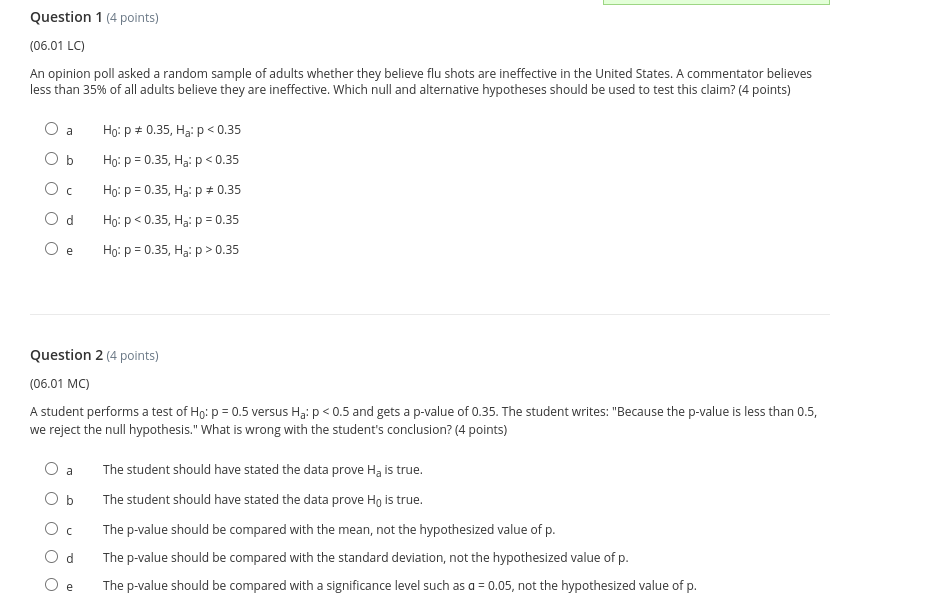
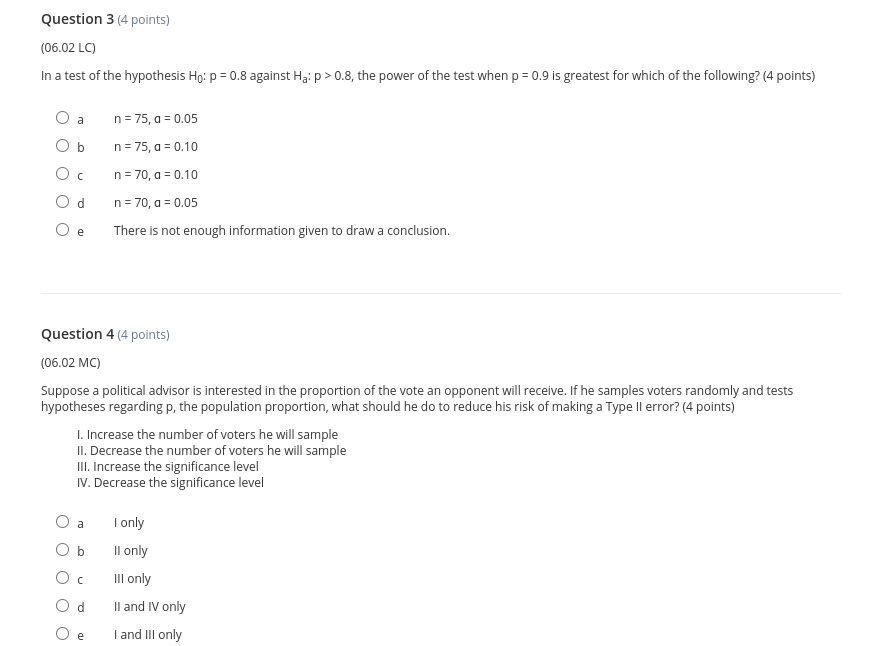
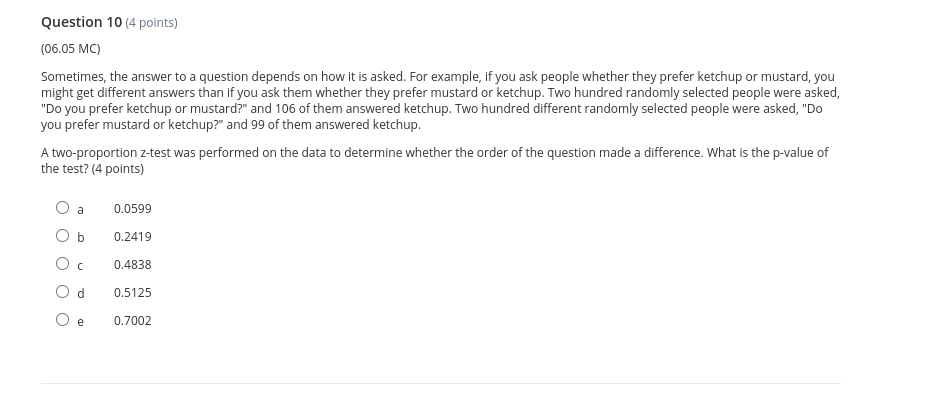
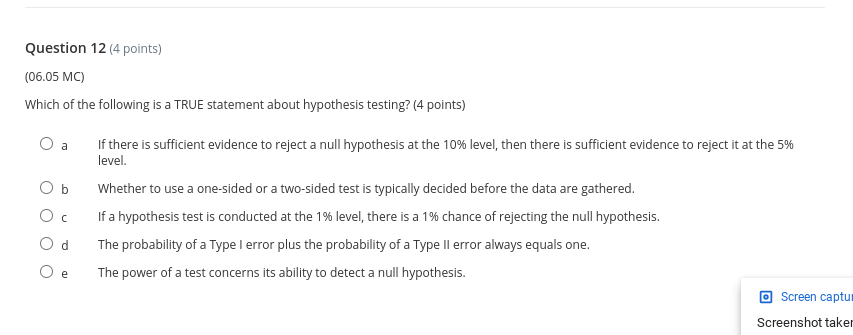
Thank you so much.
Question 1 (4 points) (06.05 LC) At a large corporation, 25% of a random sample of male employees have an average salary of $75,000 or higher. A random sample of female employees shows that 20% have an average salary of $75,000 or higher. A representative for the Equal Pay Act wants to determine whether there is evidence of a difference in salaries between males and females. What would she write as the null and alternative hypotheses for this situation? (4 points) O a Ho:P1 - P2 = 0 and Ha:P1 - P2 > 0 Ob Ho:P1 - P2 = 0 and Haip1 - P2 0 and Ha:P1 - P2 = 0 O e Ho:P1 - P2 > 0 and Haip1 - P2 # 0Question 2 (4 points) (06.05 LC) Which of the following conditions must be met to conduct a two-proportion significance test? (4 points) I. The sample sizes are greater than 20. II. The probabilities of success multiplied by the sample sizes are greater than one and the probabilities of failure multiplied by the sample sizes are greater than one for each population. Ill. The populations are independent. O a I only Ob II only OC Ill only O d I and II only O e I, ll, and IllQuestion 3 (4 points) (06.05 MC) A new anxiety medication has been manufactured and a study is being conducted to determine whether its effectiveness depends on dose. When 40 milligrams of the medication was administered to a simple random sample (SRS) of 60 patients, 21 of them demonstrated lower stress levels. When 75 milligrams of the medication was administrated to another SRS of 85 patients, 34 of them demonstrated lower stress levels. Which of the following test statistics is an appropriate hypothesis test? (4 points) a ( 0.35-0.4)-0 Z= 0.3793 ( 1-0.3793 ) 0.3793 (1-0.3793 ) + 60 85 Ob ( 0.35-0.4)-0 Z= 0.3793 ( 1-0.3793 ) 0.3793 ( 1-0.3793 ) 145 145 OC (0.35-0.4 )-0 Z= 0.35 ( 1-0.35 ) 0.4 (1-0.4 ) 60 85 O d ( 0.35-0.4)-0 Z= 0.35 ( 1-0.35 ) 0.4 (1-0.4) 145 145 Oe ( 0.35-0.4)-0 Z= 0.3793 ( 1-0.3793 ) 0.3793 ( 1-0.3793 ) 40 75Question 4 (4 points) (06.05 MC) For a hypothesis test of Ho:p1 - p2 = 0 against the alternative Ha:p1 - p2 # 0, the test statistic is found to be 2.2. Which of the following statements can you make about this finding? (4 points) O a The result is significant at both a = 0.05 and a = 0.01. Ob The result is significant at a = 0.05 but not at a = 0.01. O c The result is significant at a = 0.01 but not at a = 0.05. Od The result is not significant at either a = 0.05 or a = 0.01. Oe The result is inconclusive because we don't know the value of p.Question 5 (4 points) (06.05 HC) A new technical cooking class compared 4,200 students who had not taken the class with 3,275 students who did. Of those students who did not take the cooking class, 2,760 increased their scores on the chef's examination compared to 2,135 who did take the class. A significance test was conducted to determine whether there is evidence that the students who took the cooking class were more likely to increase their scores on the chef's exam. What is the p-value for an appropriate hypothesis test? (4 