The concentration in the blood resulting from a single dose of drug normally decreases with time as the drug is eliminated from the body.
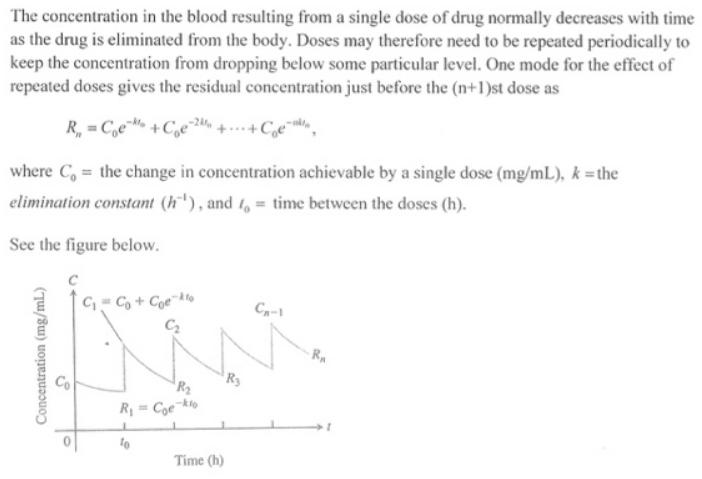

The concentration in the blood resulting from a single dose of drug normally decreases with time as the drug is eliminated from the body. Doses may therefore need to be repeated periodically to keep the concentration from dropping below some particular level. One mode for the effect of repeated doses gives the residual concentration just before the (n+1)st dose as R, = C,e +Ce4 where C, the change in concentration achievable by a single dose (mg/mL), k =the elimination constant (h), and , time between the doses (h). See the figure below. G= C, + Coe"o C-1 RA R2 R = Coe kio Time (h) Concentration (mg/mL) A) Write R, in closed form as a single fraction, and find R= lim R. B) Calculate R, and R, for C, =1 mg/ml., k = 0.1h" and 1, = 10h. How good an estimate of R is R,? C) If k = 0.01h and t, = 10h, find the smallest n such that R, >(1/2)R. Use
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Answer Sel Grven that ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


