Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
table 4.3 and 4.4 Solution Table 4.2: Measured pH of different solutions. Color Approximate pH Acidic/Basic/Neutral 2. 100 mM HCI 0.1 MM HCI 100 mM
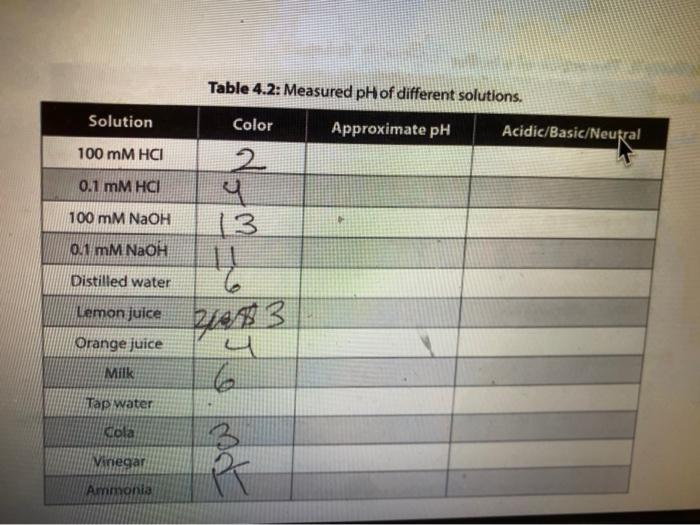

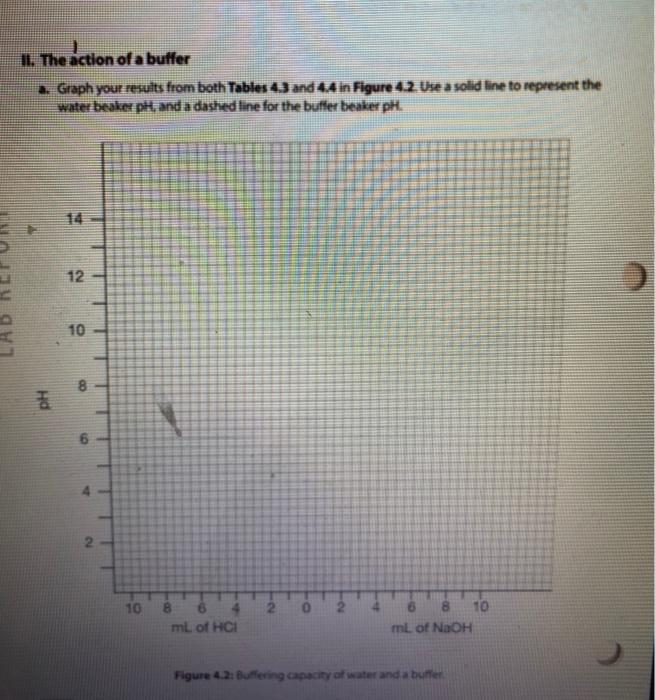
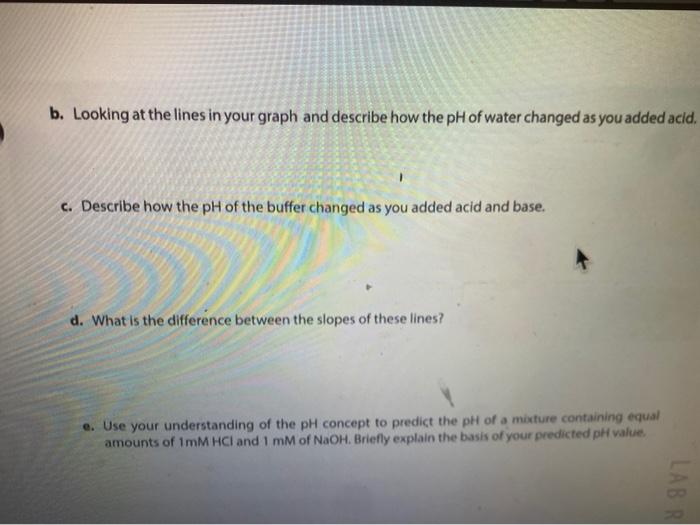
table 4.3 and 4.4 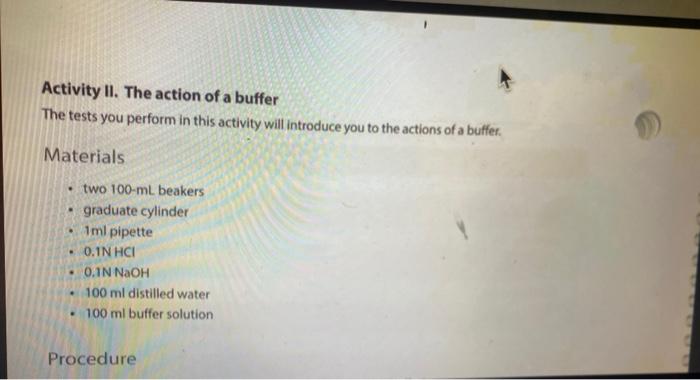
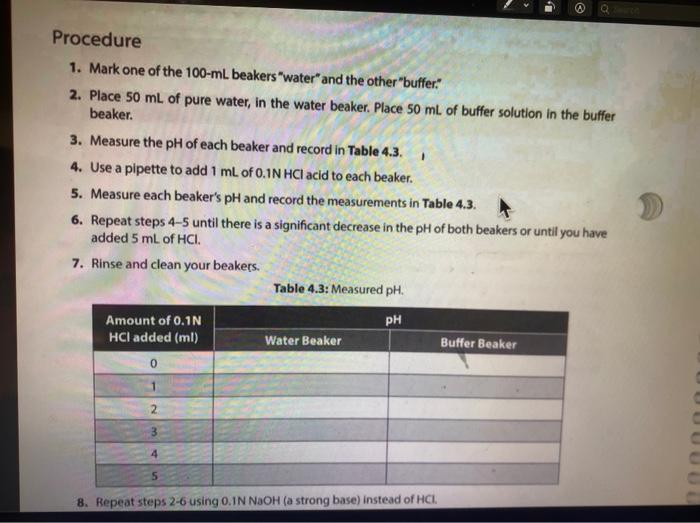

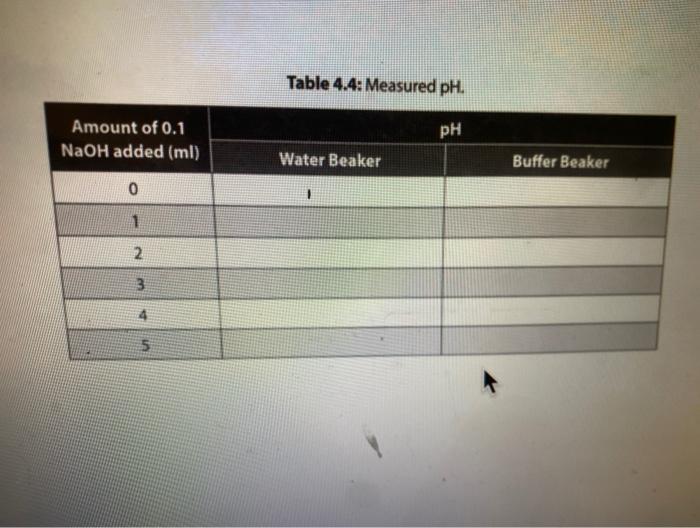
Solution Table 4.2: Measured pH of different solutions. Color Approximate pH Acidic/Basic/Neutral 2. 100 mM HCI 0.1 MM HCI 100 mM NaOH (3 0.1 mM NAOH Distilled water Lemon juice Orange juice Milk Tap water kola Vinegar red Ammonia g. Compare the pH of milk and vinegar, which one is more acidic? How much is the difference between pH of these two solutions? How much is the difference between the hydrogen ion (H+) concentrations of these two solutions? Show your work. 11. The action of a buffer a. Graph your results from both Tables 43 and 4.4 in Figure 4:2. Use a solid line to represent the water beaker pis, and a dashed line for the butter beaker ph. 14 12 T 1 10 8 pH 2 2 10 8 6 mL of HCI 4 6 8 10 mL of NAOH Figure 4.2. Buffering capacity of water and a butter b. Looking at the lines in your graph and describe how the pH of water changed as you added acid. c. Describe how the pH of the buffer changed as you added acid and base. d. What is the difference between the slopes of these lines? e. Use your understanding of