Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
theyre asking to complete the summary table please using these filled tables the last picture where it says summary table is the one im having

theyre asking to complete the summary table please using these filled tables


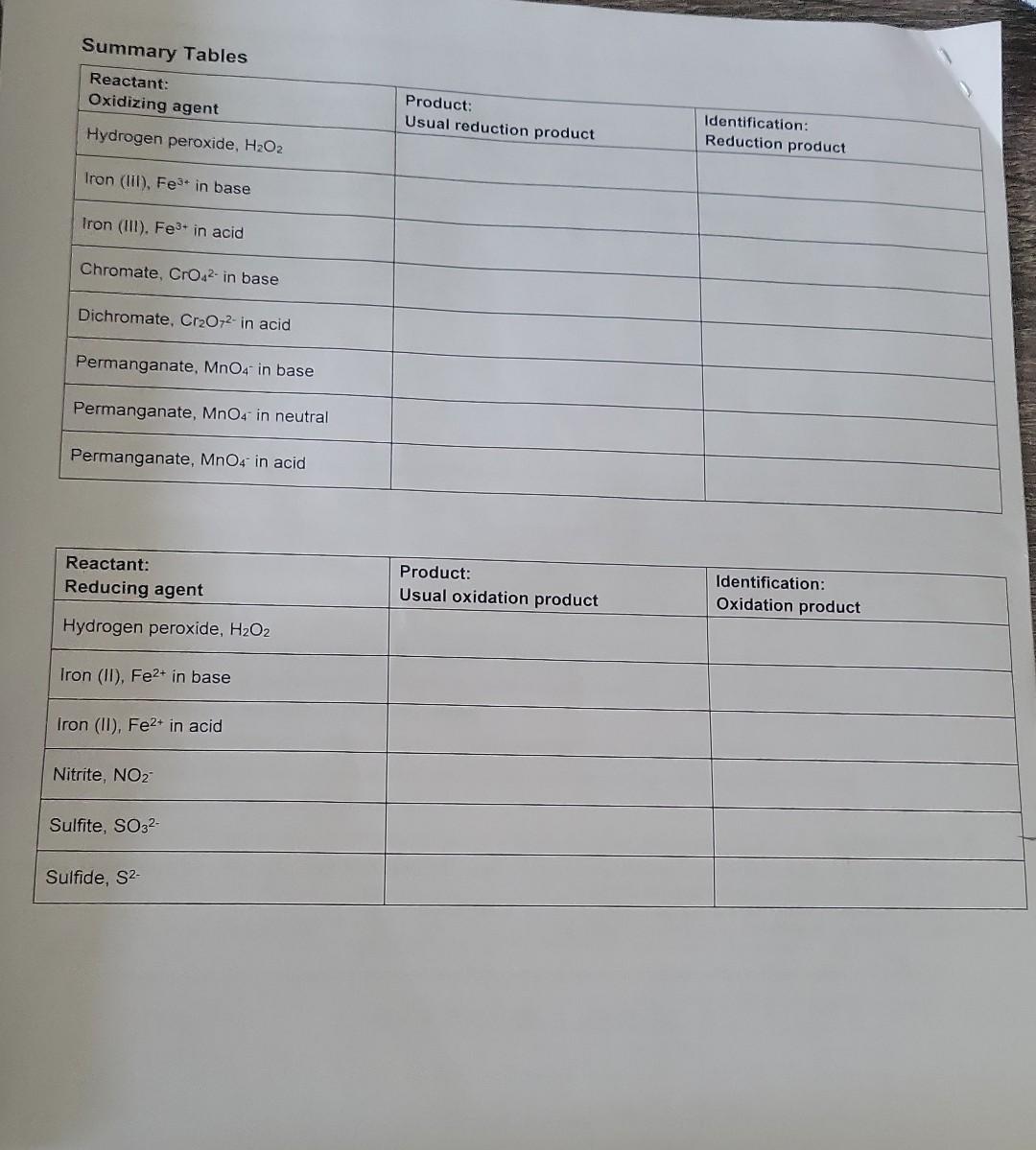
the last picture where it says summary table is the one im having trouble filling it out
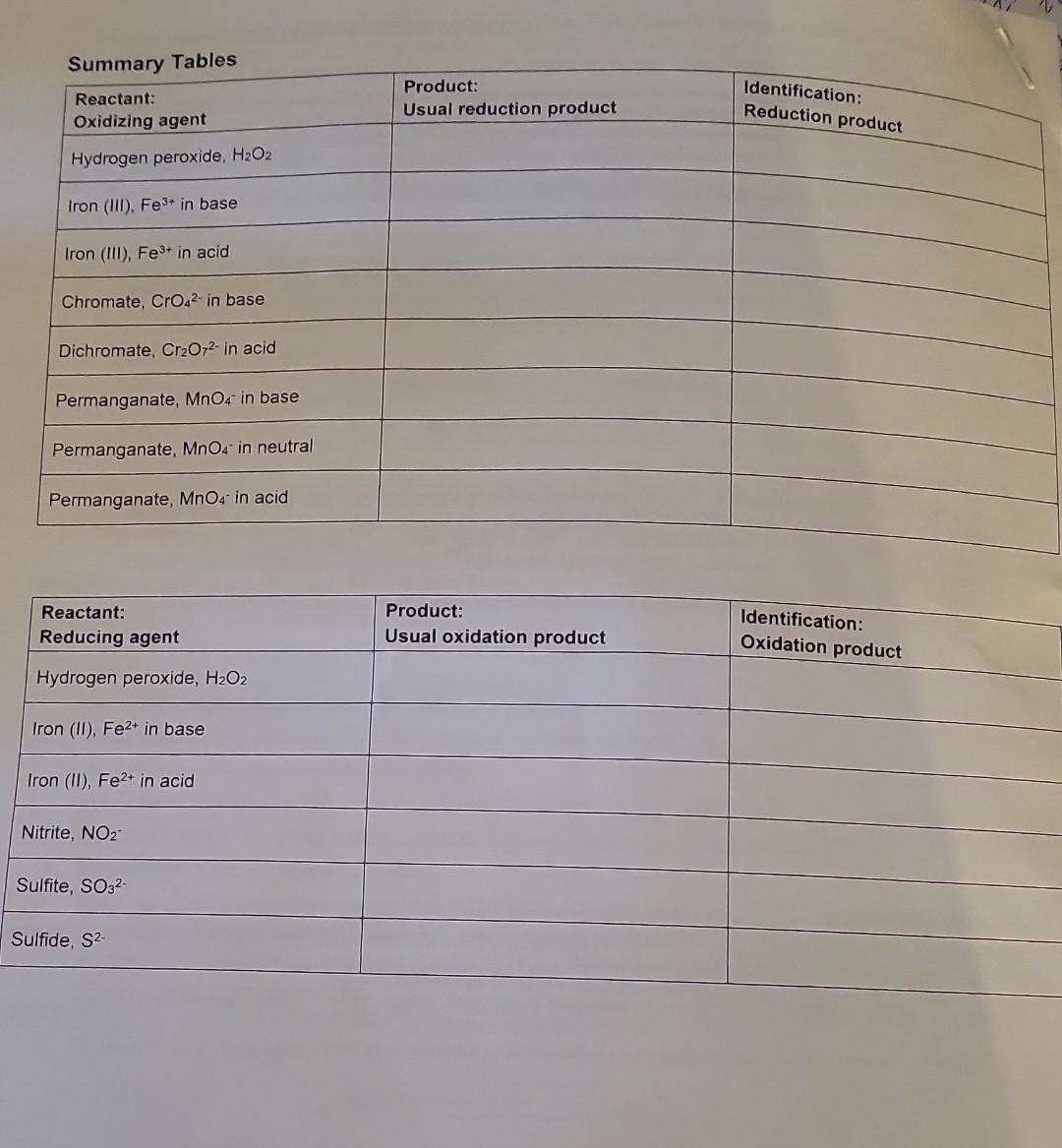
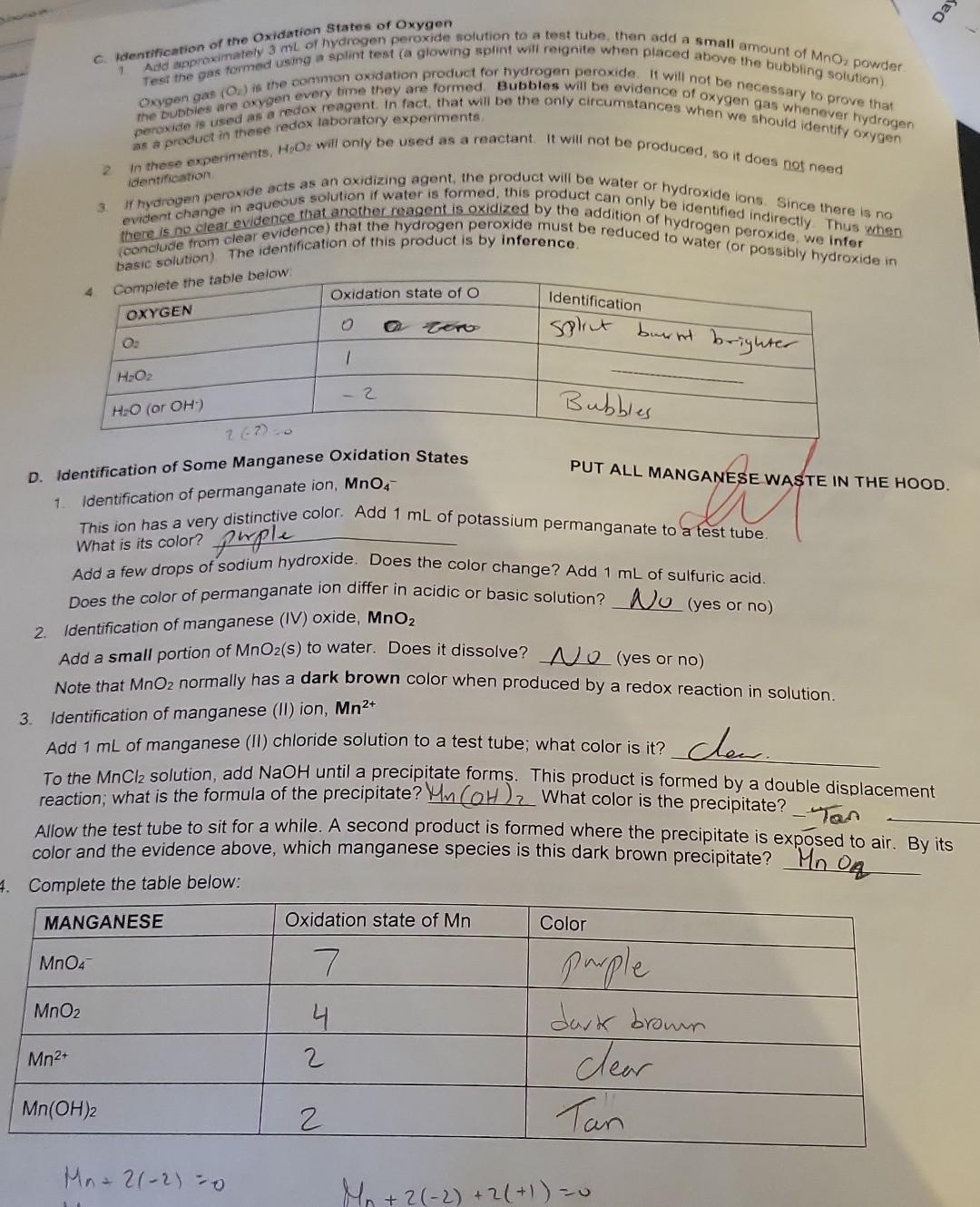
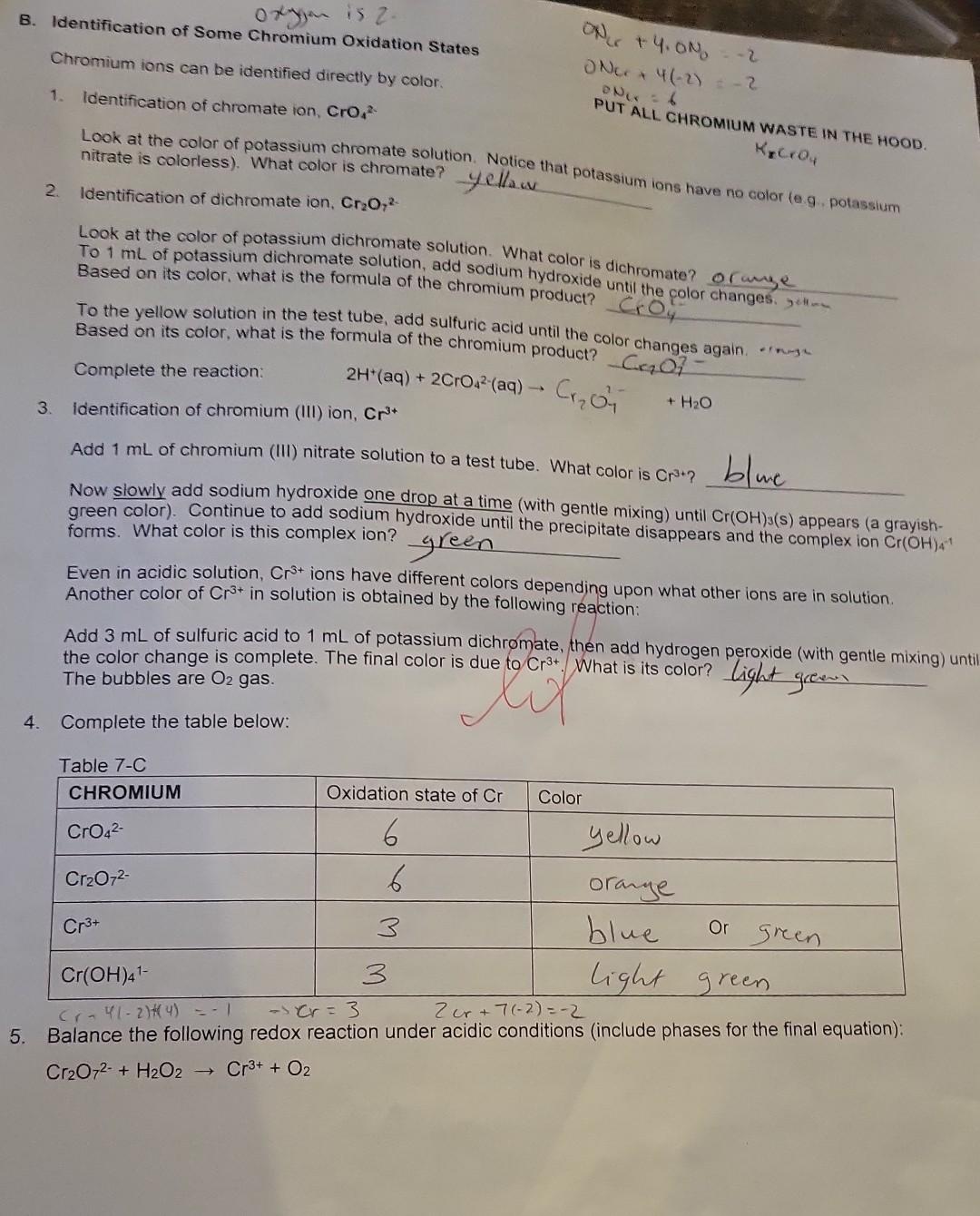
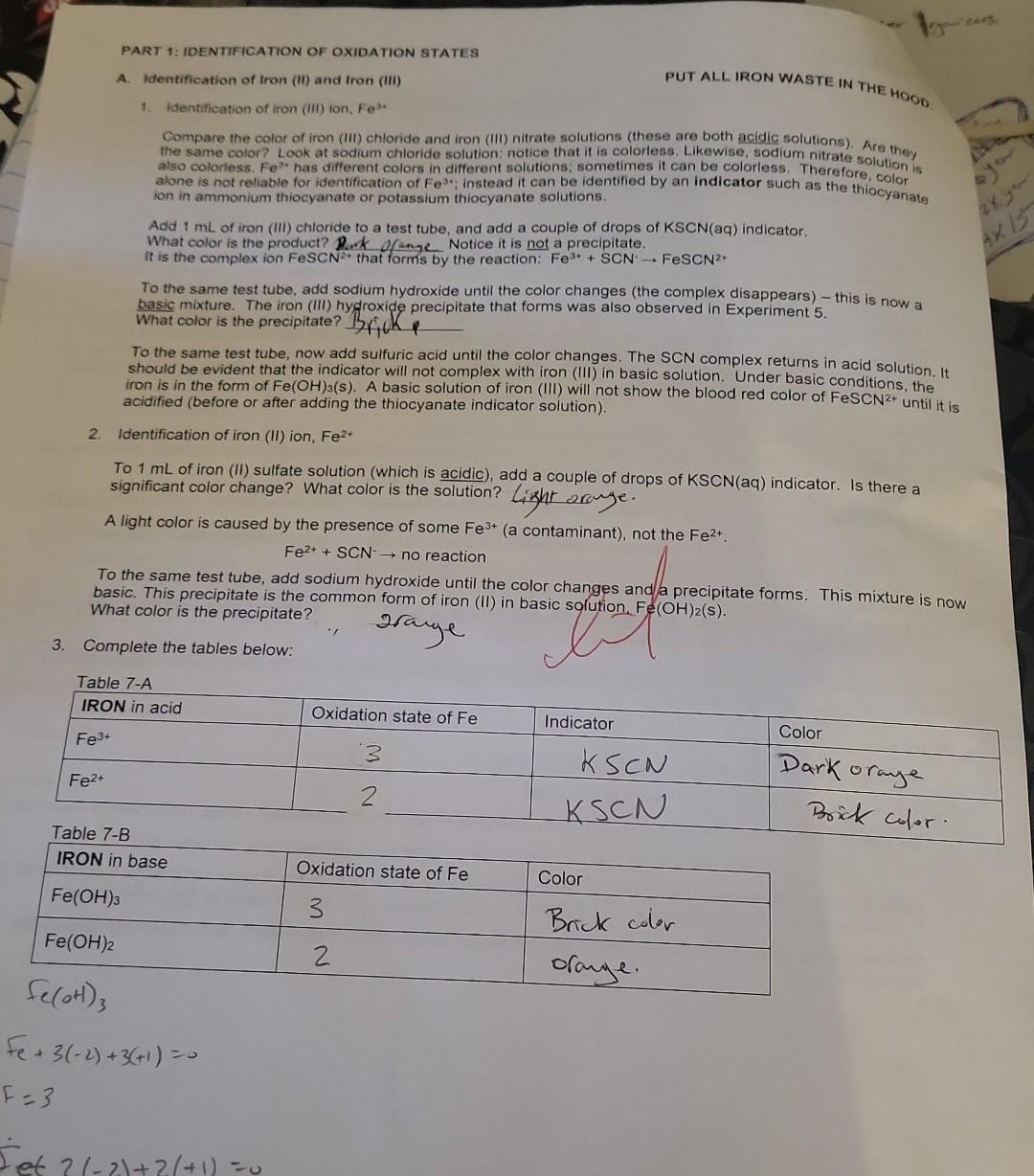
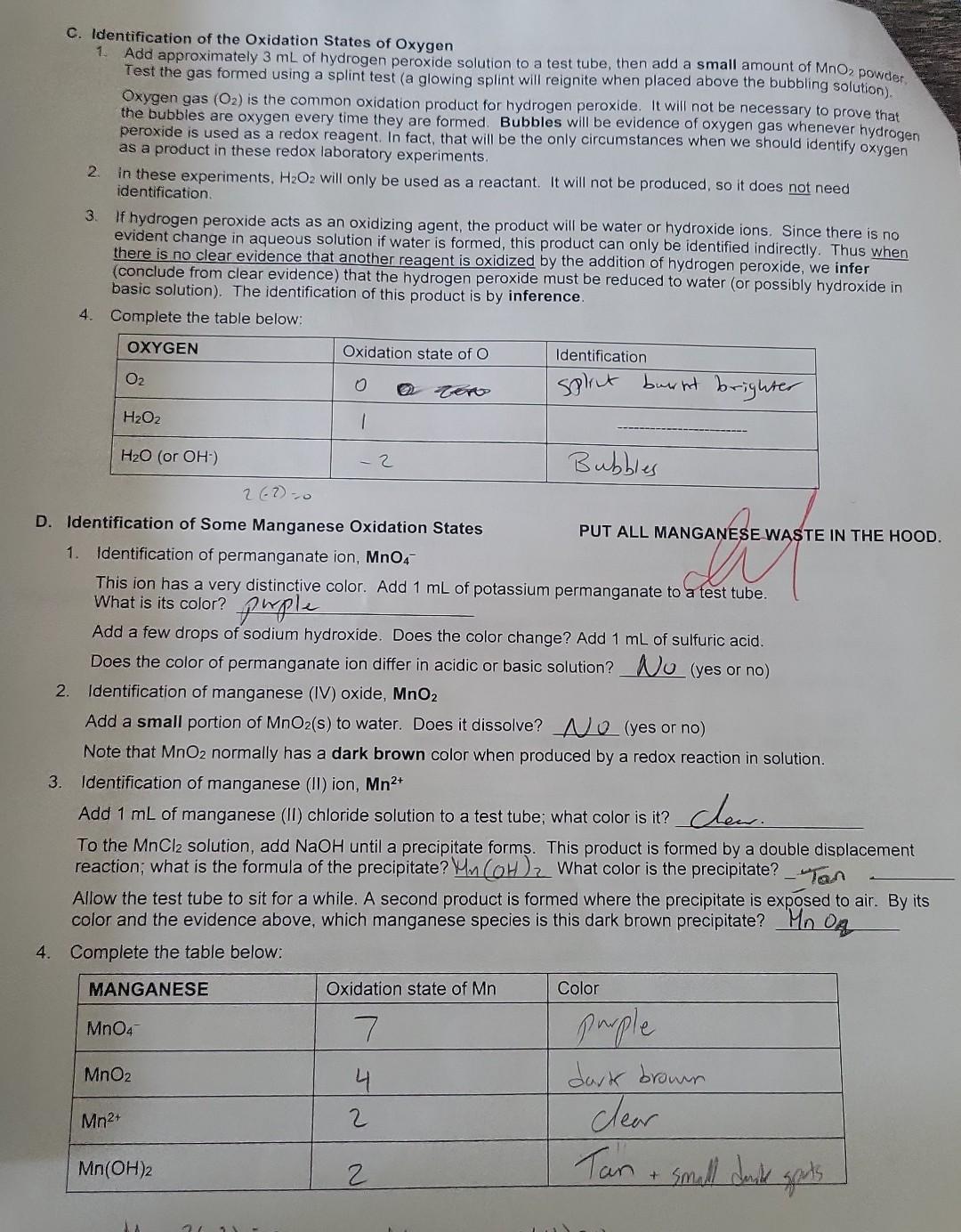
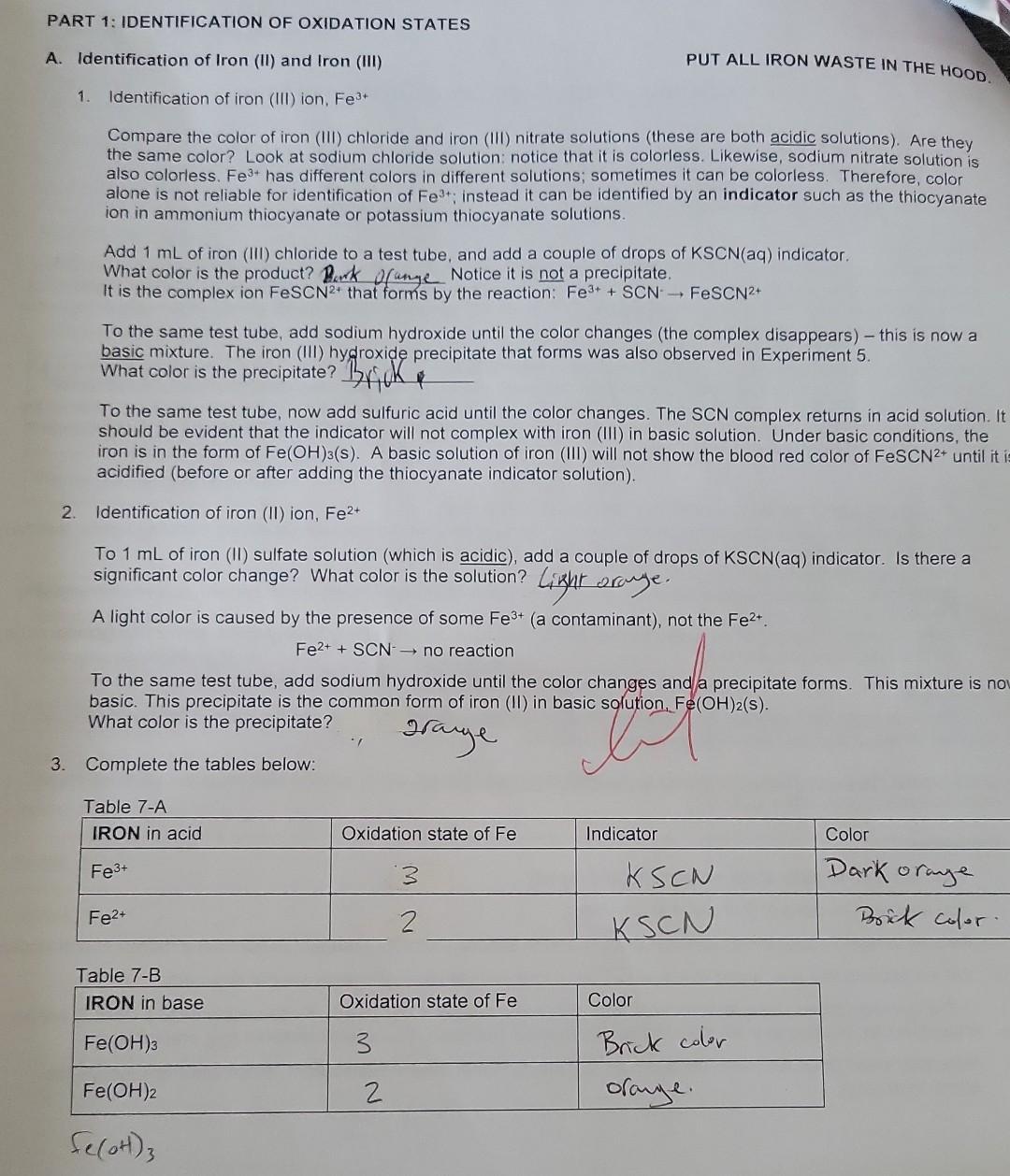
Summary Tables Complete the table below: \begin{tabular}{|l|c|l|} \hline MANGANESE & Oxidation state of Mn & Color \\ \hline MnO4 & 7 & purple \\ \hline MnO2 & 4 & dark bromm \\ \hline Mn2+ & 2 & Clear \\ \hline Mn(OH)2 & 2 & Tan \\ \hline \end{tabular} C. Identification of the Oxidation states of Oxygen the buobies are oxygenedox reagent. in fact, that will be the only circumstances when we gas whenever hydrogen 2. In these experiments. H,Oz will only be used as a reactant. It will not be produced, so it does not need D. Identification of Some Manganese Oxidation States PUT ALL MANGANESE WASTE IN THE HOOD. 1. Identification of permanganate ion, MnO4 This ion has a very distinctive color. Add 1mL of potassium permanganate to a test tube. What is its color? phple Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide. Does the color change? Add 1mL of sulfuric acid. Does the color of permanganate ion differ in acidic or basic solution? U (yes or no) 2. Identification of manganese (IV) oxide, MnO2 Add a small portion of MnO2 (s) to water. Does it dissolve? U (yes or no) Note that MnO2 normally has a dark brown color when produced by a redox reaction in solution. 3. Identification of manganese (II) ion, Mn2+ Add 1mL of manganese (II) chloride solution to a test tube; what color is it? Cec. To the MnCl2 solution, add NaOH until a precipitate forms. This product is formed by a double displacement reaction; what is the formula of the precipitate? 4m(OH)2. What color is the precipitate? Allow the test tube to sit for a while. A second product is formed where the precipitate is exposed to air. By its color and the evidence above, which manganese species is this dark brown precipitate? Mn Complete the table below: Mn+2(2)=0 3. Identification of chromium (III) ion, Cr3+ Add 1mL of chromium (III) nitrate solution to a test tube. What color is Cr3+ ? bC Now slowly add sodium hydroxide one drop at a time (with gentle mixing) until Cr(OH)3(s) appears (a grayishgreen color). Continue to add sodium hydroxide until the precipitate disappears and the complex ion Cr(OH)41 forms. What color is this complex ion? green Even in acidic solution, Cr3+ ions have different colors depending upon what other ions are in solution. Another color of Cr3+ in solution is obtained by the following reaction: Add 3mL of sulfuric acid to 1mL of potassium dichromate, then add hydrogen peroxide (with gentle mixing) ur the color change is complete. The final color is due to Cr3+. What is its color? light greew 4. Complete the table below: 5. Balance the following redox reaction under acidic