Question
The contents of an int array will be provided to you on eLearning. (Please check in theHomework Input Files folder of the Course Homepage. The
The contents of an int array will be provided to you on eLearning. (Please check in theHomework Input Files folder of the Course Homepage. The file is called Array Analysis Array Input.txt.)
Every element of this array is an int between 0 and 3000, except for the last element, which is -1. Since we did not provide a size declarator in the array declaration, nor do we know how many elements are in the array until we process it, that last -1 can be used as a sentinel value for our array processing. It is not considered part of the data set in the array and should not be included in the following calculations. You may safely dimension your input array to 600 elements.
Lets do two types of analysis on this array: (a) statistical, and (b) locating duplicate elements. Since both exercises will be done on the same data set, you can do them both in a single program.
Statistical Analysis
Have your program open the input file (Array Analysis Array Input.txt), read the data into an array, and then close the input file. (You dont really need the array for the statistical analysis section, but you will need it for the duplicate detection to follow.) Dont forget that there is a -1 in the data set that will function as a sentinel value. Then determine the following statistics on it:
1) the number of elements.
2) the average of the elements.
3) the minimum and maximum values.
4) the second to last minimum and second to last maximum values.
Your program should analyze the array, determine the above statistics, and print out the results in the following format. (Note that these numbers are dummy numbers and are not intended to be correct.)
Total number: 700 Average: 2462.9 Min element: 15 Min2 element: 21 Max element: 2984 Max2 element: 2976
The average should be printed as a floating point value with one decimal position. All numbers should be right justified as indicated. Min2 refers to the second-to-last minimum element, andMax2 refers to the second-to-last maximum element. Note that it is not necessary to create an output file for this project. Printing the results to the console will be sufficient.
Duplicate Detection
For the second problem within Program 1, please take the above array and determine how many duplicate values there are in the array and their index positions within the array. Note that the meaning of a duplicate is two numbers at different index positions that have the same value.Your program should also count the number of duplicates found and report that to the user.
Your program should display the results in two different ways.
Display 1:
This simple method displays each duplicate on its own line. (Note that any number that only appears once in the data set will not have a line in this report.)
Duplicate of 1899, index 1, was found at index 9. Duplicate of 1059, index 20, was found at index 224. Duplicate of 1059, index 20, was found at index 475. ....
Duplicate of 2535, index 415, was found at index 488. Total Duplicates found: XX
This report indicates that the value 1899, which was found at index 1, was also found at index 9. The value 1059, which was found at index 20, was also found at indexes 224 and 475. (If you look at the array values, you will see that these results are true.) The total number of duplicates for a single number is equal to the number of lines in the report for that number.
Display 2:
This display method prints all of the instances of a single number on one line:
Value 1899 was found at indices: 1, 9. Value 1059 was found at indices: 20, 224, 475. ....... Value 2535 was found at indices: 415, 488.
Total Duplicates found: XX
If you use this format, your program should not have more than one entry for the same number.
Note that the meaning of a duplicate is two numbers at different index positions that have the same value. This means that if a number appears n times in the array, there are a total of
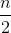 =
= 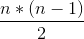
duplicates for that number. Thus, if a number appears twice in the array, that counts as 1 duplicate. If a number appears 3 times, that counts as 3 duplicates. And if a number appears 4 times, that counts as (4*3)/2 = 6 duplicates.
You can use this formula to count the total number of duplicates for each number and accumulate them to get an overall number of duplicates. That number should equal the number obtained in Display 1.
