Question
Using Assemply... encrypt.asm This part of the program will input two strings, with appropriate prompts. The program will then take, character by character, the original
Using Assemply...
encrypt.asm
This part of the program will input two strings, with appropriate prompts. The program will then take, character by character, the original message and the key and apply the Vigene?re cipher [1] (algorithm for encryption) to it. To collect a single byte from memory, try something like the following:
mov dl, [rax]
In the above example, dl is an 8bit register (actually, the low order 8 bits of the 64bit register rdx). Similarly, there are al, bl, cl (and even ah, bh, ch, and dh).
The Vigene?re cipher is a relatively old idea. It takes a key of any size, which is a series of letters (e.g. a word). The key is used repeatedly so that each character in the plaintext has a corresponding letter from the key. For example, here is the matchup for the key OPENSESAME and the message MEETUSATTWELVEOCLOCKSHARP:
Key: OPENSESAMEOPENSESAMEOPENS Plaintext: MEETUSATTWELVEOCLOCKSHARP
Note: Duplicating the key so that it is the same length as the message is one of the trickiest parts of this program. Create a sufficiently large string variable for the result (e.g. duplicatedKey), copy the letters from key until you get to the nullterminator (a character equal to zero). Keep a count of how many characters have been copied, and stop when that count reaches the message length. Whenever you get to the end of the key, go back to the first character.
The letter O above the M in the leftmost column in the above example means that your algorithm will apply a CaesarO shift. This is a fancy way of saying that you will add 14 to the ASCII value for M (with wraparound if the value goes beyond Z). A full table of the shifts is given in the table below. For example, in the leftmost column in the above example, the result would be the ASCII value of M + 14, which would be A (due to wraparound).
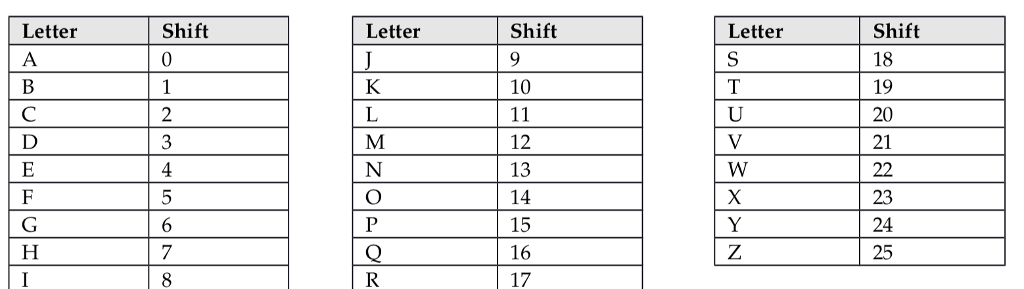
Hint: Instead of a 26part if/elseif/else statement, a much better way is to subtract the value of 'A' from whichever letter you have in the key to get the shift value.
The complete example, along with its ciphertext is given below:
Key: OPENSESAMEOPENSESAMEOPENS Plaintext: MEETUSATTWELVEOCLOCKSHARP Ciphertext: ATIGMWSTFASAZRGGDOOOGWEEH
After collecting the key and the plaintext from the user, your program will output the ciphertext to the console.
Note: You can limit the length of these strings to 100 characters in your program, and you do not have to handle the case when the user types more than 100 characters. You can also limit the string to only uppercase letters (as shown in the examples), to make the logic simpler. If there are no spaces, that also means that you can use scanf(%s, str) to enter the string(s).
Sample Output
Enter the message: MEETUSATTWELVEOCLOCKSHARP Enter the key: OPENSESAME Encrypted message: ATIGMWSTFASAZRGGDOOOGWEEH
decrypt.asm
This program will do the opposite of encrypt.asm. It will apply the Vigene?re cipher in reverse. It will subtract the offset from the ciphertext characters, producing the plaintext.
Sample Output
Enter the encrypted message: ATIGMWSTFASAZRGGDOOOGWEEH Enter the key: OPENSESAME Decrypted message: MEETUSATTWELVEOCLOCKSHARP23 24 25 8901-2 S1122222 UVWXYZ 01234567 S01-2345678 23 24 25 8901-2 S1122222 UVWXYZ 01234567 S01-2345678
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


