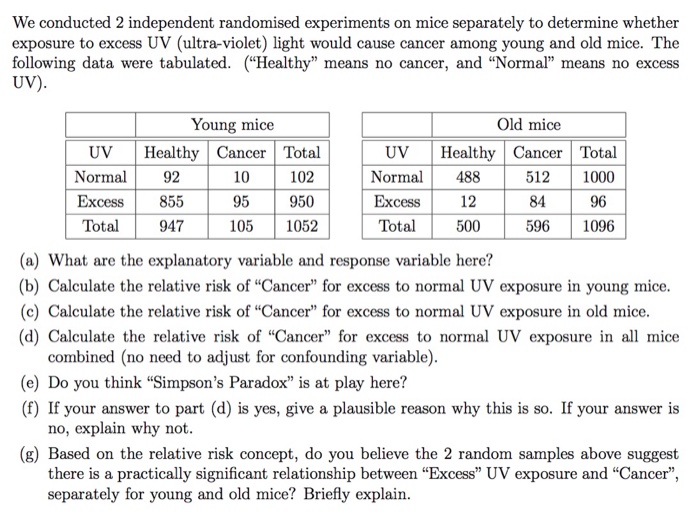
We conducted 2 independent randomised experiments on mice separately to determine whether exposure to excess UV {ultraviolet} light would cause cancer among young and old mice. The following data were tabulated. {\"Healthy" means no cancer. and "Normal\" means no excess {a} What are the explanatory variable and response variable here? {1:} Calculate the relative risk of \"Cancer\" for excms to normal UV exposure in young mice. (c} Calculate the relative risk of \"Genes? for excess to normal UV exposure in old mice. {d} Calculate the relative risk of \"Cancer" for to normal UV exposure in all mice combined (no need to adjust for confounding variable}. {e} Do you think \"Simpson's Paradox" is at play here? {i} If your answer to part (d) is yes, give a plausible reason why this is so. Ifyonr answer is no, explain why not. {g} Based on the relative risk concept, do you believe the 2 random samples above suggest there is a practically signicant relationship between \"Excess" UV exposure and \"(L'anoel separately for young and old mice? Briefly explain. Researchers conducted a study on the effectiveness of a knee surgery to cure arthritis. It was randomly determined whether people got the knee surgery. Everyone who underwent the surgery reported feeling less pain. Is this evidence that the surgery causes a decrease in pain? Select one: O a. No, because there may be confounding variables such as prior illnesses and exercise habits. b. No, as the study does not have a control or comparison group. O c. Yes, because everyone who underwent the surgery reported feeling less pain. O d. Yes, because this is a randomised experiment where it was randomly determined whether people got the knee surgery.This is not conducted in a laboratory but rather in a natural setting, but still has some control over variables. With this method the researcher is more able to generalize to 'real-world' settings. O Observational Study Natural Experiment Laboratory Experiment Field Experiment Case Study Correlational Study Survey Secondary Data Analysis18. Which of the following represents the most appropriate natural experiment to evaluate the relationship between distance away from school and class attendance. a. Comparing people who have cars versus people who don't have cars, as cars reduce time of travel. b. Comparing people who live along the bus route versus people who live further away from bus route. c. An implementation of randomly assigned shuttle routes across town, which reduces time of travel for those living closer to the newer route. d. Comparing people living in rich versus poor neighborhood based on neighborhood income. 19. To evaluate the causal effects of maternal education and infant health outcomes, Currie and Moretti (2003) use a. compulsory education reform implemented during an individual's college going age as a natural experiment. b. expansion of GI Bills during an individual's college going age as a natural experiment. c. construction of colleges in an individual's neighborhood during the time of one's college going age as a natural experiment. d. expansion of the EITC (Earned Income Tax Credit) during an individual's college going age as a natural experiment