Question: Use this function to fill in interQuartile Interquartile Range (IQR) in a Linked List: Slow and Fast Pointers Quartiles Quartiles are used in statistics to



Use this function to fill in interQuartile
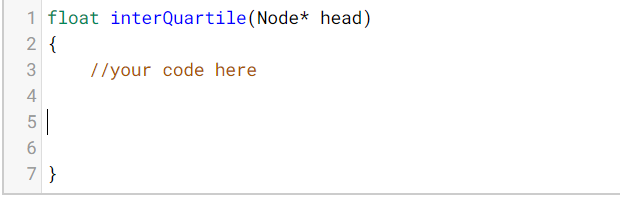
Interquartile Range (IQR) in a Linked List: Slow and Fast Pointers Quartiles Quartiles are used in statistics to classify data. Per their name, they divide data into quarters. Given a set of data: 2, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 A A A Q1 Q2 Q3 The lower quartile would be the value that separates the lowest quarter of the data from the rest of the data set. So in this instance it would be the first 4. The middle quartile (also known as the median) separates the lowest 2 quarters of the data from the rest of the data set. The upper quartile separates the lowest 3 quarters of the data from the rest of the data set. The interquartile range is the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile: Q3 - Q1. In case the number of values in the list are odd, the central element is a unique element. Example, if the list has size = 9. The fifth element in the list will be the median. In case the number of values in the list are even, the central element is a average of two elements. Example, if the list has size = 10. The average of fourth and fifth element in the list will be the median. Q1 is the median of the beginning and the element preceding median, and Q3 is the median of the element succeeding median and the end. Another example, 1,2,3,4 Q1Q2Q3 Here, Q2 = Average of 2 and 3 = 2.5 Q1 = List consists of elements: 1, 2 (everything before median) = Average of 1 and 2 = 1.5 Q3 = List consists of elements: 3,4 (everything after median) = Average of 3 and 4 = 3.5 IQR = 3.5 - 1.5 = 2.0 Problem Statement We've given you sorted data in the form of a linked list (e.g, the above data would be inputted as 2->4->4->5->6->7->8). Given a singly linked list of integers that represents a data set (with head node head ), return the interquartile range of the data set using the slow and fast pointer approach OR using a methodology that does not iterate over the linked list twice (for example: finding the count of number of elements in first iteration). You cannot use arrays, vectors, lists or an STL implementation of List ADT. If you use the latter, you will lose 3 points. The following Node class was already defined for you: class Node { public: int value; Node* next = NULL; }; Constraints . The list is limited to positive numbers The list will have at least 4 values The list will not be empty The list is sorted . . Test cases We have implemented the main() for you. The main calls your interQuartile() function. Input: Line 1 is the number of elements in the list and Line 2 is the Linked List passed into the interQuartile() function. Output: Interquartile Range of the list, a floating point value. Explanation . You will be given a set of data, integers in this case, that are all interconnected in a linked list. For example, the data set 2, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 will given to you as the following linked list: 2->4->4->5->6->7->8. Your job is to find the interquartile range of the data set. The interquartile range is defined as the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile. In case of odd number of elements in the list, the median value is the central value. In a list that consists of 1->2->3, median is 2. If the list has even number of elements, then the median will be the average of the two central values. If we had 1->1->2->3, it would be (1+2)/2 = 1.5. Note you are expected to return a floating point value. Note that the Q1 is the median of the beginning and the element preceding median, and Q3 is the median of the element succeeding median and the end. 3 1 float interQuartile (Node* head) 2 { 3 //your code here 4 5 6 7}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