Numbers from array analysis array input:
71, 1899, 272, 1694, 1697, 296, 722, 12, 2726, 1899,
1374, 1541, 1923, 1904, 1083, 1462, 2981, 1929, 304, 2550, 1059, 1860, 1963, 516, 647, 1607, 590, 157, 2351, 753, 2455, 349, 79, 1634, 368, 1992, 2401, 357, 1478, 1601, 239, 365, 2453, 2283, 2432, 1223, 2739, 2487, 2714, 1391, 1972, 2805, 1504, 413, 1647, 2750, 44, 64, 934, 1008, 1429, 1427, 315, 2499, 1620, 1816, 2441, 2557, 2188, 531, 1514, 2825, 449, 265, 2064, 1022, 34, 1864, 1861, 1516, 1465, 2327, 398, 2769, 563, 194, 429, 942, 1795, 223, 2406, 780, 780, 61, 133, 195, 495, 1774, 1934, 2171, 433, 1417, 292, 324, 2929, 1597, 1470, 764, 593, 891, 679, 47, 1778, 2532, 1862, 2636, 549, 2923, 2270, 1101, 1607, 2395, 726, 1111, 892, 1988, 555, 379, 224, 298, 1660, 2203, 2385, 2159, 2574, 705, 2513, 1755, 313, 173, 148, 2449, 259, 1006, 1221, 2259, 2020, 1484, 2717, 2400, 266, 1203, 2206, 357, 1294, 1153, 2820, 1858, 2062, 1499, 1422, 2343, 956, 2677, 468, 910, 2719, 1850, 825, 362, 288, 963, 843, 689, 2800, 1363, 1384, 1926, 1816, 746, 124, 2970, 1577, 2727, 1344, 276, 494, 1252, 333, 1862, 502, 2277, 890, 322, 70, 2969, 1745, 2205, 2919, 2837, 744, 203, 1699, 37, 767, 2611, 1262, 2052, 2118, 1412, 2642, 741, 1841, 1520, 892, 1659, 1030, 2016, 1158, 1566, 2070, 2272, 20, 2631, 1059, 2277, 2234, 1807, 921, 588, 965, 251, 175, 1452, 1138, 114, 648, 2223, 1509, 1513, 1061, 1221, 1035, 911, 2973, 2250, 2337, 1181, 832, 2137, 334, 1144, 1312, 2137, 2662, 2987, 778, 943, 1665, 38, 875, 1148, 2483, 2715, 814, 520, 1645, 2571, 1085, 150, 2933, 2156, 2878, 1090, 1353, 510, 2872, 1209, 801, 1518, 1805, 128, 1286, 922, 2515, 1352, 1470, 1039, 1990, 288, 2489, 2935, 1360, 819, 392, 2519, 2612, 2972, 1173, 2136, 2087, 2255, 62, 427, 1488, 1378, 798, 219, 993, 2916, 1773, 630, 1221, 1868, 1726, 1420, 1006, 2053, 2386, 1451, 2128, 1905, 2588, 1050, 1768, 1548, 284, 989, 545, 2538, 192, 2121, 2837, 251, 1720, 208, 603, 1445, 1392, 70, 2665, 507, 108, 445, 451, 470, 2814, 2278, 290, 1225, 1420, 857, 2415, 1313, 520, 1359, 666, 124, 1744, 190, 2383, 1177, 2855, 1261, 2624, 2625, 99, 2417, 1961, 1276, 769, 2447, 159, 895, 1957, 626, 2123, 1668, 2231, 1791, 974, 163, 2410, 2160, 2100, 2496, 599, 1190, 2494, 1349, 2490, 2922, 2379, 1705, 1299, 1109, 2680, 713, 1223, 2943, 2784, 550, 1615, 2853, 388, 2839, 74, 879, 734, 1432, 2031, 1073, 2611, 1939, 1566, 2535, 1687, 599, 2048, 2990, 1637, 1638, 2075, 257, 1352, 2939, 570, 1642, 1108, 2859, 1412, 1177, 392, 1643, 1996, 1682, 1136, 1339, 1042, 2106, 2229, 1890, 328, 122, 1392, 1706, 623, 823, 2703, 2693, 842, 2329, 1815, 2647, 1883, 2698, 1371, 1086, 2006, 2650, 1652, 488, 1123, 17, 290, 1324, 2495, 1221, 2361, 1244, 813, 2716, 1808, 2328, 2840, 1059, 2382, 2391, 2453, 1672, 1469, 778, 2639, 357, 2691, 1113, 2131, 23, 2535, 1514, 2317, 45, 1465, 1799, 2642, 557, 1846, 1824, 1144, -1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


