Question
The Association of Computing Machinery (ACM), one of the largest computing associations in the world, is having difficulty maintaining its membership information because its information
The Association of Computing Machinery (ACM), one of the largest computing associations in the world, is having difficulty maintaining its membership information because its information system is old and no longer reflects its growing needs. The following is a typical national organizational hierarchy of the ACM in the US.
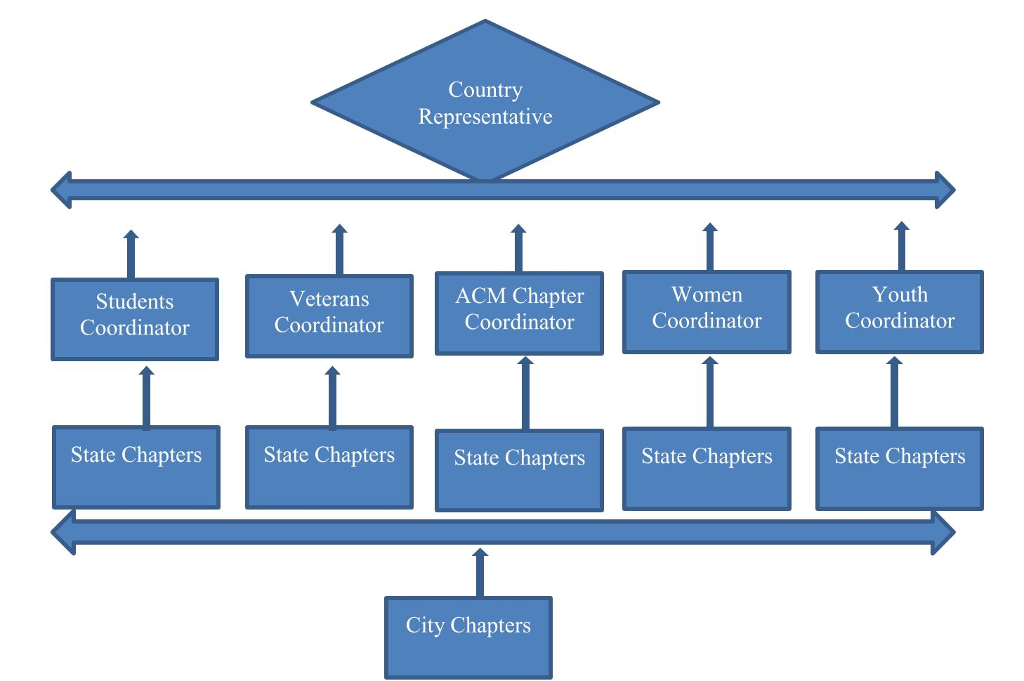
As can be seen above, the ACM is big organization with a complex leadership structure.
The organization currently has chapters in 17 states. These are Texas, Tennessee, Missouri, Nebraska, Minnesota, Iowa, South Dakota, North Dakota, New York, District of Columbia, Alaska, Maine, Washington, Colorado, Arizona, California, and Utah.
In order to be an ACM member, you apply for ACM membership in the city or state where you reside. Once membership is granted and membership dues are paid, you have a full ACM membership with all of its privileges. In addition, it is possible to apply for a sub-membership. There are four sub-memberships types available. These are student, youth, veteran, and women. Each of the four sub-entities has its own chapters in the 17 states as well. Because each sub-membership comes with its perks, there are additional membership subscription fees to become a member, but you have to be a full ACM member before you can qualify for a sub-membership. Also, some members are employed in the offices of the Representative and the Chapter Coordinator and may be required to pay occasional minimal dues.
Reporting mechanism are upward. This means the lowest entity reports to the one above it. To be specific, ACM city chapters report to their state chapter leadership. For instance, state leaders for students, youth, women, and veteran chapters report to their national coordinators; ACM state chapter chairman/chairwomen reports to the ACM Chapter Coordinator; the ACM Chapter Coordinator reports to the Country ACM Representative who also receives reports from the student, youth, women, and veteran Coordinators. However, other relationships aside from reporting, are possible both ways.
ACM maintains the following data (attributes) from each member: Full name, ID number, position, address, age, country, state, county, citizenship, Other Citizenship, tribe, region, date of birth, date of joining, university attended, highest degree earned, veteran status, marital status, whether they work in the office of the Representative or not, whether they work in the office of the Chapter Coordinator or not, and submembership.
Having been given the necessary information by the ACM IT manager, who hired you to develop a robust and efficient relational database to address the organizational need, it is up to you to come up with an ER diagram, showing the necessary relationships- including cardinality and modality that you have deduced from the chart and description.
Country Representative Students Coordinator Veterans Coordinator ACM Chapter Coordinator Women Coordinator Youth Coordinator State ChaptersState ChaptersState ChaptersState ChaptersState Chapters City Chapters Country Representative Students Coordinator Veterans Coordinator ACM Chapter Coordinator Women Coordinator Youth Coordinator State ChaptersState ChaptersState ChaptersState ChaptersState Chapters City ChaptersStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