points) O a 0.3184 Ob 0.6367 OC 0.6816 Od 0 OeQuestion 1 (4 points) (06.01 LC) An opinion poll asked a random sample of adults whether they believe flu shots are ineffective in the United States. A commentator believes less than 35% of all adults believe they are ineffective. Which null and alternative hypotheses should be used to test this claim? (4 points) O a Ho: p # 0.35, Ha: p 0.35 Question 2 (4 points) (06.01 MC) A student performs a test of Ho: p = 0.5 versus Ha: p 0.8, the power of the test when p = 0.9 is greatest for which of the following? (4 points) O a n = 75, a = 0.05 Ob n = 75, a = 0.10 OC n = 70, a = 0.10 Od n = 70, a = 0.05 O e There is not enough information given to draw a conclusion. Question 4 (4 points) (06.02 MC) Suppose a political advisor is interested in the proportion of the vote an opponent will receive. If he samples voters randomly and tests hypotheses regarding p, the population proportion, what should he do to reduce his risk of making a Type II error? (4 points) I. Increase the number of voters he will sample Il. Decrease the number of voters he will sample Ill. Increase the significance level IV. Decrease the significance level O a I only Ob II only O c Ill only O d ll and IV only O e I and Ill onlyQuestion 5 (4 points) (06.02 MC) Officials of a hunting club want to know whether a majority of members support a 1% increase in monthly dues to fund a hunting trip across the country. To investigate, they survey a random sample of 100 members and use the results to test the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.50 and Ha: p > 0.50, where p is the proportion of all members who support a 1% increase in monthly dues to fund a cross-country trip. In the context of this study, how could a Type II error occur? (4 points) O a The hunting club officials find convincing evidence that a majority of members supports the dues increase, when in reality there isn't convincing evidence that a majority supports the increase. Ob The hunting club officials find convincing evidence that a majority of members support the dues increase, when in reality, at most, 50% of the members supports the increase. OC The hunting club officials find convincing evidence that a majority of members support the monthly increase, when in reality more than 50% of the members do support the increase. O d The hunting club officials do not find convincing evidence that a majority of members support the dues increase, when in reality more than 50% of the members do support the increase. Oe The hunting club officials do not find convincing evidence that a majority of homeowners support the dues increase, when in reality, at most, 50% of the members do support the increase.Question 6 (4 points) (06.02 MC) A female is picked up by the police for stealing jewelry, but she claims she is innocent and this is a case of mistaken identity. The case goes to trial and the judge informs the jury the accused is innocent until she is proved guilty. That is, jurors should find her guilty only if there is overwhelming evidence to reject the assumption of innocence. What risk is involved in the jury making a Type II error? (4 