conditions (include phases for the final equation): Cr2O72+H2O2Cr3++O2 PART 1: IDENTIFICATION OF OXIDATION STATES A. Identification of Iron (ii) and Iron (III) PUT ALL IRON WASTE IN THE HOO0 1. Identification of iron (iii) ion, Fe3. Compare the color of iron (iii) chloride and iron (IIi) nitrate solutions (these are both acidic solutions). Are they the same color? Look at sodium chloride solution: notice that it is coloriess. Likewise, sodium nitrate solution is also colorless. Fe" has different colors in different solutions; sometimes it can be colorless. Therefore, color Add 1mL of iron (iii) chloride to a test tube, and add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. What color is the product? Park ofange Notice it is not a precipitate. It is the complex ion FeSCN 2+ that forms by the reaction: Fe3++SCNFeSCN2+ To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes (the complex disappears) - this is now a basic mixture. The iron (III) hydroxide precipitate that forms was also observed in Experiment 5. What color is the precipitate? Brifk To the same test tube, now add sulfuric acid until the color changes. The SCN complex returns in acid solution. It should be evident that the indicator will not complex with iron (III) in basic solution. Under basic conditions, the iron is in the form of Fe(OH)3(s). A basic solution of iron (III) will not show the blood red color of FeSCN2+ until it is acidified (before or after adding the thiocyanate indicator solution). 2. Identification of iron (II) ion, Fe2+ To 1mL of iron (II) sulfate solution (which is acidic), add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. Is there a significant color change? What color is the solution? Lizht oraye. A light color is caused by the presence of some Fe3+ (a contaminant), not the Fe2+. Fe2++SCNnoreaction To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes and a precipitate forms. This mixture is now basic. This precipitate is the color is the precipitate? 3. Complete the tables below: 2range DAY 2: IDENTIFICATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PRODUCTS UNDER VARYING CONDITIONS i. Basic conditions: Add 2mL of sodium hydroxide to 1mL change is complete. What color is the motassium permanganate. Then add hydrogen peroxide until the color Using this color, identify the manganese product. What is its dormul brow What evidence identifies the product from hydrogen peroxide? What evidence identifies the manganese product. What is its formula? Complete the redox reaction and balance it under basic conditions (include phases for for the final equation): 4MnO4+3H2O22MnO2+3H2+3H2O+2H2+CO3 Add hydrogen peroxide directly to 1mL of potassium permanganate until the color change is What color is the manganese product? Davhe Browe. Using this color, identify the manganese product. What is its formula? iii. Acidic conditions What evidence identifies the product from hydrogen peroxide? (evidence)bwbbles indicate the product is Hsay. Complete the redox reaction and balance it under acidic conditions (include phases for the final equation): 2H2SO4+2MnO4+3H2O22MnO2+2HSO4+3SO2+3H2O C. Identification of the Oxidation States of Oxygen 1. Add approximately 3mL of hydrogen peroxide solution to a test tube, then