Question: Summarize and relate to a real world event. Use key terms relevant to topic ?! 9-4d Review Organizational Mission, Values, Goals, and Policies and Define
Summarize and relate to a real world event. Use key terms relevant to topic ?!

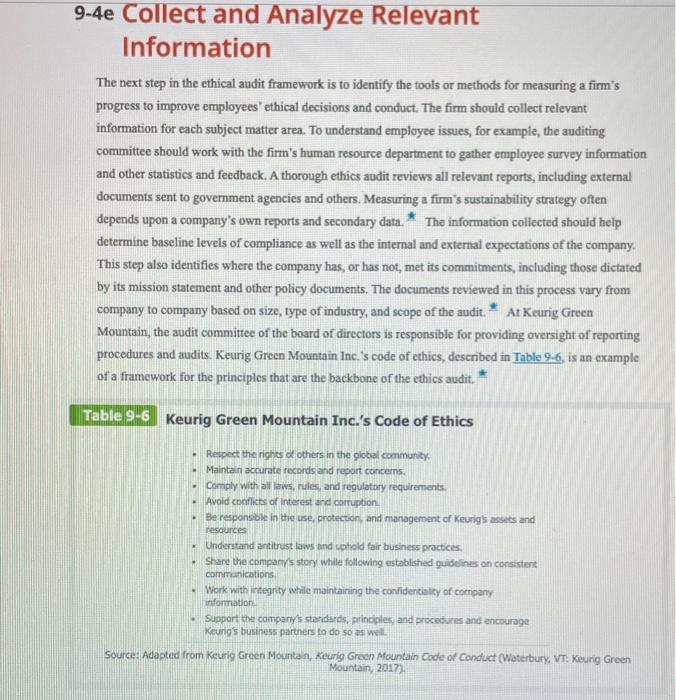
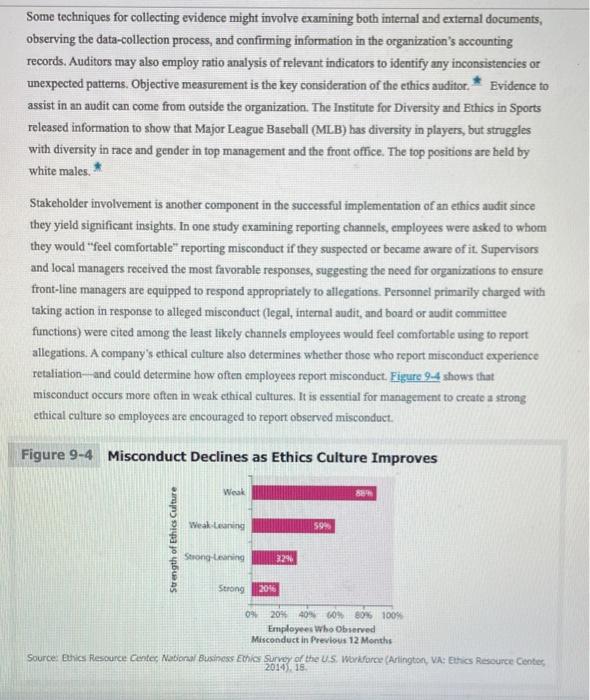
9-4d Review Organizational Mission, Values, Goals, and Policies and Define Ethical Priorities Because ethics audits generally involve comparing an organizations ethical performance to its goals, values, and policies, the audit process should include a review of the mission statement and strategic objectives. A company's overall mission may incorporate ethics objectives, but these may be located in separate documents, including those that focus on social responsibility. For example, a firm's ethics statement or statement of values may offer guidance for managing transactions and human relationships that support the firm's reputation, thereby fostering the confidence of the firm's external stakeholders. Franklin Energy specifies the five core values it uses in managing its business which contributes to its success: ingenuity, results orientation, frugality, integrity, and environmental stewardship This review should include an examination of all formal documents that make explicit commitments to ethical, legal, or social responsibility, as well as less formal documents. Informal documents include marketing materials, workplace policies, ethics policies, and standards for suppliers or vendors. This review may reveal a need to create additional statements to fill the identified gaps or create a new comprehensive mission statement or ethical policy that addresses any deficiencies. It is important to examine all of the firm's policies and practices with respect to the specific areas covered by the audit. In an audit that scrutinizes discrimination issues, this review step would consider the company's goals and objectives as well as its policies related to discrimination. It would consider the means available for communicating the timm's policies and assess their effectiveness. Such an evaluation should look at whether and how managers are rewarded for meeting their goals and the systems employees have to give and receive feedback. An effective ethics audit reviews all these systems and assesses their strengths and weaknesses. Concurrent with this step in the auditing process, the firm should define its ethical priorities. Determining these priorities is a balancing act because identifying the needs and assessing the priorities of each stakeholder can be difficult. Because there are no legal requirements for ethical priorities, it is up to management's strategic planning processes to determine risks, designate appropriate standards, and outline processes of communication with stakeholders. It is important to articulate the firm's ethical priorities and values as a set of parameters or performance Indicators that can be objectively and quantitatively assessed Because the ethics audit is a structured report with quantitative and descriptive assessments, actions should be measurable by quantitative indicators. However, it is sometimes not possible to go beyond description At some point, a firm must demonstrate action-oriented responsiveness to ethics issues of top priority. Electricity and gas company National Grid has a long history of minimizing damage to the environment. The firm adopted the international standard for environmental management systems, ISO 14001, and the guidelines that require extemal auditing by a certified auditor. Additionally, National Grid has a global Corporate Responsibility Summary Report on its website. 9-4e Collect and Analyze Relevant Information The next step in the ethical audit framework is to identify the tools or methods for measuring a firm's progress to improve employees' ethical decisions and conduct. The firm should collect relevant information for each subject matter area. To understand employee issues, for example, the auditing committee should work with the firm's human resource department to gather employee survey information and other statistics and feedback. A thorough ethics audit reviews all relevant reports, including external documents sent to government agencies and others. Measuring a firm's sustainability strategy often depends upon a company's own reports and secondary data. The information collected should help determine baseline levels of compliance as well as the internal and external expectations of the company. This step also identifies where the company has, or has not, met its commitments, including those dictated by its mission statement and other policy documents. The documents reviewed in this process vary from company to company based on size, type of industry, and scope of the audit. * At Keurig Green Mountain, the audit committee of the board of directors is responsible for providing oversight of reporting procedures and audits. Keurig Green Mountain Inc. is code of ethics, described in Table 9-6, is an example of a framework for the principles that are the backbone of the ethics audit. * Table 9-6 Keurig Green