points) O a She is guilty, but the jury finds her innocent and she goes free. Ob She is guilty, and the jury finds her guilty, and she goes to jail. OC She is innocent, and the jury finds her innocent, and she goes free. O d She is innocent, but the jury finds her guilty, and she goes to jail. O e A conclusion cannot be made based on the information given.Question 7 (4 points) (06.04 MC) A few months before a high school election, 200 individuals responded to a survey of 500 randomly selected students, indicating they favored candidate X for class president (p 1 = 0.4). One month before the election, a second survey of 700 students is conducted and 450 individuals respond who indicate they favor candidate X (p 2 = 0.6429). A 98% two-proportion z confidence interval for the true difference between the proportions favoring candidate X in the first and second surveys was constructed and found to be (-0.3090, -0.1767). Which of the following is the best interpretation of this interval? (4 points) O a There has been no change in support for candidate X. Ob There has been a significant decrease in support for candidate X. O c There has been a significant gain in support for candidate X. O d Because the confidence interval is negative, the candidate is unlikely to win a majority of votes in the general election. O e Because support for candidate X has increased more than 50%, this candidate is likely to win a majority of votes in the general election.Question 8 (4 points) (06.04 LC) Do electric lights on the beach affect the birth rate of sea turtles? A study in a local paper reported that, although 24 of 60 shielded (from lights) eggs hatched, only 21 of 70 unshielded eggs hatched. Which of the following is the 99% confidence interval for the true difference between the proportions of shielded and unshielded eggs that hatch? (4 points) O a 24 24 21 21 1 - 24 21 60 60 70 70 +1.961 + 60 70 60 70 Ob 24 21 45 65 + 2.576 + 60 70 130 130 60 70 OC 24 21 45 65 11.96 + 60 70 130 130 60 70 O d 24 21 45 65 24 21 + 2.576 + 60 70 V 130 1 130 60 70 O e 24 24 21 21 1 - 60 70 24 21 60 70 + 2.5761 + 60 70 60 70Question 9 (5 points) (06.05 MC) A researcher wants to determine whether a newly developed antidrug program can be successful. She lets py equal the proportion of students who succeed in the control program and py equal the proportion of students who succeed in the newly developed program (the treatment program). A test of Ho: P1 = pz and Ha p1 # p2 is performed on a sample of 500 high school students accused of using drugs at their school. These students are divided randomly into two groups of 250 students. Each group receives a set of antidrug materials and a lecture from a teacher and an ex-drug user about the dangers of drug use. In addition, the treatment group receives materials from the newly developed program. At the end of two months, 148 of the 250 people in the control group (the group that did not receive the new materials) report they no longer use drugs. Of the 250 people in the treatment group, 175 report they no longer use drugs. Using a significance level of a = 0.05, which of the following is an appropriate conclusion for