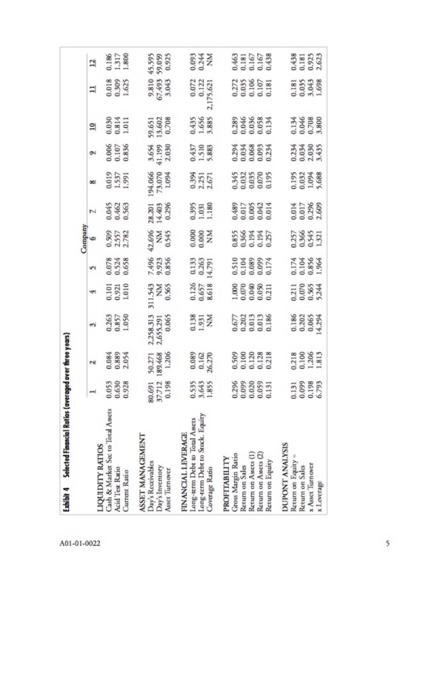
THUNDERBIRD FINANCIAL ANALYSIS-IDENTIFYING THE INDUSTRY fo 12 difir induis Common-siaed balance sh Call em ed by oal ae.com The 12 compunis are membe of the blowing 12 dffeen indutio Advetising Electic utility producer and distrb qer producer and distibu) Reail gcey Assignment ndastry THUNDERBIRD FINANCIAL ANALYSISIDENTIFYING THE INDUSTRY Companies within an industry face similar opportunities and constraints, and comequendly, dhey ofien make similar operating, investing and financing decisions. Therefore,companics within the same in- dustry tend to exhibit similar financial characteristics, as measured by financial ratios For cxample, "ol economy businesses with large amounts of tangible assets may have higher leverge ratios chan "new economy" businesses with large amounts of intangible asets such as knowledge assets or a large and loyal customer base. On the other hand, since opportunitics and constraints tend so be different across in different industries tend to hibin dTerent financial ratios. With some know edge of the different operating, investing and financing decisions across industries, financial ratios ca be used to identify an indusry (see Exhibit 1 for the definition of ratios used). Balance sheets and income statements for the mos recent chree years were gathered for 12 compa nies from 12 different industries. Common-sized balance sheets (all items scaled by sotal assets), com- mon-sized income statements (all items scaled by net sales), and selected financial ratios for the most recent three years were prepared. Since unusual deviation from target values may occur in any given year, the values were averaged over three years. The three-year average common-sied balance sheet, com- mon-sized income statement, and financial ratios are reported in Exhibits 2, 3, and 4, respectively The 12 companies are members of the following 12 different industries Airline Commercial banking (items fitted into the same categories as the non-financial Erm) Computer software development Department store chain (with its own in-store credit card Electric utility (producer and distributor) (producer and distributor) and gas (upstream explorer and producer) Retail drug Retail grocery Sporting (organized as a master limited partnership (MLP), hence no corporate taxes Using the financial statement data providedinExhibis 2,3, and 4, manch the companis with cheir industry. EXHIBIT1 Definitions of Some Key Financial Ratios LIQUIDITY RATIOS Cash & Marketable Securities to Total Assets- (Cash+Market Securities) Total Assets Acid Test Ratio Current ratio (Cash +Market Securities Receivables)/Current Liabilities Current Assets/Current Liabilities ASSET MANAGEMENT Day's Receivable Day's Inventory Asset Turnover 365/ Sales / Receivables) 365/ (Cost of Sales/Iaventory) Sales/Total Assets FINANCIAL LEVERAGE Long-term Debt to Total Assets (Convertible Debt + Long-term Debt + Non-current Capital Leases+Other Long-term Liai)Total Assets Long-term Debt to Stockholders' EquityConvertible Debt Long-term Debe Non-current Leases Coverage Ratio Income Before Taxes + Interest Expense) / Intere Expense PROFITABILITY Gross Margin Ratio Return on Sales Returm on Assets(1) Return on Assets (2) Return on Equity Gross Profit /Sales Net Income/Sales - Net Income /Total Assets = (Net Income + Interest Expense) / Total Assets Net Income / Stockholders Equity DUPONT ANALYSIS Return on Equity Return on Sales *Asset Turnover Leverage - (Net Income / Sales) x (Sales / Assets) x (Assets Stockholders Equity) A01-01-0022 A01-01-0022 THUNDERBIRD FINANCIAL ANALYSIS-IDENTIFYING THE INDUSTRY fo 12 difir induis Common-siaed balance sh Call em ed by oal ae.com The 12 compunis are membe of the blowing 12 dffeen indutio Advetising Electic utility producer and distrb qer producer and distibu) Reail gcey Assignment ndastry THUNDERBIRD FINANCIAL ANALYSISIDENTIFYING THE INDUSTRY Companies within an industry face similar opportunities and constraints, and comequendly, dhey ofien make similar operating, investing and financing decisions. Therefore,companics within the same in- dustry tend to exhibit similar financial characteristics, as measured by financial ratios For cxample, "ol economy businesses with large amounts of tangible assets may have higher leverge ratios chan "new economy" businesses with large amounts of intangible asets such as knowledge assets or a large and loyal customer base. On the other hand, since opportunitics and constraints tend so be different across in different industries tend to hibin dTerent financial ratios. With some know edge of the different operating, investing and financing decisions across industries, financial ratios ca be used to identify an indusry (see Exhibit 1 for the definition of ratios used). Balance sheets and income statements for the mos recent chree years were gathered for 12 compa nies from 12 different industries. Common-sized balance sheets (all items scaled by sotal assets), com- mon-sized income statements (all items scaled by net sales), and selected financial ratios for the most recent three years were prepared. Since unusual deviation from target values may occur in any given year, the values were averaged over three years. The three-year average common-sied balance sheet, com- mon-sized income statement, and financial ratios are reported in Exhibits 2, 3, and 4, respectively The 12 companies are members of the following 12 different industries Airline Commercial banking (items fitted into the same categories as the non-financial Erm) Computer software development Department store chain (with its own in-store credit card Electric utility (producer and distributor) (producer and distributor) and gas (upstream explorer and producer) Retail drug Retail grocery Sporting (organized as a master limited partnership (MLP), hence no corporate taxes Using the financial statement data providedinExhibis 2,3, and 4, manch the companis with cheir industry. EXHIBIT1 Definitions of Some Key Financial Ratios LIQUIDITY RATIOS Cash & Marketable Securities to Total Assets- (Cash+Market Securities) Total Assets Acid Test Ratio Current ratio (Cash +Market Securities Receivables)/Current Liabilities Current Assets/Current Liabilities ASSET MANAGEMENT Day's Receivable Day's Inventory Asset Turnover 365/ Sales / Receivables) 365/ (Cost of Sales/Iaventory) Sales/Total Assets FINANCIAL LEVERAGE Long-term Debt to Total Assets (Convertible Debt + Long-term Debt + Non-current Capital Leases+Other Long-term Liai)Total Assets Long-term Debt to Stockholders' EquityConvertible Debt Long-term Debe Non-current Leases Coverage Ratio Income Before Taxes + Interest Expense) / Intere Expense PROFITABILITY Gross Margin Ratio Return on Sales Returm on Assets(1) Return on Assets (2) Return on Equity Gross Profit /Sales Net Income/Sales - Net Income /Total Assets = (Net Income + Interest Expense) / Total Assets Net Income / Stockholders Equity DUPONT ANALYSIS Return on Equity Return on Sales *Asset Turnover Leverage - (Net Income / Sales) x (Sales / Assets) x (Assets Stockholders Equity) A01-01-0022 A01-01-0022