Question
(Use this question below to complete exercise 6) Exercise 4: Review the following completed example for a bond issued at a price of 100. A
(Use this question below to complete exercise 6)
Exercise 4: Review the following completed example for a bond issued at a price of 100. A $50,000, 10 year, 9% (Stated rate) bond is issued on January 1. The bond pays interest semi-annually, each January 1 and July 1. The bonds Stated rate is equal to the Effective rate at the time of issue so the bond price is 100. Review the following entries.
Exercise 6: Complete the following example for a bond issued at a price of 106. T-accts below. The same bond from Exercise 4 is issued at a price of 106. This price indicates that the Effective rate of interest is less than the Stated rate of interest. As a result, the bond issues at a Premium. 1. Entry required upon issuance of the bond. Cash proceeds: $________ x ________ = $__________ Note: Even though a Premium is recorded, the company must still repay just $50,000 at the end of the bond term. 2. Entry on first interest payment date: a. Actual Interest payment $___________ x _____% x 6/12 = $_________ b. Amortization of the Premium $_________ / ____ Interest periods = $______ NOTE: Much like amortizing a discount, use the total number of interest periods to amortize the premium using the straight-line method. In this case the premium amortization effectively decreases Interest Expense. Why? Once again, since the bond was issued at a premium the company received cash proceeds greater than the principal amount ($50,000). However, the company only has to pay back the principal at the end of the bond term. So, the premium received up front effectively reduces the overall interest expense to the company over the life of the bond. Another way to think about it is that the interest paid combined with the premium amortization lowers the Interest Expense recognized to the full Effective rate of interest (remember in this case the Effective rate was less than the Stated rate). In the end, the company will really pay the Effective (market) rate of interest over the life of the bond.
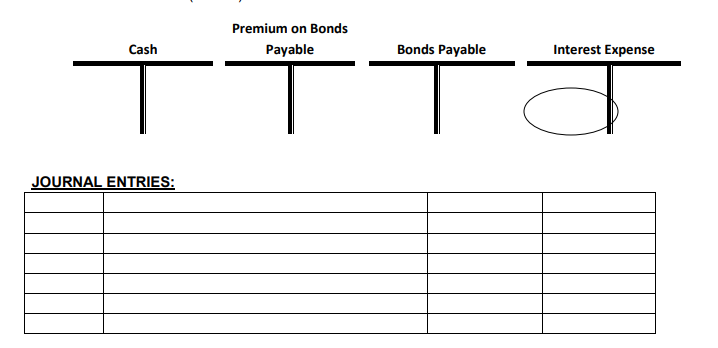
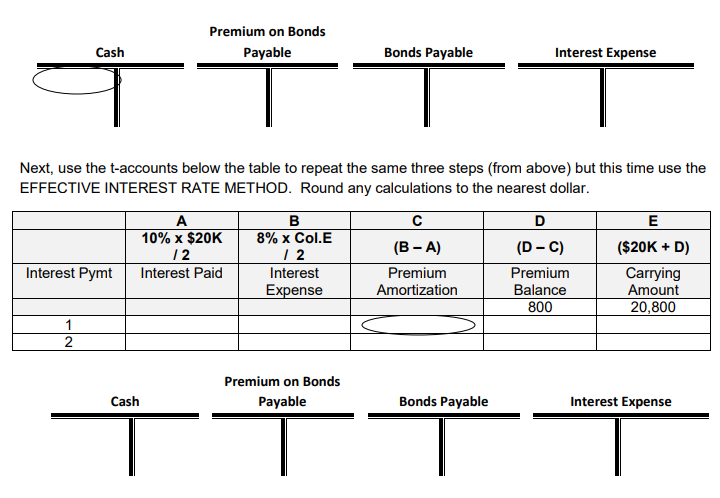
Exercise 8: Complete the following problem. A $20,000, 2 year, 10% (Stated rate) bond is sold when the Effective (Market) rate is 8%. The bond pays interest semi-annually. Assuming a price of 104 at issuance record the following. 1. Entry required upon issuance of the bond. Cash proceeds: $________ x ________ = $_________ 2. Entry on the first interest payment date. Use STRAIGHT-LINE method for amortization. a. Actual Interest payment $________ x _____% x 6/12 = $________ b. Amortization of the Premium using the STRAIGHT-LINE method. $____/___ periods= $___ 3. Entry on the second interest payment date. Use STRAIGHT-LINE method for amortization. a. Actual Interest payment b. Amortization of the Premium using the STRAIGHT-LINE method.
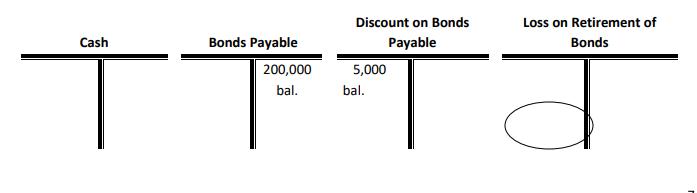
Example 10: Use the t-accounts below to record the following bond retirement. A $200,000 callable bond with a $5,000 discount is called at a price of 104.
Premium on Bonds Cash Payable Bonds Payable Interest Expense JOURNAL ENTRIES
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


