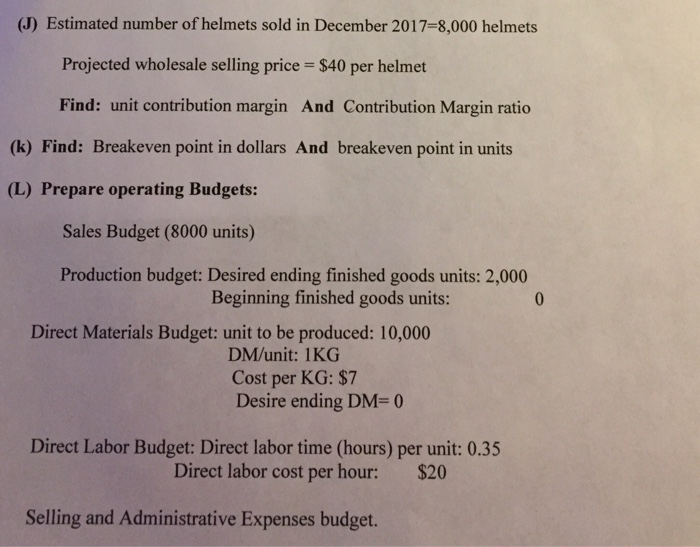
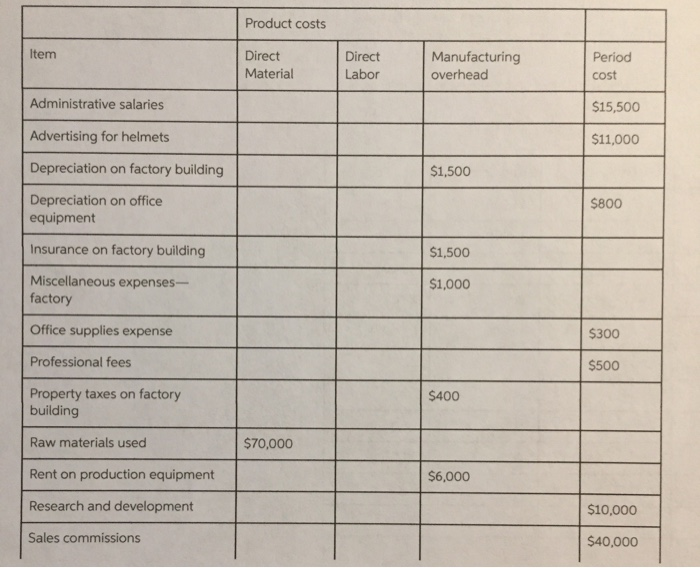
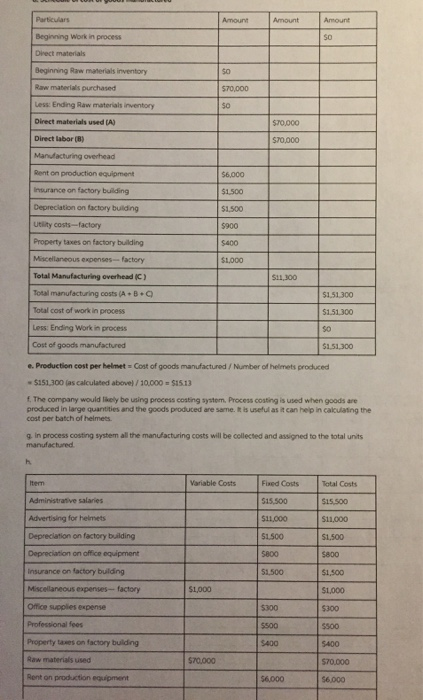
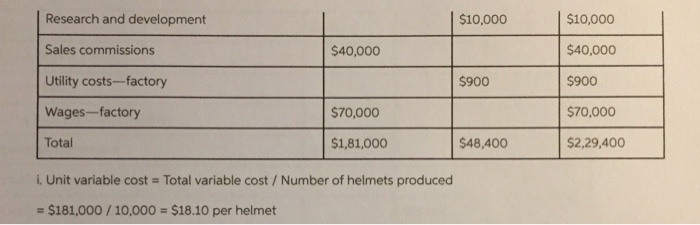
The directions that are not shown here are A-i.but the charts that you see are A-i already done. i just need help with J and on please.
