Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
QUESTION 1 Super Drive is a computer hard drive manufacturer. The company's balance sheet for the fiscal year ended on November 30 appears below: Super
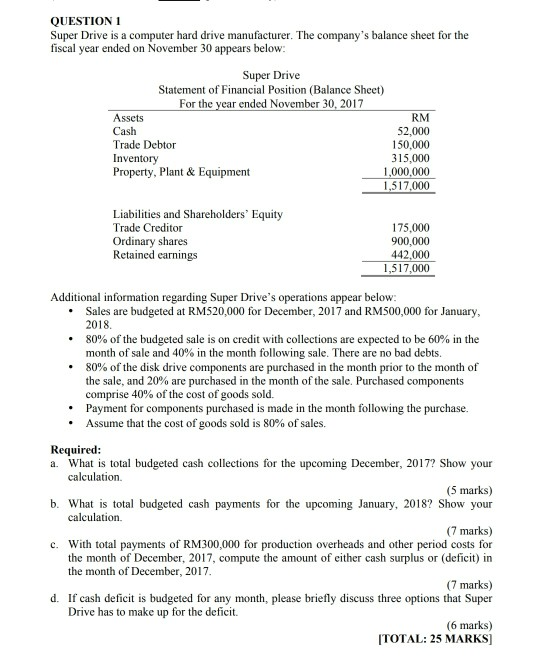
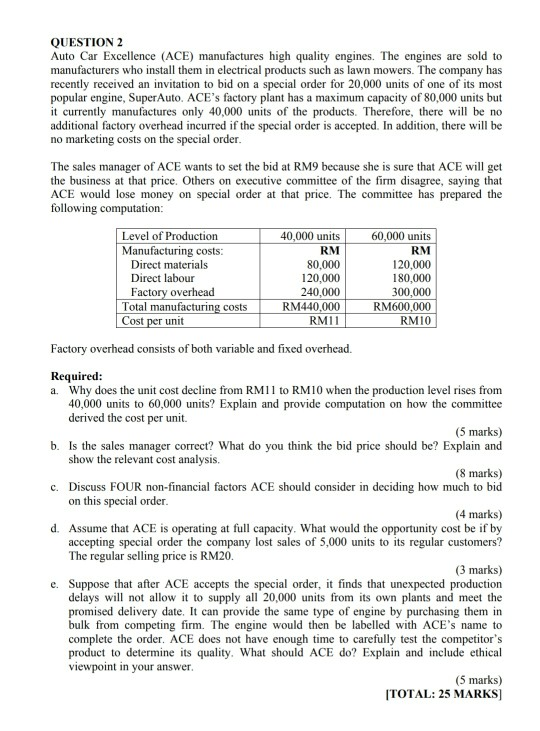

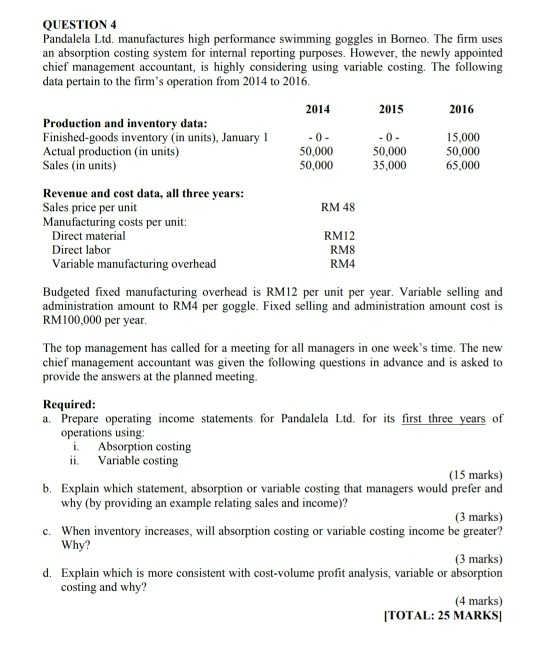
QUESTION 1 Super Drive is a computer hard drive manufacturer. The company's balance sheet for the fiscal year ended on November 30 appears below: Super Drive Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) For the year ended November 30, 2017 Assets RM Cash 52.000 Trade Debtor 150,000 Inventory 315,000 Property, Plant & Equipment 1,000,000 1,517,000 Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Trade Creditor Ordinary shares Retained earnings 175.000 900,000 442,000 1,517,000 Additional information regarding Super Drive's operations appear below: Sales are budgeted at RM520,000 for December, 2017 and RM500,000 for January, 2018 . 80% of the budgeted sale is on credit with collections are expected to be 60% in the month of sale and 40% in the month following sale. There are no bad debts. 80% of the disk drive components are purchased in the month prior to the month of the sale, and 20% are purchased in the month of the sale. Purchased components comprise 40% of the cost of goods sold. Payment for components purchased is made in the month following the purchase Assume that the cost of goods sold is 80% of sales. Required: a. What is total budgeted cash collections for the upcoming December, 2017? Show your calculation (5 marks) b. What is total budgeted cash payments for the upcoming January, 2018? Show your calculation (7 marks) c. With total payments of RM300,000 for production overheads and other period costs for the month of December, 2017, compute the amount of either cash surplus or (deficit) in the month of December, 2017 (7 marks) d. If cash deficit is budgeted for any month, please briefly discuss three options that Super Drive has to make up for the deficit. (6 marks) [TOTAL: 25 MARKS] QUESTION 2 Auto Car Excellence (ACE) manufactures high quality engines. The engines are sold to manufacturers who install them in electrical products such as lawn mowers. The company has recently received an invitation to bid on a special order for 20,000 units of one of its most popular engine, Super Auto. ACE's factory plant has a maximum capacity of 80,000 units but it currently manufactures only 40,000 units of the products. Therefore, there will be no additional factory overhead incurred if the special order is accepted. In addition, there will be no marketing costs on the special order. The sales manager of ACE wants to set the bid at RM9 because she is sure that ACE will get the business at that price. Others on executive committee of the firm disagree, saying that ACE would lose money on special order at that price. The committee has prepared the following computation: Level of Production Manufacturing costs: Direct materials Direct labour Factory overhead Total manufacturing costs Cost per unit 40,000 units RM 80,000 120,000 240,000 RM440,000 RM11 60,000 units RM 120,000 180,000 300,000 RM600,000 RMIO Factory overhead consists of both variable and fixed overhead. Required: a. Why does the unit cost decline from RM11 to RM10 when the production level rises from 40,000 units to 60,000 units? Explain and provide computation on how the committee derived the cost per unit. (5 marks) b. Is the sales manager correct? What do you think the bid price should be? Explain and show the relevant cost analysis. (8 marks) c. Discuss FOUR non-financial factors ACE should consider in deciding how much to bid on this special order. (4 marks) d. Assume that ACE is operating at full capacity. What would the opportunity cost be if by accepting special order the company lost sales of 5,000 units to its regular customers? The regular selling price is RM20. (3 marks) Suppose that after ACE accepts the special order, it finds that