Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The purpose of this experiment is to introduce a basic configuration of the emitter follower circuit. Emitter followers are used to buffer signals, which
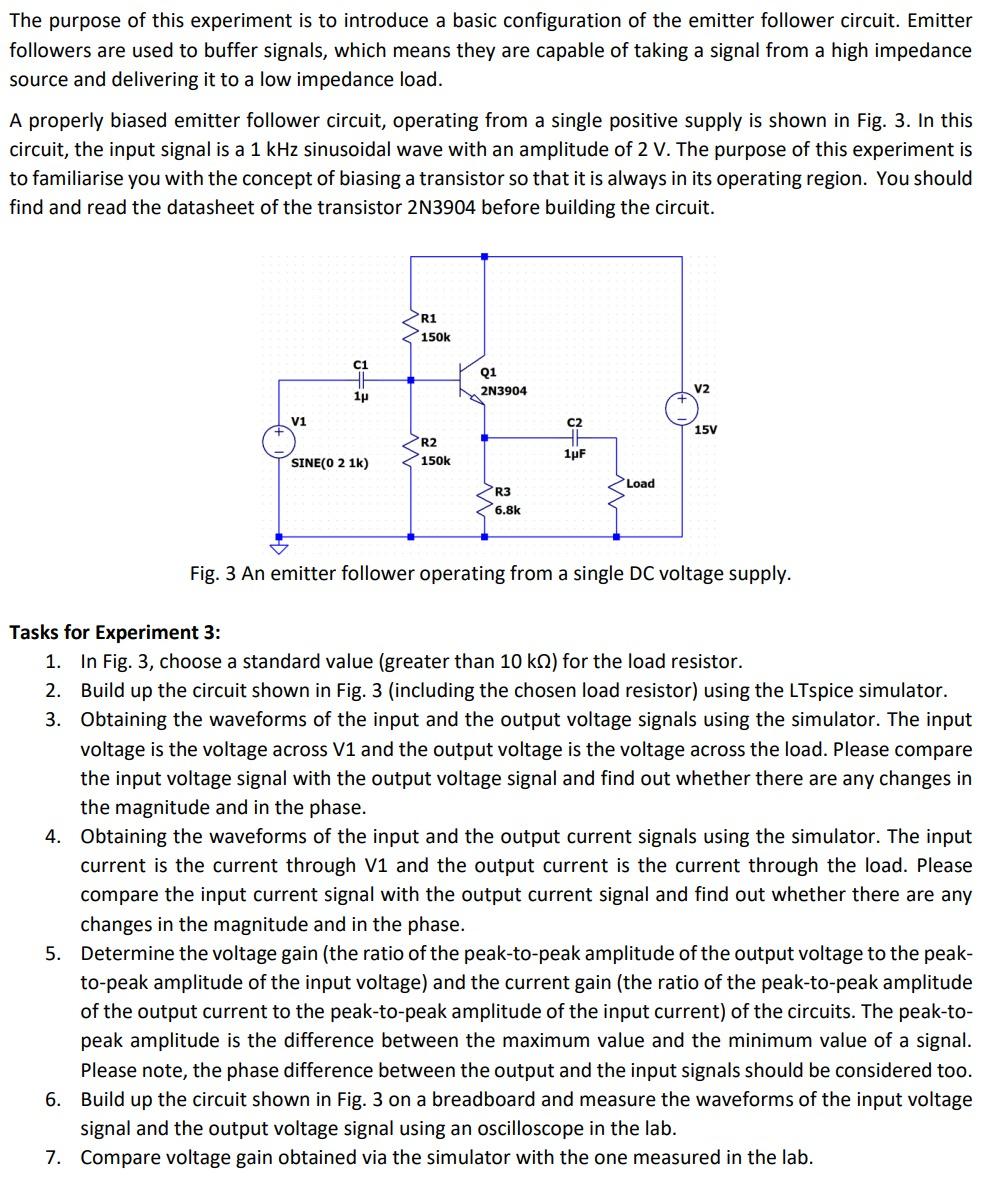
The purpose of this experiment is to introduce a basic configuration of the emitter follower circuit. Emitter followers are used to buffer signals, which means they are capable of taking a signal from a high impedance source and delivering it to a low impedance load. A properly biased emitter follower circuit, operating from a single positive supply is shown in Fig. 3. In this circuit, the input signal is a 1 kHz sinusoidal wave with an amplitude of 2 V. The purpose of this experiment is to familiarise you with the concept of biasing a transistor so that it is always in its operating region. You should find and read the datasheet of the transistor 2N3904 before building the circuit. V1 7. C1 1 SINE(0 2 1k) R1 150k R2 150k Q1 2N3904 R3 6.8k C2 1F Load V2 15V Fig. 3 An emitter follower operating from a single DC voltage supply. Tasks for Experiment 3: 1. In Fig. 3, choose a standard value (greater than 10 k) for the load resistor. 2. Build up the circuit shown in Fig. 3 (including the chosen load resistor) using the LTspice simulator. 3. Obtaining the waveforms of the input and the output voltage signals using the simulator. The input voltage is the voltage across V1 and the output voltage is the voltage across the load. Please compare the input voltage signal with the output voltage signal and find out whether there are any changes in the magnitude and in the phase. 4. Obtaining the waveforms of the input and the output current signals using the simulator. The input current is the current through V1 and the output current is the current through the load. Please compare the input current signal with the output current signal and find out whether there are any changes in the magnitude and in the phase. 5. Determine the voltage gain (the ratio of the peak-to-peak amplitude of the output voltage to the peak- to-peak amplitude of the input voltage) and the current gain (the ratio of the peak-to-peak amplitude of the output current to the peak-to-peak amplitude of the input current) of the circuits. The peak-to- peak amplitude is the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of a signal. Please note, the phase difference between the output and the input signals should be considered too. Build up the circuit shown in Fig. 3 on a breadboard and measure the waveforms of the input voltage signal and the output voltage signal using an oscilloscope in the lab. 6. Compare voltage gain obtained via the simulator with the one measured in the lab.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.46 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Here are the steps to complete the experiment 1 I chose 22k for the load resistor R3 which is a stan...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


