Question
This week's homework will have you putting together both an income statement along with a cash flow statement. Why do organizations need cash flow statements
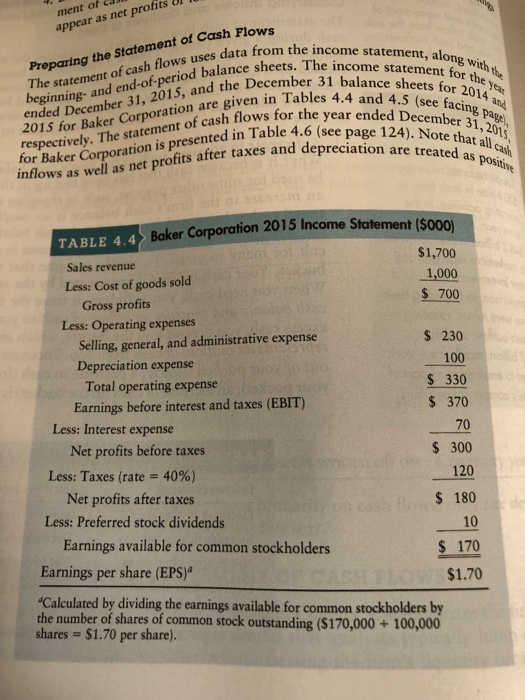
This week's homework will have you putting together both an income statement along with a cash flow statement. Why do organizations need cash flow statements in addition to income statements? What makes cash flow statements important? Please take a look at the income statement and Statement of Cash Flows below and talk about why the a company needs both. Share any thoughts you have about specific things covered in the statement of cash flows that are not covered in the income statment and balance sheet. You may find the additional online resources below helpful. Be sure to share thoughts you have about operating, investing and financing activities and how they are different.
https://youtu.be/38WcNba0Ic0
https://youtu.be/KAOrqyzgYzA
https://youtu.be/Dt6ClHG34RM
https://youtu.be/TXmm2EV2QWg
https://youtu.be/xdCIksxKUdQ
https://youtu.be/jVdL_mVyJFQ
https://youtu.be/yTpHTQal8d4


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