add a small amount of MnO2powder2 Test the gas formed using a splint test (a glowing splint will reignite when placed above the bubbling solution). Oxygen gas (O2) is the common oxidation product for hydrogen peroxide. It will not be necessary to prove that the bubbles are oxygen every time they are formed. Bubbles will be evidence of oxygen gas whenever hydrogen peroxide is used as a redox reagent. In fact, that will be the only circumstances when we should identify oxygen as a product in these redox laboratory experiments. 2. In these experiments, H2O2 will only be used as a reactant. It will not be produced, so it does not need identification. 3. If hydrogen peroxide acts as an oxidizing agent, the product will be water or hydroxide ions. Since there is no evident change in aqueous solution if water is formed, this product can only be identified indirectly. Thus when there is no clear evidence that another reagent is oxidized by the addition of hydrogen peroxide, we infer (conclude from clear evidence) that the hydrogen peroxide must be reduced to water (or possibly hydroxide in basic solution). The identification of this product is by inference. 4. Complete the table below: D. Identification of Some Manganese Oxidation States 1. Identification of permanganate ion, MnO4 This ion has a very distinctive color. Add 1mL of potassium permanganate to a test tube. What is its color? phple Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide. Does the color change? Add 1mL of sulfuric acid. Does the color of permanganate ion differ in acidic or basic solution? UU (yes or no) 2. Identification of manganese (IV) oxide, MnO2 Add a small portion of MnO2 (s) to water. Does it dissolve? O (yes or no) Note that MnO2 normally has a dark brown color when produced by a redox reaction in solution. 3. Identification of manganese (II) ion, Mn2+ Add 1mL of manganese (II) chloride solution to a test tube; what color is it? Cheer. To the MnCl2 solution, add NaOH until a precipitate forms. This product is formed by a double displacement reaction; what is the formula of the precipitate? Mn(OH)2 What color is the precipitate? - Tan Allow the test tube to sit for a while. A second product is formed where the precipitate is exposed to air. By its color and the evidence above, which manganese species is this dark brown precipitate? MnO q 4. Complete the table below: Identification of Some Chromium Oxidation States Chromium ions can be identified directly by color. ONL+4.ON0=2 0Ncr+4(2)=2 1. Identification of chromate ion, CrO42 DNCr =6 PUT ALL CHROMIUM WASTE IN THE HOOD. Look at the color of potassium chromate solution. Notice that potassium ions have no color (e.g., potassium nitrate is colorless). What color is chromate? yellow 2. Identification of dichromate ion, Cr2O72. Look at the color of potassium dichromate solution. What color is dichromate? or ange To 1mL of potassium dichromate solution, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes. yctlm Based on its color, what is the formula of the chromium product? To the yellow solution in the test tube, add sulfuric acid until the color changes again. . imys Based on its color, what is the formula of the chromium product? C2O72 Complete the reaction: 