Question
The following production cost data for 23 historical missile systems has been collected by your team of analysts from a variety of sources and should
The following production cost data for 23 historical missile systems has been collected by your team of analysts from a variety of sources and should be used for problems 1-5:
| System | Nomenclature | Production Quantity | Avg Unit Cost ($M) | FY | Length (m) | Diameter (mm) | Launch Weight (kgs) |
| AIM-120 A-C | AMRAAM | 270 | 0.347 | 2004 | 3.7 | 177.8 | 152 |
| MGM-140A | ATACMS | 789 | 0.782 | 2002 | 3.96 | 609.6 | 1700 |
| XM-141 | BDM | 253 | 0.014 | 2005 | 0.823 | 81.28 | 7.3 |
| RIM-162A | ESSM | 26 | 1.643 | 2005 | 3.81 | 254 | 297 |
| AGM-114K | HELLFIRE II | 220 | 0.099 | 2003 | 1.65 | 177.8 | 45.3 |
| AGM-158A | JASSM | 71 | 0.632 | 2004 | 4.27 | 457.2 | 1021 |
| FGM-148 | JAVELIN | 4271 | 0.091 | 2006 | 1.22 | 127 | 12.25 |
| GBU-31/32 | JDAM | 21294 | 0.034 | 2006 | 3.9 | 457.2 | 932.5 |
| AGM-154A-C | JSOW | 35 | 0.807 | 2008 | 4.08 | 335.28 | 483 |
| AGM-114L | LB HELLFIRE | 2530 | 0.099 | 2002 | 1.74 | 177.8 | 49 |
| M-26 | MLRS ER | 485 | 0.393 | 2004 | 3.69 | 228.6 | 293 |
| AGM-119B | PENGUIN | 36 | 1.053 | 2002 | 3.2 | 284.48 | 370 |
| AGM-130A-C | POWERED GBU-15 | 18 | 1.094 | 2002 | 3.93 | 457.2 | 1323 |
| AIM-54 | Phoenix | 358 | 0.497 | 2004 | 4 | 380 | 460 |
| RIM-116A | RAM | 81 | 0.517 | 2007 | 2.81 | 127 | 73.5 |
| AGM-142A-D | RAPTOR | 14 | 1.482 | 2002 | 5.76 | 520.7 | 1361 |
| CBU-97B | SFW | 281 | 0.451 | 2004 | 2.32 | 406.4 | 421 |
| AIM-9X | SIDEWINDER | 157 | 0.475 | 2005 | 2.89 | 127 | 86 |
| AGM-84H | SLAM-ER | 41 | 0.971 | 2006 | 4.36 | 342.9 | 663.5 |
| RIM-156A | SM-2 ER | 33 | 4.235 | 2004 | 6.55 | 347.98 | 1497 |
| RIM-66C | SM-2 MR | 88 | 1.764 | 2008 | 4.69 | 347.9 | 706 |
| RGM-109E | TAC TOMAHAWK | 29 | 2.358 | 2004 | 5.58 | 518.16 | 1814.4 |
| BGM-109A-D | TOMAHAWK | 581 | 1.873 | 2003 | 6.25 | 520 | 1600 |
The table above has been included as an attachment to the final, 'Prob 1-5 inputs.xlsx'.
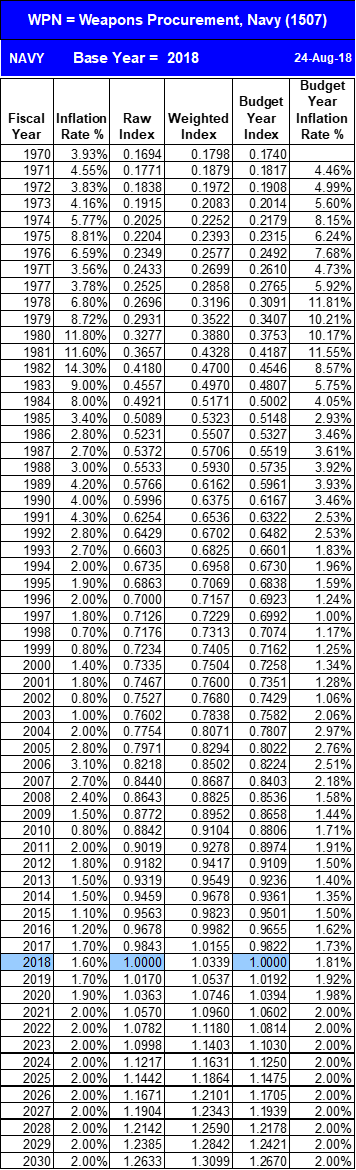
1. (5 points) Normalize the Average Unit Cost of each data point to FY23$M using the Inflation Indices on the last page.
2. (10 points) Using the normalized data from Problem 1, calculate the unit theory theoretical first unit costs (T1) for each data point. Assume each program experienced a 79% learning rate.
3. (15 points) Now that you have a database of T1s, lengths, diameters, and launch weights, develop a CER of the form that predicts T1. Try each independent variable, one at a time, and choose the best CER. There is no need to try any combination of variables, just test each of the three independently. Use GERM. Be sure to show all work, and indicate the best CER, your reason(s) for selecting it, and its relevant statistics.
4. (10 points) Now, assuming your best CER was Y = 0.110*X^1.271, develop a cost estimate for the theoretical first unit cost (T1) of the new NPS-3011 missile. The design parameters are given below:
Length: 5.89 m
Diameter: 390 mm
Launch wt: 1370 kgs
What is your estimate for T1? What is the standard deviation of your estimate of T1?
5. (10 points) Using your estimate for T1 (from (4)), calculate the total production cost of the first 75 NPS-3011 missiles assuming an 79% unit theory learning curve. Also calculate the average unit cost of the first 75 missiles.
6. (5 points)If you are developing a cost estimate for a new air-to-air missile, is this a useful collection of historical data to use in your estimating process? Why or why not? What changes would you make, if any? Do NOT change any of your previous answers based on your responses to this question.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


