Question
Using #include #include // data structures typedef struct _Node{ void* data; struct _Node* next; struct _Node* prev; } Node; typedef struct _LList{ Node* first; Node*
Using
#include
// data structures
typedef struct _Node{ void* data; struct _Node* next; struct _Node* prev; } Node;
typedef struct _LList{ Node* first; Node* last; int size; int itemSize; char* type; } LinkedList;
// forward declarations LinkedList* llist_initialize(int dataTypeSize, char* name); bool llist_add_at(LinkedList* list, int index, void* element); bool llist_add_first(LinkedList* list, void* element); bool llist_add_last(LinkedList* list, void* element);
LinkedList* llist_initialize(int dataTypeSize, char* name) { // creating the list LinkedList* list = (LinkedList*) malloc(sizeof(LinkedList)); // initializing the list *list = (LinkedList) { .first = NULL, .last = NULL, .size = 0, .itemSize = dataTypeSize, .type = name }; // returning the list return list; } bool llist_add_at(LinkedList* list, int index, void* element) { if(list == NULL) { // list is NULL return false; } if(!(0 size)) { // invalid index return false; } if(index == 0) { // add at first return llist_add_first(list, element); } if(index == list->size) { // add at last return llist_add_last(list, element); } // iterating to the position before index Node* it = list->first; while(--index > 0) { it = it->next; } // creating node Node* node = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node)); *node = (Node) { .data = element, .next = it->next, .prev = it, }; // inserting it->next->prev = node; it->next = node; // updating size ++list->size; // successful insertion return true; } bool llist_add_first(LinkedList* list, void* element) { if(list == NULL) { // list is NULL return false; } // creating node Node* node = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node)); // inserting if(list->first == NULL) { // list is empty *node = (Node) { .data = element, .next = NULL, .prev = NULL, }; list->first = list->last = node; } else { *node = (Node) { .data = element, .next = list->first, .prev = NULL, }; list->first->prev = node; } // updating size ++list->size; // successful insertion return true; } bool llist_add_last(LinkedList* list, void* element) { if(list == NULL) { // list is NULL return false; } // creating node Node* node = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node)); // inserting if(list->last == NULL) { // list is empty *node = (Node) { .data = element, .next = NULL, .prev = NULL, }; list->first = list->last = node; } else { *node = (Node) { .data = element, .next = NULL, .prev = list->last, }; list->last->next = node; } // updating size ++list->size; // successful insertion return true; }
create functions
C Programming
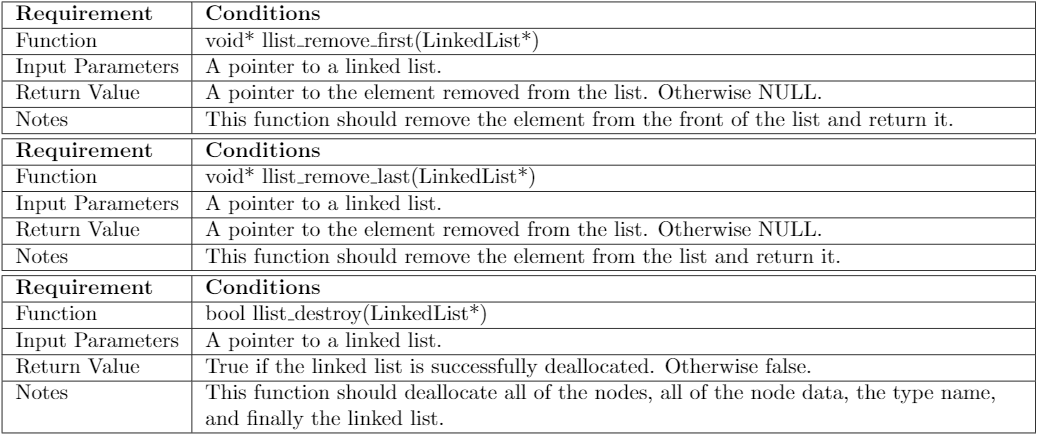
Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Conditions void* llist_remove_first (Linked List*) A pointer to a linked list. A pointer to the element removed from the list. Otherwise NULL. This function should remove the element from the front of the list and return it. Conditions void* llist_remove_last (Linked List*) A pointer to a linked list. A pointer to the element removed from the list. Otherwise NULL. This function should remove the element from the list and return it. Conditions bool llist_destroy (LinkedList*) A pointer to a linked list. True if the linked list is successfully deallocated. Otherwise false. This function should deallocate all of the nodes, all of the node data, the type name, and finally the linked listStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