Mountain Inc.'s Code of Ethics - Respect the rights of others in the global community Maintain accurate records and report concerns. Comply with all laws, rules, and regulatory requirements. Avoid conflicts of interest and corruption Be responsible in the use, protection, and management of Keurig's assets and resources Understand antitrust laws and uphold fair business practices Share the company's story while following established guidelines on consistent communications - Work with integrity while maintaining the confidentiality of company information - Support the company's standards, principles, and procedures and encourage Keurios business partners to do so as well. Source Adapted from Keurig Green Mountain, Keurig Green Mountain Code of Conduct (Waterbury, VT: Keurig Green Mountain, 2017) Some techniques for collecting evidence might involve examining both internal and external documents, observing the data-collection process, and confirming information in the organization's accounting records. Auditors may also employ ratio analysis of relevant indicators to identify any inconsistencies or unexpected patterns. Objective measurement is the key consideration of the ethics auditor. * Evidence to assist in an audit can come from outside the organization. The Institute for Diversity and Ethics in Sports released information to show that Major League Baseball (MLB) has diversity in players, but struggles with diversity in race and gender in top management and the front office. The top positions are held by white males. * Stakeholder involvement is another component in the successful implementation of an ethics audit since they yield significant insights. In one study examining reporting channels, employees were asked to whom they would "feel comfortable reporting misconduct if they suspected or became aware of it. Supervisors and local managers received the most favorable responses, suggesting the need for organizations to ensure front-line managers are equipped to respond appropriately to allegations. Personnel primarily charged with taking action in response to alleged misconduct (legal, internal audit, and board or audit committee functions) were cited among the least likely channels employees would feel comfortable using to report allegations. A company's ethical culture also determines whether those who report misconduct experience retaliation--and could determine how often employees report misconduct. Figure 9-4 shows that misconduct occurs more often in weak ethical cultures. It is essential for management to create a strong ethical culture so employees are encouraged to report observed misconduct. Figure 9-4 Misconduct Declines as Ethics Culture Improves Weak Web Leaning 594 Strength of Ethics Culture Strong eng 329 Strong 20% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Employees who Observed Misconduct in Previous 12 Months Source: Ethics Resource Center National Business Ethics Survey of the US. Workforce (Arlington, VA: Ethics Resource Center 2014). 15 Because integrating the stakeholder feedback step in the ethics audit process is so crucial, these stakeholders must be defined and interviewed during the data collection stage. For most companies, stakeholders include employees, customers, investors, suppliers, community groups, regulators, nongovernment organizations, and the media. Both social and ethics audits typically interview and conduct focus groups with these stakeholders to gain an understanding of their perception of the company. The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) conducted an ethics audit to determine whether control activities had been implemented that effectively emphasized the importance of values and ethics in achieving organizational goals. The CSA used staff interviews and reviews of internal documentation to determine how values and ethics were communicated and integrated within the organization. * Some companies might also choose to survey customers and other stakeholders in order to gain a view of their ethics program from all angles. The more stakeholders auditors include in this measurement stage, the more time and resources the audit consumes. However, a larger sample of stakeholders yields a useful variety of opinions about the company. Multinational corporations must decide whether to include in the audit only the main office or all facilities around the globe. * Because employees carry out business operations, understanding employee issues is vital to a successful audit. Useful indicators include staff tumover and employee satisfaction. High tumover rates could indicate poor working conditions, an unethical culture, inadequate compensation, or general employee dissatisfaction. Companies can analyze these factors to determine key areas for improvement. * Questionnaires that survey employees' perceptions of the ethics of their company serve as benchmarks in an ongoing assessment of ethical performance. Then, if unethical behavior increases, management will better understand what types of unethical practices may be occurring and why. Most organizations recognize employees behave in ways that lead to recognition and rewards and