2H+(aq)+2CrO42(aq)Cr2O72+H2O 3. Identification of chromium (III) ion, Cr3+ Add 1mL of chromium (III) nitrate solution to a test tube. What color is Cr3+ ? blwe Now slowly add sodium hydroxide one drop at a time (with gentle mixing) until Cr(OH)3(s) appears (a grayishgreen color). Continue to add sodium hydroxide until the precipitate disappears and the complex ion Cr(OH)41 forms. What color is this complex ion? green Even in acidic solution, Cr3+ ions have different colors depending upon what other ions are in solution. Another color of Cr3+ in solution is obtained by the following reaction: Add 3mL of sulfuric acid to 1mL of potassium dichromate, then add hydrogen peroxide (with gentle mixing) unt the color change is complete. The final color is due to Cr3+. What is its color? light green The bubbles are O2 gas. 4. Complete the table below: 5. Balance the following redox reaction under acidic conditions (include phases tor me maal eyuatum. Cr2O72+H2O2Cr3++O2 A. Identification of Iron (II) and Iron (III) PUT ALL IRON WASTE IN THE HOOD. 1. Identification of iron (III) ion, Fe3+ Compare the color of iron (III) chloride and iron (III) nitrate solutions (these are both acidic solutions). Are they the same color? Look at sodium chloride solution: notice that it is colorless. Likewise, sodium nitrate solution is also colorless. Fe3+ has different colors in different solutions; sometimes it can be colorless. Therefore, color alone is not reliable for identification of Fe3+; instead it can be identified by an indicator such as the thiocyanate ion in ammonium thiocyanate or potassium thiocyanate solutions. Add 1mL of iron (III) chloride to a test tube, and add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. What color is the product? Burk orange Notice it is not a precipitate. It is the complex ion FeSCN2+ that forms by the reaction: Fe3++SCNFeSCN2+ To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes (the complex disappears) - this is now a basic mixture. The iron (III) hydroxide precipitate that forms was also observed in Experiment 5. What color is the precipitate? Brif To the same test tube, now add sulfuric acid until the color changes. The SCN complex returns in acid solution. It should be evident that the indicator will not complex with iron (III) in basic solution. Under basic conditions, the iron is in the form of Fe(OH)3(S). A basic solution of iron (III) will not show the blood red color of FeSCN2+ until it i acidified (before or after adding the thiocyanate indicator solution). 2. Identification of iron (II) ion, Fe2+ To 1mL of iron (II) sulfate solution (which is acidic), add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. Is there a significant color change? What color is the solution? Likht draye. A light color is caused by the presence of some Fe3+ (a contaminant), not the Fe2+. Fe2++SCNnoreaction To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes and/a precipitate forms. This mixture is no basic. This precipitate is the common form of iron (II) in basic solution, Fe(OH)2(s). What color is the precipitate? . Jarye 3. Complete the tables below: Summary Tables \begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|} \hline Reactant:Reducingagent & Product:Usualoxidationproduct & Identification:Oxidationproduct \\ \hline Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 & & \\ \hline Iron (II), Fe2+ in base & & \\ \hline Iron (II), Fe2+ in acid & & \\ \hline Nitrite, NO2 & & \\ \hline Sulfite, SO32 & & \\ \hline Sulfide, S2 & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} Summary Tables Complete the table below: \begin{tabular}{|l|c|l|} \hline MANGANESE & Oxidation state of Mn & Color \\ \hline MnO4 & 7 & purple \\ \hline MnO2 & 4 & dark bromm \\ \hline Mn2+ & 2 & Clear \\ \hline Mn(OH)2 & 2 & Tan \\ \hline \end{tabular} C. Identification of the Oxidation states of Oxygen the buobies are oxygenedox reagent. in fact, that will be the only circumstances when we gas whenever hydrogen 2. In these experiments. H,Oz will only be used as a reactant. It will not be produced, so it does not need D. Identification of Some Manganese Oxidation States PUT ALL MANGANESE WASTE IN THE HOOD. 1. Identification of permanganate ion, MnO4 This ion has a very distinctive color. Add 1mL of potassium permanganate to a test tube. What is its color? phple Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide. Does the color change? Add 1mL of sulfuric acid. Does the color of permanganate ion differ in acidic or basic solution? U (yes or no) 2. Identification of manganese (IV) oxide, MnO2 Add a small portion of MnO2 (s) to water. Does it dissolve? U (yes or no) Note that MnO2 normally has a dark brown color when produced by a redox reaction in solution. 3. Identification of manganese (II) ion, Mn2+ Add 1mL of manganese (II) chloride solution to a test tube; what color is it? Cec. To the MnCl2 solution, add NaOH until a precipitate forms. This product is formed by a double displacement reaction; what is the formula of the precipitate? 4m(OH)2. What color is the precipitate? Allow the test tube to sit for a while. A second product is formed where the precipitate is exposed to air. By its color and the evidence above, which manganese species is this dark brown precipitate? Mn Complete the table below: Mn+2(2)=0 3. Identification of chromium (III) ion, Cr3+ Add 1mL of chromium (III) nitrate solution to a test tube. What color is Cr3+ ? bC Now slowly add sodium hydroxide one drop at a time (with gentle mixing) until Cr(OH)3(s) appears (a grayishgreen color). Continue to add sodium hydroxide until the precipitate disappears and the complex ion Cr(OH)41 forms. What color is this complex ion? green Even in acidic solution, Cr3+ ions have different colors depending upon what other ions are in solution. Another color of Cr3+ in solution is obtained by the following reaction: Add 3mL of sulfuric acid to 1mL of potassium dichromate, then add hydrogen peroxide (with gentle mixing) ur the color change is complete. The final color is due to Cr3+. What is its color? light greew 4. Complete the table below: 5. Balance the following redox reaction under acidic conditions (include phases for the final equation): Cr2O72+H2O2Cr3++O2 PART 1: IDENTIFICATION OF OXIDATION STATES A. Identification of Iron (ii) and Iron (III) PUT ALL IRON WASTE IN THE HOO0 1. Identification of iron (iii) ion, Fe3. Compare the color of iron (iii) chloride and iron (IIi) nitrate solutions (these are both acidic solutions). Are