Question
The manometer is a simple device where the differences in the height of a fluid are influenced by a difference in pressure. One common laboratory
The manometer is a simple device where the differences in the height of a fluid are influenced by a difference in pressure. One common laboratory application is to measure the pressure drop of a fluid as it flows in a pipe as shown in the diagram below:
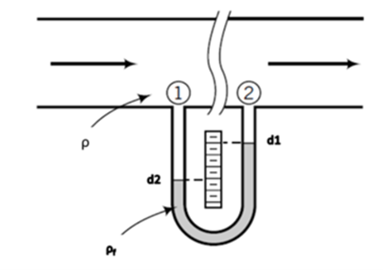
For a particular case the fluid in the pipe is non polar liquid hydrocarbon having specific gravity of 0.8 and the manometer fluid is polar compound having a specific gravity of 1.24. The value of d1 is read as 6.8 cm whereas d2 is read as 62.9 cm on the same scale. Determine the:
a) difference in pressure (P1 P2) in kPa
The manometer fluid is changed to a different polar compound with an unknown density. The same nonpolar hydrocarbon is flowing in the pipe. If the pressure difference is the same as in the previous part but the readings are d1 = 6.7 cm and d2 = 47.2 cm. determine the:
b) specific gravity of the new manometer fluid
With this new manometer fluid in place, it is desired to measure a pressure difference (P1-P2) of 5 kPa. Determine the:
c) vertical difference in height in cm at this pressure difference.
2 d1 d2Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


