Question
Thermodynamics of Citrate Synthase Reaction in Cells Citrate is formed by the condensation of acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate, catalyzed by citrate synthase: Oxaloacetate + acetyl-CoA
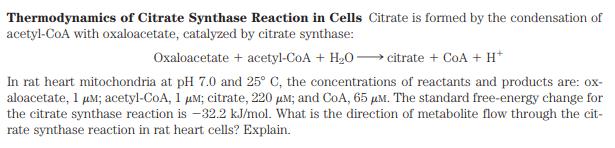
Thermodynamics of Citrate Synthase Reaction in Cells Citrate is formed by the condensation of acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate, catalyzed by citrate synthase: Oxaloacetate + acetyl-CoA + HO citrate + CoA + H+ In rat heart mitochondria at pH 7.0 and 25 C, the concentrations of reactants and products are: ox- aloacetate, 1 M; acetyl-CoA, 1 M; citrate, 220 m; and CoA, 65 M. The standard free-energy change for the citrate synthase reaction is -32.2 kJ/mol. What is the direction of metabolite flow through the cit- rate synthase reaction in rat heart cells? Explain.
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (143 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get StartedRecommended Textbook for
Organic Chemistry
Authors: John McMurry
7 Edition
978-0495112587, 0495112585
Students also viewed these Biology questions
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
View Answer in SolutionInn App