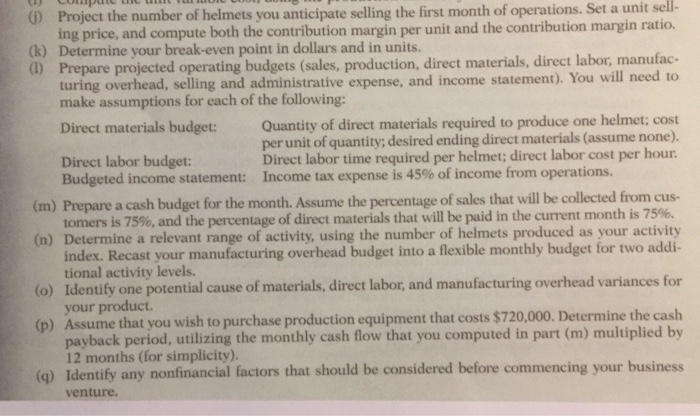
) Project the number of helmets you anticipate selling the first month of operations. Set a unit sell- ing price, and compute both the contribution margin per unit and the contribution margin ratio. (k) Determine your break-even point in dollars and in units. (1) Prepare projected operating budgets (sales, production, direct materials, direct labor, manufac- turing overhead, selling and administrative expense, and income statement). You will need to make assumptions for each of the following: Quantity of direct materials required to produce one helmet; cost per unit of quantity; desired ending direct materials (assume none). Direct labor time required per helmet; direct labor cost per hour. Income tax expense is 45% of income from operations. Direct materials budget: Direct labor budget: Budgeted income statement: (m) Prepare a cash budget for the month. Assume the percentage of sales that will be collected from cus- tomers is 75%, and the percentage of direct materials that will be paid in the current month is 75%. (n) Determine a relevant range of activity, using the number of helmets produced as your activity index. Recast your manufacturing overhead budget into a flexible monthly budget for two addi- tional activity levels. (o) Identify one potential cause of materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead variances for your product. (p) Assume that you wish to purchase production equipment that costs $720,000. Determine the cash payback period, utilizing the monthly cash flow that you computed in part (m) multiplied by 12 months (for simplicity). (q) Identify any nonfinancial factors that should be considered before commencing your business venture. (J) Estimated number of helmets sold in December 2017-8,000 helmets Projected wholesale selling price = $40 per helmet Find: unit contribution margin And Contribution Margin ratio (k) Find: Breakeven point in dollars And breakeven point in units (L) Prepare operating Budgets: Sales Budget (8000 units) Production budget: Desired ending finished goods units: 2,000 Beginning finished goods units: Direct Materials Budget: unit to be produced: 10,000 DM/unit: 1KG Cost per KG: $7 Desire ending DM= 0 Direct Labor Budget: Direct labor time (hours) per unit: 0.35 Direct labor cost per hour: $20 Selling and Administrative Expenses budget. Budgeted Income Statement. (m) Prepare: Cash budget (n) Prepare: Monthly flexible manufacturing costs budget (0) Identify one potential cause of materials, direct labor, and MOH variances for your product. (p) Determine the cash payback period commencing (q) Identify any nonfinancial factors that should be considered your business venture ... before Other Info 1-Bicycle Helmet Company's selling price is $40.00 per device. 2-Each helmet requires 1 kilogram (KG) of material, at a unit cost of $7.00 per kg, to produce. 3-It takes 0.35 direct labor hours to produce one helmet, at a unit price of $20 hour. per 4-Income tax expense is 45% of income from operation. 5-The types of manufacturing and period costs that would be incurred in making helmet, and assumed total dollar amounts are as follows: Rent on production equipment: $6,000 a. Insurance on factory building: $1,500 b. Raw Materials: $70,000 c. Utility costs for the factory: $900 d. Office supplies: $300 e. Direct labor: $70,000 f. g. Depreciation on office equipment: $800 h. Miscellaneous manufacturing items: $1,000 i. Administrative salaries: $15,500 j. Property taxes on factory building: $400 Advertising for the Helmets: $11,000 k. 1. Sales commissions: $40,000 Depreciation on factory building: $1,500 m. Professional fees: $500 n. Research and development: $10,000 0. Product costs Item Direct Manufacturing overhead Direct Period Material Labor cost Administrative salaries $15,500 Advertising for helmets $11,000 Depreciation on factory building $1,500 Depreciation on office equipment $800 Insurance on factory building $1,500 Miscellaneous expenses- factory $1,000 Office supplies expense $300 Professional fees $500 Property taxes on factory building $400 Raw materials used $70,000 Rent on production equipment $6,000 Research and development $10,000 Sales commissions $40,000 Particulars Amount Amount Amount Beginning Work in process Direct materials Beginning Ravw materials inventory Raw materials purchased $70,000 Less: Ending Raw materials inventory $0 Direct materials used (A) S70,000 Direct labor (B) S70,000 Manufacturing overhead Rent on production equipment $6,000 Insurance on factory bulding $1,500 Depreciation on factory building $1,500 Utlity costs-factory $900 Property taxes on factory building $400 Miscellaneous expenses- factory $1,000 Total Manufacturing overhead (C) S11,300 Total manufacturing costs (A.B.Q $1.51300 Total cost of work in process $1.51 300 Less: Ending Work in process SO Cost of goods manufactured $1.51,300 e. Production cost per helmet = Cost of goods manufactured / Number of helmets produced $151,300 (as calculated above) / 10,000 = $15.13 E. The company would likely be using process costing system. Process costing is used when goods are produced in large quantities and the goods produced are same. Itis useful as it can help in calculating the cost per batch of helmets. g in process costing system all the manufacturing costs will be collected and assigned to the total units manufactured h. Item Variable Costs Fixed Costs Total Costs Administrative salaries $15,500 S15,500 Advertising for helmets $11,000 S11,000 Depreciation on factory building $1.500 $1.500 Depreciation on office equipment S800 S800 Insurance on factory building S1.500 $1,500 Miscellaneous expenses- factory $1,000 $1,000 Office supplies expense $300 $300 Professional fees $500 $500 Property tawes on factory bulding $40 S400 Raw materials used S70,000 S70.000 Rent on production equipment $6,000 $6.000 Research and development $10,000 $10,000 Sales commissions $40,000 $40,000 Utility costs-factory $900 $900 $70,000 Wages-factory $70,000 $2,29,400 Total $1,81,000 $48,400 i. Unit variable cost = Total variable cost / Number of helmets produced = $181,000 / 10,000 = $18.10 per helmet