this study? (5 points) O a Because the p-value of this test is greater than a = 0.05, we cannot conclude the newly developed program is significantly different from the control program at reducing drug use. Ob Because the proportion of people who have quit using drugs in the experimental group is greater than in the control group, we can conclude the new program is effective at reducing drug use. O c Because the p-value of this test is less than a = 0.05, we can conclude the newly developed program is significantly different from the control program at reducing drug use. O d Because the difference in the proportions of those who have quit using drugs in the control group (59.2%) and the experimental group (70%) is so small, we cannot conclude there is a statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of reducing drug use. O e The standard deviation of the difference between the two sample proportions is about 0.0764. This deviation is so small it provides good evidence that the new program is more effective at reducing drug use.Question 10 (4 points) {06.05 MC} Sometlmesr the answer to a question depends on how It is asked. For example, If you ask people whether they prefer ketchup or mustard. you might get different answers than If you ask them whether they prefer mustard or ketchup. Two hundred randomly selected people were asked, "Do you prefer ketchup or mustard?" and 106 ofthem answered ketchup. Two hundred different randomly selected people were asked, "Do you prefer mustard or ketchup?" and 99 of them answered ketchup. A twop roportion ztest was performed on the data to determine whether the order of the question made a difference. What is the pualue of the test? [4 points} 0 a 0.0599 0 b 0.2419 0 c 0.4333 0 d 0.5125 0 e 0.?002 Question 11 (5 points) (06.05 LC) A sample survey was used to interview a simple random sample of 300 female college students and 350 male college students. Researchers want to determine whether more males, in the proportion of male and female college students, had a pet the previous semester. In all, 246 females and 312 males reported they had a pet the previous semester. Take pm and py to be the proportions of all college males and females, respectively, who had a pet the previous semester. Which hypotheses are to be tested? (5 points) O a Ho: Pm - pf = 0 versus Hai Pm - Pf * 0 Ob Ho: Pm - pf = 0 versus Hai Pm - Pf > 0 OC Ho: Pm - Pf = 0 versus Hai Pm - Pf 0 versus Hai Pm - Pf = 0 O e Ho: Pm - pf * 0 versus Hai Pm - Pf = 0Question 12 (4 points) (06.05 MC) Which of the following is a TRUE statement about hypothesis testing? (4 points) Oa If there is sufficient evidence to reject a null hypothesis at the 10% level, then there is sufficient evidence to reject it at the 5% level. Ob Whether to use a one-sided or a two-sided test is typically decided before the data are gathered. OC If a hypothesis test is conducted at the 1% level, there is a 1% chance of rejecting the null hypothesis. O d The probability of a Type I error plus the probability of a Type II error always equals one. O e The power of a test concerns its ability to detect a null hypothesis. Screen captur Screenshot take