Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
We are given a COMPLETE BINARY TREE where nodes and edges have positive weights. Node weights are stored in a 1-dimensional array WN. Edge weights
We are given a COMPLETE BINARY TREE where nodes and edges have positive weights. Node weights are stored in a 1-dimensional array WN. Edge weights are stored in a 2-dimensional array WE where 0 denotes no edge. Starting at the root of the tree and moving to either one of the children from the current node, the goal is to find the minimum total weight (i.e. sum of node and edge weights) path from the root to any one of the leaves. 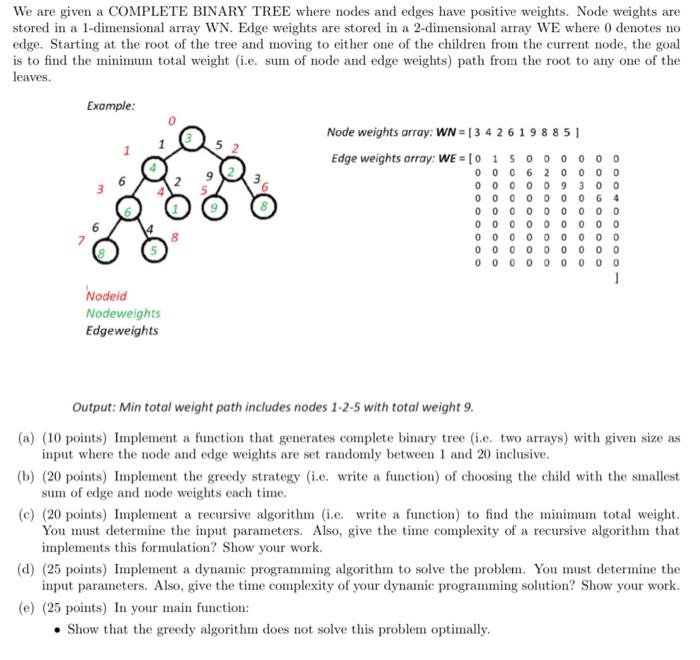
We are given a COMPLETE BINARY TREE where nodes and edges have positive weights. Node weights are stored in a 1-dimensional array WN. Edge weights are stored in a 2-dimensional array WE where 0 denotes no edge. Starting at the root of the tree and moving to either one of the children from the current node, the goal is to find the minimum total weight (i.e. sum of node and edge weights) path from the root to any one of the leaves. Edgeweightsarray:WE=0000000000100000000500000000060000000020000000009000000003000000000600000000400000] Output: Min total weight path includes nodes 1-2-5 with total weight 9. (a) (10 points) Implement a function that generates complete binary tree (i.e. two arrays) with given size as input where the node and edge weights are set randomly between 1 and 20 inclusive. (b) (20 points) Implement the greedy strategy (i.e. write a function) of choosing the child with the smallest sum of edge and node weights each time. (c) (20 points) Implement a recursive algorithm (i.e. write a function) to find the minimum total weight. You must determine the input parameters. Also, give the time complexity of a recursive algorithm that implements this formulation? Show your work. (d) (25 points) Implement a dynamic programming algorithm to solve the problem. You must determine the input parameters. Also, give the time complexity of your dynamic programming solution? Show your work. (e) (25 points) In your main function: - Show that the greedy algorithm does not solve this problem optimally (a) (10 points) Implement a function that generates complete binary tree (i.e. two arrays) with given size as input where the node and edge weights are set randomly between 1 and 20 inclusive.
(b) (20 points) Implement the greedy strategy (i.e. write a function) of choosing the child with the smallest sum of edge and node weights each time.
(c) (20 points) Implement a recursive algorithm (i.e. write a function) to find the minimum total weight. You must determine the input parameters. Also, give the time complexity of a recursive algorithm that implements this formulation? Show your work.
(d) (25 points) Implement a dynamic programming algorithm to solve the problem. You must determine the input parameters. Also, give the time complexity of your dynamic programming solution? Show your work.
(e) (25 points) In your main function:
Show that the greedy algorithm does not solve this problem optimally.
Run each of the recursive and dynamic functions with three different input sizes and compute the actual running times (in milliseconds or seconds) of these three algorithms. You will need to calculate the time passed before and after making a call to each function. Provide a 2x3 table involving the actual running times.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