they the same color? Look at sodium chloride solution: notice that it is coloriess. Likewise, sodium nitrate solution is also colorless. Fe" has different colors in different solutions; sometimes it can be colorless. Therefore, color Add 1mL of iron (iii) chloride to a test tube, and add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. What color is the product? Park ofange Notice it is not a precipitate. It is the complex ion FeSCN 2+ that forms by the reaction: Fe3++SCNFeSCN2+ To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes (the complex disappears) - this is now a basic mixture. The iron (III) hydroxide precipitate that forms was also observed in Experiment 5. What color is the precipitate? Brifk To the same test tube, now add sulfuric acid until the color changes. The SCN complex returns in acid solution. It should be evident that the indicator will not complex with iron (III) in basic solution. Under basic conditions, the iron is in the form of Fe(OH)3(s). A basic solution of iron (III) will not show the blood red color of FeSCN2+ until it is acidified (before or after adding the thiocyanate indicator solution). 2. Identification of iron (II) ion, Fe2+ To 1mL of iron (II) sulfate solution (which is acidic), add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. Is there a significant color change? What color is the solution? Lizht oraye. A light color is caused by the presence of some Fe3+ (a contaminant), not the Fe2+. Fe2++SCNnoreaction To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes and a precipitate forms. This mixture is now basic. This precipitate is the color is the precipitate? 3. Complete the tables below: 2range DAY 2: IDENTIFICATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PRODUCTS UNDER VARYING CONDITIONS i. Basic conditions: Add 2mL of sodium hydroxide to 1mL change is complete. What color is the motassium permanganate. Then add hydrogen peroxide until the color Using this color, identify the manganese product. What is its dormul brow What evidence identifies the product from hydrogen peroxide? What evidence identifies the manganese product. What is its formula? Complete the redox reaction and balance it under basic conditions (include phases for for the final equation): 4MnO4+3H2O22MnO2+3H2+3H2O+2H2+CO3 Add hydrogen peroxide directly to 1mL of potassium permanganate until the color change is What color is the manganese product? Davhe Browe. Using this color, identify the manganese product. What is its formula? iii. Acidic conditions What evidence identifies the product from hydrogen peroxide? (evidence)bwbbles indicate the product is Hsay. Complete the redox reaction and balance it under acidic conditions (include phases for the final equation): 2H2SO4+2MnO4+3H2O22MnO2+2HSO4+3SO2+3H2O C. Identification of the Oxidation States of Oxygen 1. Add approximately 3mL of hydrogen peroxide solution to a test tube, then add a small amount of MnO2powder2 Test the gas formed using a splint test (a glowing splint will reignite when placed above the bubbling solution). Oxygen gas (O2) is the common oxidation product for hydrogen peroxide. It will not be necessary to prove that the bubbles are oxygen every time they are formed. Bubbles will be evidence of oxygen gas whenever hydrogen peroxide is used as a redox reagent. In fact, that will be the only circumstances when we should identify oxygen as a product in these redox laboratory experiments. 