unexpected production delays will not allow it to supply all 20,000 units from its own plants and meet the promised delivery date. It can provide the same type of engine by purchasing them in bulk from competing firm. The engine would then be labelled with ACE's name to complete the order. ACE does not have enough time to carefully test the competitor's product to determine its quality. What should ACE do? Explain and include ethical viewpoint in your answer. (5 marks) TOTAL: 25 MARKS] QUESTION 3 Clear Sound Ltd. produces stereo speakers. The company is considering a modification to one of its models - CSIIX, that would make it more attractive to customers. One unit of CSIIX currently costs RM250 and sells for RM300. Unit cost RM150 90 Variable manufacturing cost Fixed manufacturing cost Variable selling and administrative Total costs RM250 Clear Sound's marketing department carried out a market research at a cost of RM50,000 and as a result, has discovered that the following modifications are necessary Unit cost RM12 Modification Add Bluetooth technology Introduce pastel colours design Extend warranty to five years Total modification costs RM25 In addition, an analysis of competitive stereo speakers in the market revealed a variety of features, with some models having all of the features that Clear Sound is considering. The current market price for the similar models averages RM315. Clear Sound uses absorption cost criteria to set the selling price for all its models Required: a. Calculate the current rate of profit margin for CSIIX. (2 marks) b. Using the current cost plus pricing approach, can Clear Sound meet the competitive market price of modified CSIIX? Why or why not? (6 marks) c. Assume that Clean Sound uses target costing in meeting the competitive market price of modified CSIIX. By how much should the current cost be reduced if the company desires to earn the same rate of profit margin that is currently being carned? (6 marks) d. Why there is a need in target costing to focus on the customer and have a marketing team become involved with product design? (4 marks) e. Explain how the use of relevant costs as the basis of setting a selling price may be appropriate for short-term pricing decisions but may be inappropriate for long-term pricing decisions. (4 marks) f. Define price discrimination. How is this "action" viewed from the Islamic perspective? Discuss (3 marks) TOTAL: 25 MARKS QUESTION 4 Pandalela Ltd. manufactures high performance swimming goggles in Bomeo. The firm uses an absorption costing system for internal reporting purposes. However, the newly appointed chief management accountant, is highly considering using variable costing. The following data pertain to the firm's operation from 2014 to 2016. 2014 2015 2016 Production and inventory data: Finished-goods inventory (in units), January 1 Actual production (in units) Sales (in units) -0- 50,000 50,000 -0- 50,000 35,000 15,000 50,000 65,000 RM 48 Revenue and cost data, all three years: Sales price per unit Manufacturing costs per unit: Direct material Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead RM12 RM8 RM4 Budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is RM12 per unit per year. Variable selling and administration amount to RM4 per goggle. Fixed selling and administration amount cost is RM100,000 per year. The top management has called for a meeting for all managers in one week's time. The new chief management accountant was given the following questions in advance and is asked to provide the answers at the planned meeting. Required: a. Prepare operating income statements for Pandalela Ltd. for its first three years of operations using: i Absorption costing ii. Variable costing (15 marks) b. Explain which statement, absorption or variable costing that managers would prefer and why (by providing an example relating sales and income)? (3 marks) c. When inventory increases, will absorption costing or variable costing income be greater? Why? (3 