the pH concept to predict the pH of a mixture containing equal amounts of ImM HCl and 1 mM of NaOH. Briefly explain the basis of your predicted pH value LABR Activity II. The action of a buffer The tests you perform in this activity will introduce you to the actions of a buffer. Materials two 100-ml beakers graduate cylinder Iml pipette 0,1N HCI : 0,1N NaOH 100 ml distilled water 100 ml buffer solution Procedure Procedure 1. Mark one of the 100-ml. beakers water and the other "buffer: 2. Place 50 mL of pure water, in the water beaker. Place 50 mL of buffer solution in the buffer beaker. 3. Measure the pH of each beaker and record in Table 4.3. 4. Use a pipette to add 1 ml of 0.1N HCl acid to each beaker. 5. Measure each beaker's pH and record the measurements in Table 4.3. 6. Repeat steps 4-5 until there is a significant decrease in the pH of both beakers or until you have added 5 mL of HCI 7. Rinse and clean your beakers. Table 4.3: Measured pH. 1 PH Amount of 0.1N HCI added (ml) 0 Water Beaker Buffer Beaker 2 4 8. Repeat steps 2-6 using O. IN NaOH (a strong base) instead of HCI. 8. Repeat steps 2-6 using 0.1N NaOH (a strong base) instead of HCI. 9. Record your results in Table 4.4. 10. Continue until there is a significant increase in the pH of both beakers or until you have added 5 ml. of NaOH. 11. Rinse and clean your beakers Table 4.4: Measured pH. Amount of 0.1 NaOH added (ml) Water Beaker Buffer Beaker 0 1 2 3 5 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


