Question
The relationship between the initial horizontal velocity of a projectile and the distance it travels on an inclined plane is governed by the principles of
The relationship between the initial horizontal velocity of a projectile and the distance it travels on an inclined plane is governed by the principles of physics, specifically kinematics.
In the context of projectile motion, the initial horizontal velocity (Vx) of a projectile is the speed at which it is launched in the horizontal direction. This velocity remains constant throughout the flight of the projectile, assuming no air resistance.
The distance a projectile travels on an inclined plane (d) is influenced by several factors, including the initial horizontal velocity, the angle of the incline (?), and the acceleration due to gravity (g).
The equation that describes this relationship is: d = (Vx^2 / g) * sin(2?)
Hypothesis
If the initial horizontal velocity of a projectile is increased, then the distance it travels on an inclined plane will also increase, assuming the mass of the ball remains constant.
Variables
| Independent variable | the initial horizontal velocity of the projectile. | |
| Dependent variable | the distance the projectile travels on the inclined plane. | |
Controlled variable | the mass of the ball. |
Materials
1. Inclined plane
2. Ball (with constant mass)
3. Measuring tape or ruler
4. Protractor
5. Stopwatch or timer
6. Safety goggles
Procedure:
1. Set up the inclined plane at a convenient height.
2. Measure the angle of inclination using the protractor.
3. Release the ball from the same starting point at the top of the inclined plane.
4. Use the stopwatch to measure the time it takes for the ball to reach the bottom of the inclined plane.
5. Measure the horizontal distance traveled by the ball using the measuring tape or ruler.
6. Repeat steps 3-5 for different angles of inclination (10, 20, 30, 40, 50).
7. Record your observations and data in a table.
Results
Calculating the average velocity of the ball
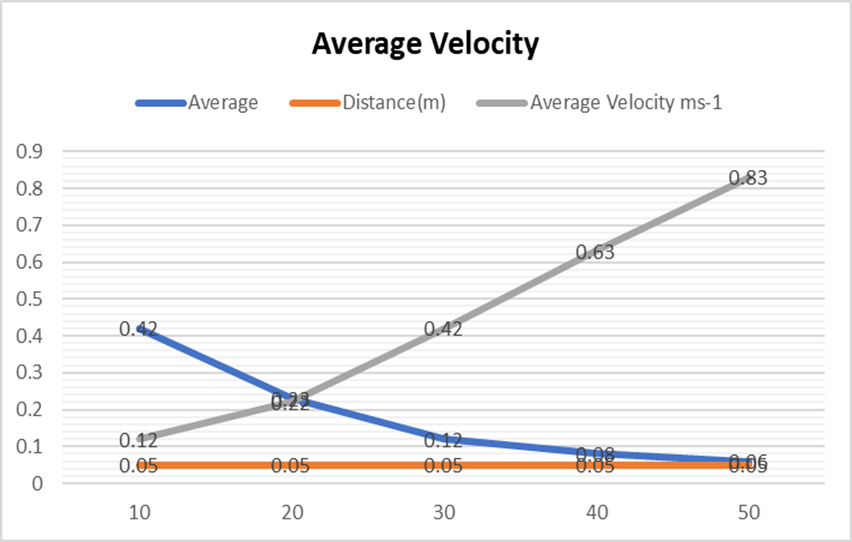
| Angle | Trial.1 | Trial.2 | Trial.3 | Average | Distance(m) | Average Velocity ms-1 |
| 10 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 0.12 |
| 20 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.22 |
| 30 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.42 |
| 40 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.63 |
| 50 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.83 |
Average Velocity Average Distance (m) - Average Velocity ms-1 0.9 0.83 0.8 0.7 0.63 0.6 0.5 0.4 0. 0.42 0.3 0.2 0:29 0.1 0.12 0.12 0.05 0.05 0.05 8:89 0.06 0 10 20 30 40 50
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