avoid behavior resulting in punishment. Therefore, companies can design and implement human resource policies and procedures for recruiting, hiring, promoting, compensating, and rewarding employees that encourage ethical behavior Customers are another primary stakeholder group because their patronage and loyalty determines a company's financial success. Providing meaningful feedback is critical to creating and maintaining customer satisfaction. Through surveys and customer-initiated communication systems such as response cards, online social networks, email, and toll-free numbers, organizations can monitor and respond to customer issues and its perceived social performance. Procter & Gamble uses online social networking sites like Facebook to determine what social issues consumers are passionate about, as well as to gain Insights into consumers' product needs and reactions to products. A growing number of investors seek to include in their investment portfolios the stocks of companies that conduct ethics and social audits. Investors are more aware of the financial benefits that stem from socially responsible management systemsas well as the negative consequences of a lack of responsibility. Even allegations of potential misconduct can harm a company in the short run. Share prices for direct selling skincare company Nu Skin plummeted after allegations arose that the company was operating a pyramid scheme in China. Nu Skin later paid $S40,000 to China for misleading claims made by its distributors and for selling products approved for retail stores through direct selling. Neither of these activities constitutes a pyramid scheme. The mass media often makes pyramid scheme accusations whenever direct sellers have allegedly engaged in any misconduct. Although shares have now recovered, the immediate aftermath of the accusations caused investors to panic, and share prices dropped by 37 percent. Even the hint of wrongdoing can affect a company's relations with investors. Many investors simply do not want to invest in companies engaging in unfavorable business practices, such as the use of sweatshops or child labor. The $100 billion chocolate industry has been accused of child labor in the raw materials. Many companies like The Hershey Company, Mars Inc., Nestl, and Cadbury are also being accused of taking a blind eye to this reality. In response, their stock prices dropped as investors shunned them. However, since it was first reported almost every name-brand chocolate maker has created or expanded its sustainability programs aimed at tackling the child labor issue by improving the lot of farmers-from Nestle's Cocoa Plan to Mondelez's Cocoa Life to Hershey's 21st-Century Plan * It is therefore critical that companies understand the issues of this important group of stakeholders and their expectations, both financially and socially Organizations can obtain feedback from stakeholders through standardized surveys, interviews, and focus groups. Companies can encourage stakeholder exchanges by inviting specific groups together for discussions. Such meetings may include an office or theility tour or a field trip by company representatives to sites in the community. Regardless of how companies collect information about stakeholders' views, the primary objective is to generate opinions about how the company is perceived and whether it is fulfilling stakeholders' expectations, Once this information is collected the firm should compare the internal perceptions to those identified in the stakeholder lissessment and summarize its findings. During this phase, the audit committee should draw some conclusions about the information obtained in the previous stages. These conclusions may include descriptive assessments of the findings, such as the costs and benefits of the company's ethics program the strengths and weaknesses of the firm's policies and practices, the nature of feedback from stakeholders, and issues to be addressed in future audits. In some cases, it may be appropriate to see how the findings fit with standards identified earlier, both quantitatively and qualitatively. * Data analysis should include an examination of other organizations in the industry and their performance in the designated subject areas. The audit committee can investigate the successes of another firm considered the best in a particular area and compare that company's performance to their own. Some common benchmarks available from corporate ethics audits are employee or customer satisfaction, community groups' perceptions, and the impact of the company's philanthropy. For example, the Ethics and Compliance Association (ECA) conducts rescarch on legal and ethical issues in the workplace. These studies allow ECA members to compare their responses to the aggregate results obtained through the study Such comparisons can assist the audit committee to identify best practices for a particular industry or establish a baseline for minimum ethies requirements. A wide variety of standards are emerging that apply to ethics accountability. The aim of these standards is to create a tool for benchmarking and a framework for businesses to follow