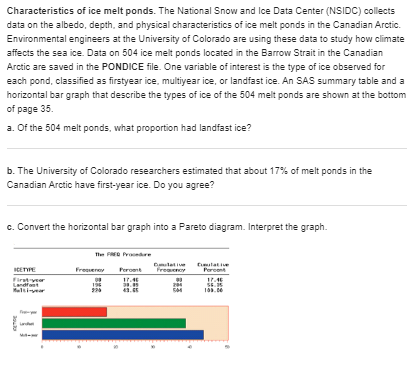
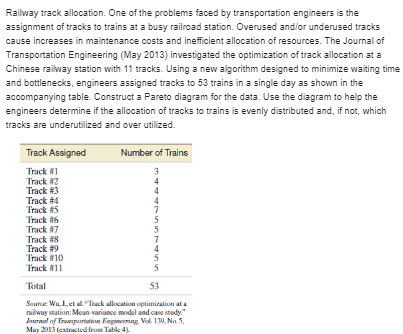
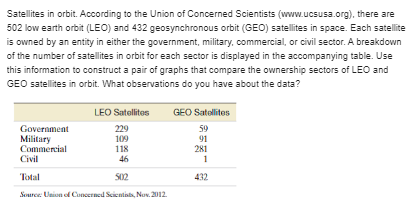
Statistic Problems:-
Use the applet entitled Mean versus Median to find the mean and median of each of the three data sets presented in Exercise 2.59. For each data set, set the lower limit to a number less than all of the data, set the upper limit to a number greater than all of the data, and then click on Update. Click on the approximate location of each data item on the number line. You can get rid of a point by dragging it to the trash can. To clear the graph between data sets, simply click on the trash can. 3. Compare the means and medians generated by the applet with those you calculated by hand in Exercise 2.50. If there are differences, explain why the applet might give values slightly different from the hand-calculated values. b. Despite providing only approximate values of the mean and median of a data set, describe some advantages of using the applet to find those values. (Reference Exercise 2.59) Calculate the mean, median, and mode for each of the following samples: a. 7. -2. 3, 3, 0. 4 b. 2 3, 5. 3. 2, 3. 4. 3, 5. 1, 2. 3. 4 C. 51, 50, 47. 50, 48, 41, 59, 68, 45, 37\f\f\f\fSatellites in orbit. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists (www.ucsusa.org), there are 502 low earth orbit (LEO) and 432 geosynchronous orbit (GEO) satellites in space. Each satellite is owned by an entity in either the government, military, commercial, or civil sector. A breakdown of the number of satellites in orbit for each sector is displayed in the accompanying table. Use this information to construct a pair of graphs that compare the ownership sectors of LEO and GEO satellites in orbit. What observations do you have about the data? LEO Satellites GEO Satellites Government 229 59 Military 109 41 Commercial 118 281 Civil 46 1 Total 432 Source. Union of Concerned Scienlets, Nov. 2012Curbing street gang gun violence. Operation Ceasefire is a program implemented to reduce street gang gun violence in the city of Boston. The effectiveness of the program was examined in the Journal of Quantitative Criminology (Mar. 2014). Over a 5-year period (2008-2010), there were 80 shootings involving a particular Boston street gang (called the Lucerne Street Doggz). The information in the table breaks down these shootings by year and by who was shot (gang members or non-gang members). Note: The Ceasefire program was implemented at the end of 2007. Shootings of Shootings of Total Gang Non-Gang Year Shootings Members Members 2006 37 30 2007 30 22 4 20309 4 2010 Totals 62 18 Source: Hriga, A A, Hercau, D. M., and Papachraions, A. V. "Deterring gang- involved gun violence: Measuring the impact of Boston's Operation Ceasefire on sirect gang behavior."Journal of Downitsnive Criminology, Vol 30, Na. 1, Mar. 2014 (adapted from Figure ]). 3. Construct a Pareto diagram for the total annual shootings involving the Boston street gang. b. Construct a Pareto diagram for the annual shootings of the Boston street gang members. c. Based on the Pareto diagrams, comment on the effectiveness of Operation Ceasefire.Explain the difference between a bar graph and a pie chart.Use the applet Mean versus Median to study the effect that an extreme value has on the difference between the mean and median. Begin by setting appropriate limits and plotting the following data on the number line provided in the applet: 0 6 7 7 8 8 8 9 9 10 a. Describe the shape of the distribution and record the value of the mean and median. On the basis of the shape of the distribution, do the mean and median have the relationship that you would expect? b. Replace the extreme value of 0 with 2, then 4, and then 8. Record the mean and median each time. Describe what is happening to the mean as 0 is replaced, in turn, by the higher numbers stated. What is happening to the median? How is the difference between the mean and the median changing? c. Now replace 0 with 8. What values does the applet give you for the mean and the median? Explain why the mean and the median should now be the same.Complete the following table: Grade on Statistics Exam | Frequency Relative Frequency A: 90-100 .08 B: 80-80 36 C: 65-79 90 D: 50-84 30 F: Below 50 28 Total 200 1.00A qualitative variable with three classes (X, Y, and Z) is measured for each of 20 units randomly sampled from a target population. The data (observed class for each unit) are as follows: X X ZX YYY X XZXYY X Z LY Y Y X a. Compute the frequency for each of the three classes. b. Compute the relative frequency for each of the three classes. c. Display the results from part a in a frequency bar graph. d. Display the results from part b in a pie chart.Study of importance of libraries. In The Canadian Journal of Information and Library Science (Vol. 33, 2000), researchers from the University of Western Ontario reported on mall shoppers opinions about libraries and their importance to today's society. Each in a sample of over 200 mall shoppers was asked the following question: "In today's world, with Internet access and online and large book sellers like Amazon, do you think libraries have become more, less, or the same in importance to their community?" The accompanying graphic summarizes the mall shoppers' responses. a. What type of graph is shown? b. Identify the qualitative variable described in the graph. c. From the graph, identify the most common response. d. Convert the graph into a Pareto diagram. Interpret the results. MOREDo social robots walk or roll? According to the United Nations, social robots now outnumber industrial robots worldwide. A social (or service) robot is designed to entertain, educate, and care for human users. In a paper published by the International Conference on Social Robotics (Vol. 8414, 2010). design engineers investigated the trend in the design of social robots. Using a random sample of 106 social robots obtained through a Web search, the engineers found that 63 were built with legs only. 20 with wheels only, 8 with both legs and wheels, and 15 with neither legs nor wheels. This information is portrayed in the accompanying graphic. 3. What type of graph is used to describe the data? b. Identify the variable measured for each of the 106 robot designs. c. Use the graph to identify the social robot design that is currently used the most. d. Compute class relative frequencies for the different categories shown in the graph. e. Use the results from part d to construct a Pareto diagram for the data. 70 None Both Los Only Whack Only Type of Rolelic Links\f\f