Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
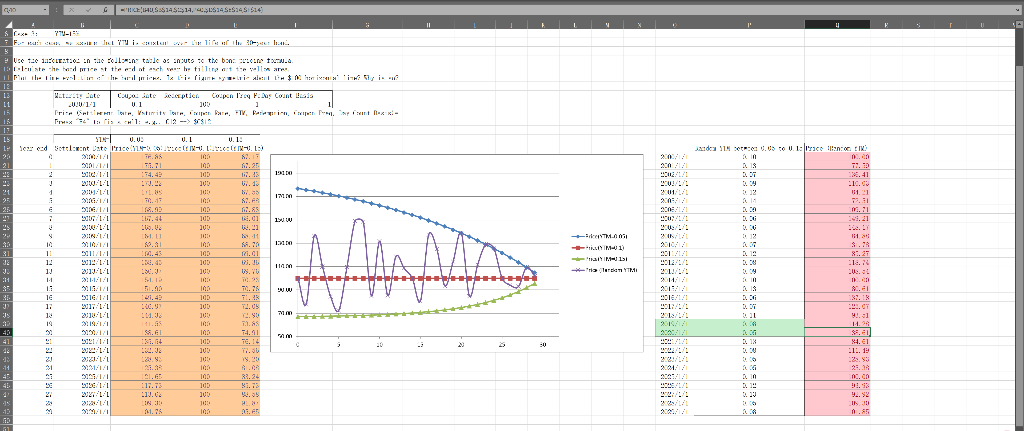
Use the project3.xlsx (Problem 1) to calculate how bond prices vary over time when the YTM is held constant at three different levels (YTM=5%, 10%,
- Use the project3.xlsx (Problem 1) to calculate how bond prices vary over time when the YTM is held constant at three different levels (YTM=5%, 10%, and 15%) or when the YTM also changes randomly over time (i.e., the future interest rate varies over time). Answer the following four questions. (4 points for the four columns of pricing formulas in the Excel file; 4 points for the following 4 questions)
- When YTM = Coupon Rate, does the bond price increases/decreases/remains unchanged over time?
- When YTM > Coupon Rate, does the bond price increases/decreases/remains unchanged over time? When YTM
- Note that YTM=5% and YTM=15% are deviating from YTM=10% by the same amount, 5%. Are the price trajectories for YTM=5% and YTM=15% symmetric about the par value (the $100 horizontal line)? Why is so?
- What is the expected holding period return from 1/1/2019 to 1/1/2020 if we believe that the YTM happen to be 0.08 and 0.05 on those two days (highlighted in green)? Dont forget the coupon payment in your HPR calculations.
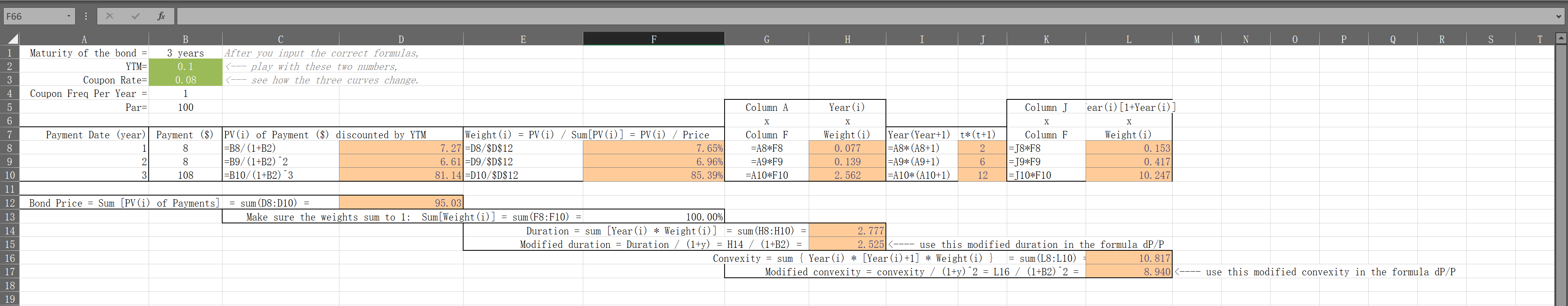
- Use the Project3.xlsx (Problem 2) to perform the following tasks (3-year $100 bond with annual coupon rate 8% and YTM 10%). (7 points)
- Fill in the cells D8:D10 with the PV of all three payments. Calculate the bond price in D12 as the summation of all PV of three payments. Calculate the weights in F8:F10 which will be used to calculate duration. Make sure the weights sum up to 1 in F13.
- The duration is equal to the PV-weighted average of maturity for each payment. Calculate weights * time to payment in H8:H10. Sum them up in H14 to get duration. Divide the duration by (1+YTM) to obtain the modified duration in H15.
- If maturity of each payment is represented by Year(i), the convexity is equal to the PV-weighted average of [Year(i)*(Year(i)+1)]. First calculate [Year(i)*(Year(i)+1)] in J8:J10. Then calculate weights * [Year(i)*(Year(i)+1)] in L8:L10. Sum them up into L16 to get convexity. Divide the convexity by (1+YTM)^2 to obtain the modified convexity in L17.