2. In these experiments, H2O2 will only be used as a reactant. It will not be produced, so it does not need identification. 3. If hydrogen peroxide acts as an oxidizing agent, the product will be water or hydroxide ions. Since there is no evident change in aqueous solution if water is formed, this product can only be identified indirectly. Thus when there is no clear evidence that another reagent is oxidized by the addition of hydrogen peroxide, we infer (conclude from clear evidence) that the hydrogen peroxide must be reduced to water (or possibly hydroxide in basic solution). The identification of this product is by inference. 4. Complete the table below: D. Identification of Some Manganese Oxidation States 1. Identification of permanganate ion, MnO4 This ion has a very distinctive color. Add 1mL of potassium permanganate to a test tube. What is its color? phple Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide. Does the color change? Add 1mL of sulfuric acid. Does the color of permanganate ion differ in acidic or basic solution? UU (yes or no) 2. Identification of manganese (IV) oxide, MnO2 Add a small portion of MnO2 (s) to water. Does it dissolve? O (yes or no) Note that MnO2 normally has a dark brown color when produced by a redox reaction in solution. 3. Identification of manganese (II) ion, Mn2+ Add 1mL of manganese (II) chloride solution to a test tube; what color is it? Cheer. To the MnCl2 solution, add NaOH until a precipitate forms. This product is formed by a double displacement reaction; what is the formula of the precipitate? Mn(OH)2 What color is the precipitate? - Tan Allow the test tube to sit for a while. A second product is formed where the precipitate is exposed to air. By its color and the evidence above, which manganese species is this dark brown precipitate? MnO q 4. Complete the table below: Identification of Some Chromium Oxidation States Chromium ions can be identified directly by color. ONL+4.ON0=2 0Ncr+4(2)=2 1. Identification of chromate ion, CrO42 DNCr =6 PUT ALL CHROMIUM WASTE IN THE HOOD. Look at the color of potassium chromate solution. Notice that potassium ions have no color (e.g., potassium nitrate is colorless). What color is chromate? yellow 2. Identification of dichromate ion, Cr2O72. Look at the color of potassium dichromate solution. What color is dichromate? or ange To 1mL of potassium dichromate solution, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes. yctlm Based on its color, what is the formula of the chromium product? To the yellow solution in the test tube, add sulfuric acid until the color changes again. . imys Based on its color, what is the formula of the chromium product? C2O72 Complete the reaction: 2H+(aq)+2CrO42(aq)Cr2O72+H2O 3. Identification of chromium (III) ion, Cr3+ Add 1mL of chromium (III) nitrate solution to a test tube. What color is Cr3+ ? blwe Now slowly add sodium hydroxide one drop at a time (with gentle mixing) until Cr(OH)3(s) appears (a grayishgreen color). Continue to add sodium hydroxide until the precipitate disappears