marks) d. Explain which is more consistent with cost-volume profit analysis, variable or absorption costing and why? (4 marks) TOTAL: 25 MARKS QUESTION 1 Super Drive is a computer hard drive manufacturer. The company's balance sheet for the fiscal year ended on November 30 appears below: Super Drive Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) For the year ended November 30, 2017 Assets RM Cash 52.000 Trade Debtor 150,000 Inventory 315,000 Property, Plant & Equipment 1,000,000 1,517,000 Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Trade Creditor Ordinary shares Retained earnings 175.000 900,000 442,000 1,517,000 Additional information regarding Super Drive's operations appear below: Sales are budgeted at RM520,000 for December, 2017 and RM500,000 for January, 2018 . 80% of the budgeted sale is on credit with collections are expected to be 60% in the month of sale and 40% in the month following sale. There are no bad debts. 80% of the disk drive components are purchased in the month prior to the month of the sale, and 20% are purchased in the month of the sale. Purchased components comprise 40% of the cost of goods sold. Payment for components purchased is made in the month following the purchase Assume that the cost of goods sold is 80% of sales. Required: a. What is total budgeted cash collections for the upcoming December, 2017? Show your calculation (5 marks) b. What is total budgeted cash payments for the upcoming January, 2018? Show your calculation (7 marks) c. With total payments of RM300,000 for production overheads and other period costs for the month of December, 2017, compute the amount of either cash surplus or (deficit) in the month of December, 2017 (7 marks) d. If cash deficit is budgeted for any month, please briefly discuss three options that Super Drive has to make up for the deficit. (6 marks) [TOTAL: 25 MARKS] QUESTION 2 Auto Car Excellence (ACE) manufactures high quality engines. The engines are sold to manufacturers who install them in electrical products such as lawn mowers. The company has recently received an invitation to bid on a special order for 20,000 units of one of its most popular engine, Super Auto. ACE's factory plant has a maximum capacity of 80,000 units but it currently manufactures only 40,000 units of the products. Therefore, there will be no additional factory overhead incurred if the special order is accepted. In addition, there will be no marketing costs on the special order. The sales manager of ACE wants to set the bid at RM9 because she is sure that ACE will get the business at that price. Others on executive committee of the firm disagree, saying that ACE would lose money on special order at that price. The committee has prepared the following computation: Level of Production Manufacturing costs: Direct materials Direct labour Factory overhead Total manufacturing costs Cost per unit 40,000 units RM 80,000 120,000 240,000 RM440,000 RM11 60,000 units RM 120,000 180,000 300,000 RM600,000 RMIO Factory overhead consists of both variable and fixed overhead. Required: a. Why does the unit cost decline from RM11 to RM10 when the production level rises from 40,000 units to 60,000 units? Explain and provide computation on how the committee derived the cost per unit. (5 marks) b. Is the sales manager correct? What do you think the bid price should be? Explain and show the relevant cost analysis. (8 marks) c. Discuss FOUR non-financial factors ACE should consider in deciding how much to bid on this special order. (4 marks) d. Assume that ACE is operating at full capacity. What would the opportunity cost be if by accepting special order the company lost sales of 5,000 units to its regular customers? The regular selling price is RM20. (3 marks) Suppose that after ACE accepts the special order, it finds that unexpected production delays will not allow it to supply all 20,000 units from its own plants and meet the promised delivery date. It can provide the same type of engine by purchasing them in