Question
The Solow growth model is one of the fundamental models of standard macroeconomic theory. He seeks to explain the comment economies converge over time, i.e.
The Solow growth model is one of the fundamental models of standard macroeconomic theory. He seeks to explain the comment economies converge over time, i.e. why poor economies (those with less capital) grow more quickly, generally, than developed economies (those with more capital). The Solow model has the following equations
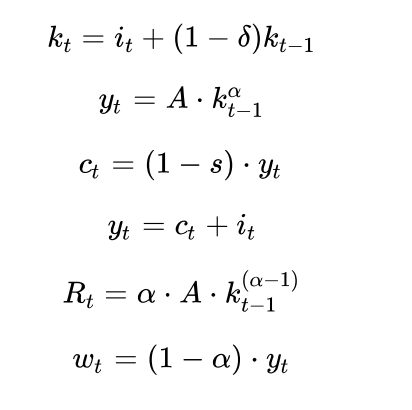
where kt is the stock of productive capital per worker at the end of period t, yt, Ct and it represent GDP, consumption and investment inproductive capital, Rt is the interest rate in the economy and wt is the wage. A is the level of productivity in the economy, is the share of capital in production, s is the constant household savings rate and is the depreciation rate of productive capital. A, s, and are therefore exogenous parameters of the model. We are interested in knowing how the economy evolves over time, if we assume that the stock of capital at the beginning of time is equal to a specific value, ie k0 = k. Thus, the endogenous variables of the model (those whose value we want to know) are Kt, yt, Ct, it, Rt and Wt .kt-1 is a pre-determined variable of the model because when we enter period t, we know the value of kt-1. From the perspective of period t, kt-1 is essentially an exogenous variable. It is possible to rewrite the Solow model as follows: 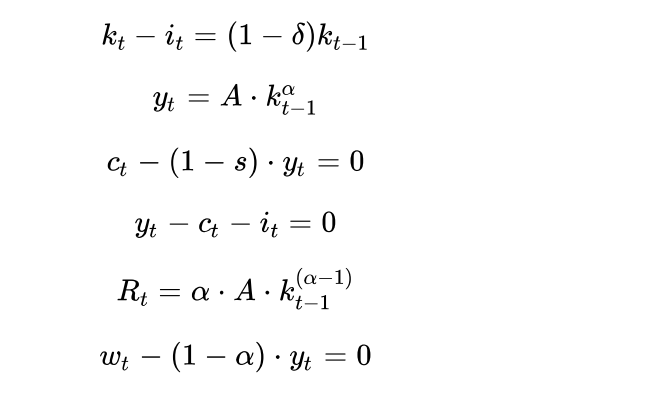
In this formulation, all endogenous (unknown) variables are on the left side of the equation, and exogenous variables are on the right side of the equation. We can therefore rewrite our model in matrix form D . x = b, with D the matrix of coefficients of the model, x the vector of endogenous variables and b the vector of exogenous values known at time t.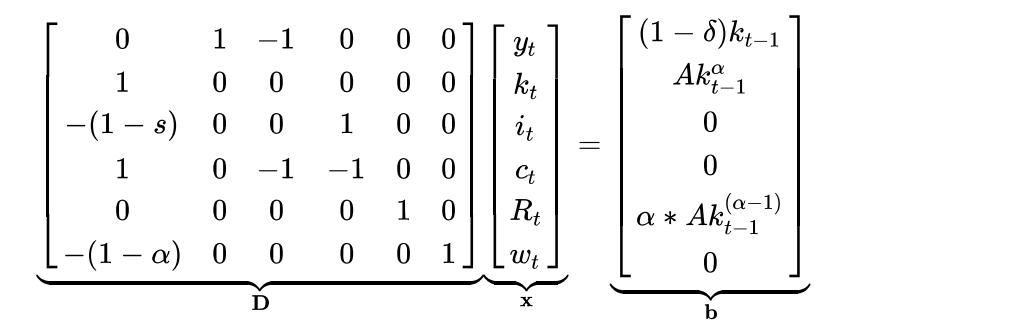
This model therefore allows us to obtain the value of the major economic variables at time t, depending on the capital stock existing at the end of period t-1.
Let us assume s = 0.20, ie households save 25 percent of their income, = 0.4, = 0.1 and A = 2. A) Construct, in R, the matrix D B) Now assume that the initial capital stock k0= 1. Construct vector b. C) Using your results in A) and B), calculate the value of the endogenous variables at period t = 1, i.e. calculate x=D-1 b D) From your answer in C), which gives you the capital stock at the end of period t=1 recalculate the new vector b and calculate the value of endogenous variables at period t=2 E) Using a loop as seen in the course notes, use the procedure proposed in D) to calculate the value of the endogenous variables for periods t = 1 to t = 200. You should find that at some point the variables stop changing value. We call this situation a steady state.
kt=it+(1)kt1yt=Akt1ct=(1s)ytyt=ct+itRt=Akt1(1)wt=(1)yt ktit=(1)kt1yt=Akt1ct(1s)yt=0ytctit=0Rt=Akt1(1)wt(1)yt=0 D01(1s)10(1)100000100100001100000010000001xytktitctRtwt=b(1)kt1Akt100Akt1(1)0Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


