Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The Last 1-12 are Matching 1. Scallon Products reports the following information about resources. At the beginning of the year, Scallon estimated it would spend
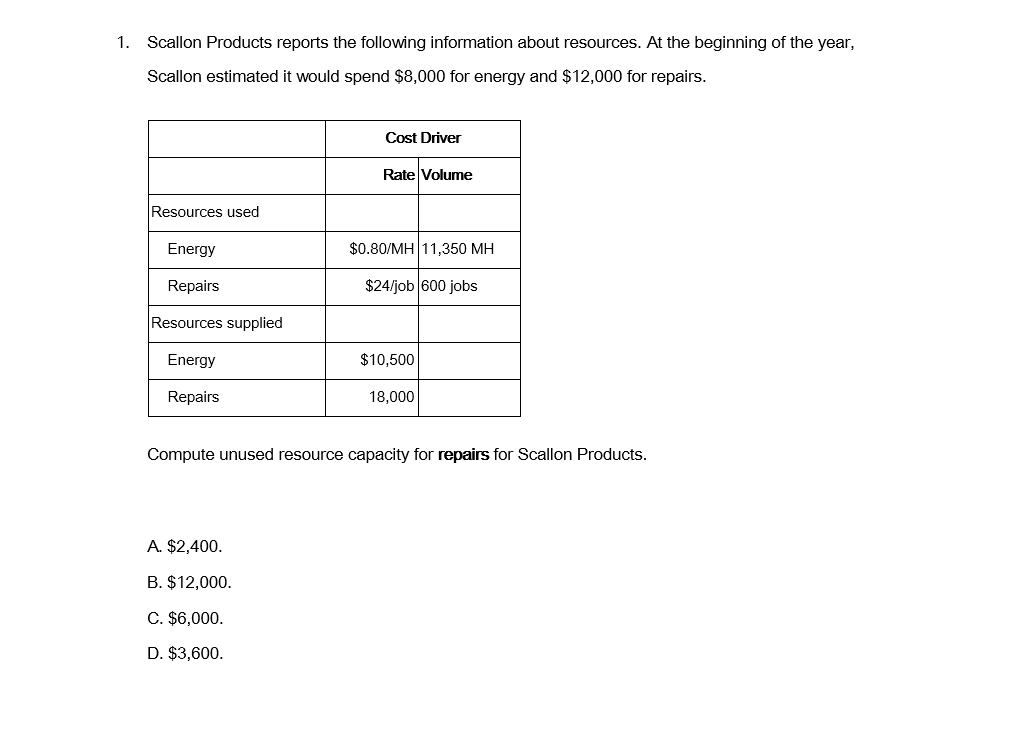





The Last 1-12 are Matching
1. Scallon Products reports the following information about resources. At the beginning of the year, Scallon estimated it would spend $8,000 for energy and $12,000 for repairs. Cost Driver Rate Volume Resources used Energy $0.80/MH 11,350 MH Repairs $24/job 600 jobs Resources supplied Energy $10,500 Repairs 18,000 Compute unused resource capacity for repairs for Scallon Products. A. $2,400. B. $12,000. C. $6,000. D. $3,600. 2. Republic Industries decides to price delivery service according to the results of a recent activity- based costing (ABC) study. The study indicates Republic should charge $8 per order, 2% of the order's value for general delivery costs, $1.25 per item, and $30 for delivery. A year later, Republic collected the following information for two of its best customers: Cost driver Customer C Customer D Number of orders Number of deliveries Number of items 2,000 4,000 Order value $120,000 $80,000 What are the total delivery costs charged to Customer C during the year? A. $5,344. B. $5,364. C. $6,900. D. $6,964. 3. Activity-based cost management (ABM) can best be defined as: A. a cost system using multiple departmental overhead rates. B. the use of cost information gathered using activity-based costing (ABC). C. a quality-control system focusing on eliminating errors and mistakes. D. an incentive system for a company's key decision-makers. 4. Which of the following items would be classified as a product-level cost in an activity-based cost management (ABM) system? A. Change order to meet a new customer's specification. B. Movement of materials for products in production. C. Long-term lease payments for factory equipment. D. Insurance and property taxes on faculty building. 5. The amount of production possible under normal working conditions, including planned downtime and scheduled vacations, is called: A. actual capacity. B. normal capacity. C. practical capacity. D. theoretical capacity. 6. Internal failure activities: A. seek to prevent defects in the products or services being produced. B. inspect inputs and attributes of individual units of products or services to detect whether they conform to specifications or customer expectations. C. correct defective processes or products and services before they are delivered to customers. D. are activities required after defective products or services are delivered to customers. 7. External failure activities: A. Seek to prevent defects in the products or services being produced. B. Inspect inputs and attributes of individual units of products or services to detect whether they conform to specifications or customer expectations. C. Correct defective processes or products and services before they are delivered to customers. D. Are activities required after defective products or services are delivered to customers. 8. Prevention activities: A. Seek to prevent defects in the products or services being produced. B. Inspect inputs and attributes of individual units of products or services to detect whether they conform to specifications or customer expectations. C. Correct defective processes or products and services before they are delivered to customers. D. Are activities required after defective products or services are delivered to customers. 9. Appraisal activities: A. Seek to prevent defects in the products or services being produced. B. Inspect inputs and attributes of individual units of products or services to detect whether they conform to specifications or customer expectations. C. Correct defective processes or products and services before they are delivered to customers. D. Are activities required after defective products or services are delivered to customers. A. Activity-based cost management J. Normal activity B. Actual activity K. Practical capacity Appraisal costs L. Prevention costs D. Conformance to specifications M. Process reengineering E. Customer expectations of quality N. Resources supplied External failure costs 0. Resources used G. Internal failure costs P. Theoretical capacity H. Lean accounting Q. Unused resource capacity 1. Lean manufacturing R. Cost of quality system nimi I lll wo N _1. Costs incurred when nonconforming products and services are detected after being delivered to customers. 2. The expenditures or the amounts spent on the activity. Approach that uses activity-based costing data to evaluate the cost of value-chain activities and to identify opportunities for improvement. The degree to which a product or service meets expectations. Costs incurred to prevent defects in the products or services from being produced. The customer's anticipated level of product or service including tangible and intangible features). Costs incurred to detect individual units of products that do not conform to specifications. The amount of production possible under ideal conditions with no time for maintenance, breakdowns, or absenteeism. The long-run expected volume produced. 10. The amount of production possible assuming only the expected downtime for scheduled maintenance and normal breaks and vacations. 11. Costs incurred when nonconforming products and services are detected before being delivered to customers. 12. The difference between resources used and resources supplied. oi 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