and the complex ion Cr(OH)41 forms. What color is this complex ion? green Even in acidic solution, Cr3+ ions have different colors depending upon what other ions are in solution. Another color of Cr3+ in solution is obtained by the following reaction: Add 3mL of sulfuric acid to 1mL of potassium dichromate, then add hydrogen peroxide (with gentle mixing) unt the color change is complete. The final color is due to Cr3+. What is its color? light green The bubbles are O2 gas. 4. Complete the table below: 5. Balance the following redox reaction under acidic conditions (include phases tor me maal eyuatum. Cr2O72+H2O2Cr3++O2 A. Identification of Iron (II) and Iron (III) PUT ALL IRON WASTE IN THE HOOD. 1. Identification of iron (III) ion, Fe3+ Compare the color of iron (III) chloride and iron (III) nitrate solutions (these are both acidic solutions). Are they the same color? Look at sodium chloride solution: notice that it is colorless. Likewise, sodium nitrate solution is also colorless. Fe3+ has different colors in different solutions; sometimes it can be colorless. Therefore, color alone is not reliable for identification of Fe3+; instead it can be identified by an indicator such as the thiocyanate ion in ammonium thiocyanate or potassium thiocyanate solutions. Add 1mL of iron (III) chloride to a test tube, and add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. What color is the product? Burk orange Notice it is not a precipitate. It is the complex ion FeSCN2+ that forms by the reaction: Fe3++SCNFeSCN2+ To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes (the complex disappears) - this is now a basic mixture. The iron (III) hydroxide precipitate that forms was also observed in Experiment 5. What color is the precipitate? Brif To the same test tube, now add sulfuric acid until the color changes. The SCN complex returns in acid solution. It should be evident that the indicator will not complex with iron (III) in basic solution. Under basic conditions, the iron is in the form of Fe(OH)3(S). A basic solution of iron (III) will not show the blood red color of FeSCN2+ until it i acidified (before or after adding the thiocyanate indicator solution). 2. Identification of iron (II) ion, Fe2+ To 1mL of iron (II) sulfate solution (which is acidic), add a couple of drops of KSCN(aq) indicator. Is there a significant color change? What color is the solution? Likht draye. A light color is caused by the presence of some Fe3+ (a contaminant), not the Fe2+. Fe2++SCNnoreaction To the same test tube, add sodium hydroxide until the color changes and/a precipitate forms. This mixture is no basic. This precipitate is the common form of iron (II) in basic solution, Fe(OH)2(s). What color is the precipitate? . Jarye 3. Complete the tables below: Summary Tables \begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|} \hline Reactant:Reducingagent & Product:Usualoxidationproduct & Identification:Oxidationproduct \\ \hline Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 & & \\ \hline Iron (II), Fe2+ in base & & \\ \hline Iron (II), Fe2+ in acid & & \\ \hline Nitrite, NO2 & & \\ \hline Sulfite, SO32 & & \\ \hline Sulfide, S2 & & \\ \hline \end{tabular}Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