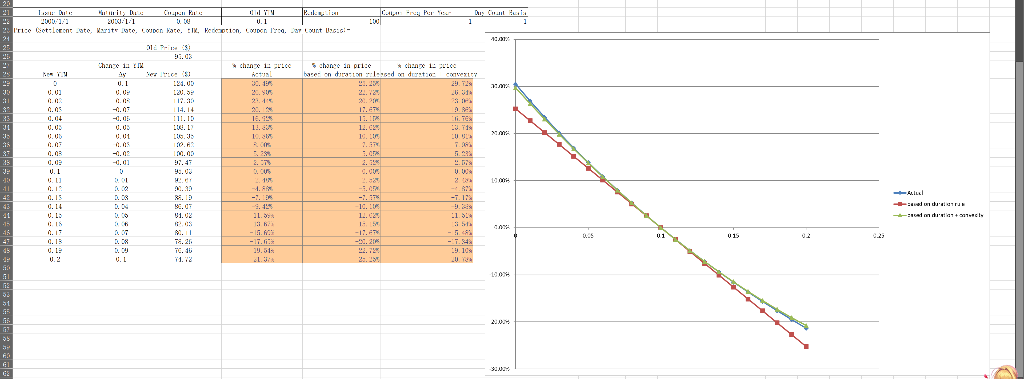
- Based on the old price in C26 and the new price in C29:C49, calculate the actual percentage change in bond price:
- Calculate the approximate percentage change in bond prices by using the duration rule: , where is the modified duration in H15.
- Calculate the approximate percentage change in bond prices by using both the duration and the modified convexity: , where is the modified convexity in L17. Note that the Convexity in Equation (11.5) on Page 346 of the textbook actually refers to the modified convexity in L17.
- Which approximation (the approximation based on Duration alone in e or the approximation based on both Duration and Convexity in f) is better and closer to the actual percentage change in bond price in d?
G - 11 CE LHD 144:21, 514 114 li ! II 1 4 - F. - Ex Yi Sex Llifi. UC C CLER:0 na 2. tales nuts ac the bac 31.tr the band print the end of esch he tillire at tells are Pili wa Irinks. 1x Lilian Lith $ xi? 13 It 15 HELL. Leto Culto deception Coupon Is My Count ia . WW11 0 205 1 I'ri Hornsturit lorem. "TV, Perrin, P. et Ilex x - , Prax2 1: l'ishl: -.4.. (? --> 31 19 15 de 14 0.03 V.1 Price : CIK 192100 2.8 3.37 21.0 01.01 171 2012 2.30 - 150 W 24.21 2 1 13210 M. M41) 31 JE MA 3.30 8.27 18. 114 "2121 2011/1/ ra YTM 911 v. U. Sorced Setcant Date Irace. CN.L.EN.1) . TFSS 102 M. 13.1! 100 2 174.49 100 11.15 u LL JU 6.13 1 24:: JU 76.15 105 50 100 W.RS SG 1:1 100 1.01 2011 10. V JUR 6.31 PIN:1:1 MU TU!! N. 100 SA 3111/11 114. 100 Ri.cl 2019 1:1 JUL Bi. 2011:L:L JU U. Tv 51. OK . 15.11 100 TO. 103 11.1 200 11.05 2010-11 114.3 2010 11.15 100 7.88 100 74.91 105 me. 14 WELL 200 22:11 JU! 79.29 100 100 14 32.24 117.1 100 213.0 200 2.1.1 LIN 19:11 11.25 102 :11 ST 8.1 2S 3.3 mm 2012 21 +9=28BRASS OT . 14.96 S. 14.61 .11.19 21 3. 13 30 .. -11 2M AA 2.1 0.00 20 3. 9.92 21/ 13 F66 x fi B E F. G H I K L M N 0 P R S 3 years 1 2 3 4 A Maturity of the bond YTM= Coupon Rate= Coupon Freq Per Year Par= C D After you input the correct formulas, --- play with these two numbers, 31 19 15 de 14 0.03 V.1 Price : CIK 192100 2.8 3.37 21.0 01.01 171 2012 2.30 - 150 W 24.21 2 1 13210 M. M41) 31 JE MA 3.30 8.27 18. 114 "2121 2011/1/ ra YTM 911 v. U. Sorced Setcant Date Irace. CN.L.EN.1) . TFSS 102 M. 13.1! 100 2 174.49 100 11.15 u LL JU 6.13 1 24:: JU 76.15 105 50 100 W.RS SG 1:1 100 1.01 2011 10. V JUR 6.31 PIN:1:1 MU TU!! N. 100 SA 3111/11 114. 100 Ri.cl 2019 1:1 JUL Bi. 2011:L:L JU U. Tv 51. OK . 15.11 100 TO. 103 11.1 200 11.05 2010-11 114.3 2010 11.15 100 7.88 100 74.91 105 me. 14 WELL 200 22:11 JU! 79.29 100 100 14 32.24 117.1 100 213.0 200 2.1.1 LIN 19:11 11.25 102 :11 ST 8.1 2S 3.3 mm 2012 21 +9=28BRASS OT . 14.96 S. 14.61 .11.19 21 3. 13 30 .. -11 2M AA 2.1 0.00 20 3. 9.92 21/ 13 F66 x fi B E F. G H I K L M N 0 P R S 3 years 1 2 3 4 A Maturity of the bond YTM= Coupon Rate= Coupon Freq Per Year Par= C D After you input the correct formulas, --- play with these two numbers,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