bulk from competing firm. The engine would then be labelled with ACE's name to complete the order. ACE does not have enough time to carefully test the competitor's product to determine its quality. What should ACE do? Explain and include ethical viewpoint in your answer. (5 marks) TOTAL: 25 MARKS] QUESTION 3 Clear Sound Ltd. produces stereo speakers. The company is considering a modification to one of its models - CSIIX, that would make it more attractive to customers. One unit of CSIIX currently costs RM250 and sells for RM300. Unit cost RM150 90 Variable manufacturing cost Fixed manufacturing cost Variable selling and administrative Total costs RM250 Clear Sound's marketing department carried out a market research at a cost of RM50,000 and as a result, has discovered that the following modifications are necessary Unit cost RM12 Modification Add Bluetooth technology Introduce pastel colours design Extend warranty to five years Total modification costs RM25 In addition, an analysis of competitive stereo speakers in the market revealed a variety of features, with some models having all of the features that Clear Sound is considering. The current market price for the similar models averages RM315. Clear Sound uses absorption cost criteria to set the selling price for all its models Required: a. Calculate the current rate of profit margin for CSIIX. (2 marks) b. Using the current cost plus pricing approach, can Clear Sound meet the competitive market price of modified CSIIX? Why or why not? (6 marks) c. Assume that Clean Sound uses target costing in meeting the competitive market price of modified CSIIX. By how much should the current cost be reduced if the company desires to earn the same rate of profit margin that is currently being carned? (6 marks) d. Why there is a need in target costing to focus on the customer and have a marketing team become involved with product design? (4 marks) e. Explain how the use of relevant costs as the basis of setting a selling price may be appropriate for short-term pricing decisions but may be inappropriate for long-term pricing decisions. (4 marks) f. Define price discrimination. How is this "action" viewed from the Islamic perspective? Discuss (3 marks) TOTAL: 25 MARKS QUESTION 4 Pandalela Ltd. manufactures high performance swimming goggles in Bomeo. The firm uses an absorption costing system for internal reporting purposes. However, the newly appointed chief management accountant, is highly considering using variable costing. The following data pertain to the firm's operation from 2014 to 2016. 2014 2015 2016 Production and inventory data: Finished-goods inventory (in units), January 1 Actual production (in units) Sales (in units) -0- 50,000 50,000 -0- 50,000 35,000 15,000 50,000 65,000 RM 48 Revenue and cost data, all three years: Sales price per unit Manufacturing costs per unit: Direct material Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead RM12 RM8 RM4 Budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is RM12 per unit per year. Variable selling and administration amount to RM4 per goggle. Fixed selling and administration amount cost is RM100,000 per year. The top management has called for a meeting for all managers in one week's time. The new chief management accountant was given the following questions in advance and is asked to provide the answers at the planned meeting. Required: a. Prepare operating income statements for Pandalela Ltd. for its first three years of operations using: i Absorption costing ii. Variable costing (15 marks) b. Explain which statement, absorption or variable costing that managers would prefer and why (by providing an example relating sales and income)? (3 marks) c. When inventory increases, will absorption costing or variable costing income be greater? Why? (3 marks) d. Explain which is more consistent with cost-volume profit analysis, variable or absorption costing and why? (4 marks) TOTAL: 25 MARKS
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


