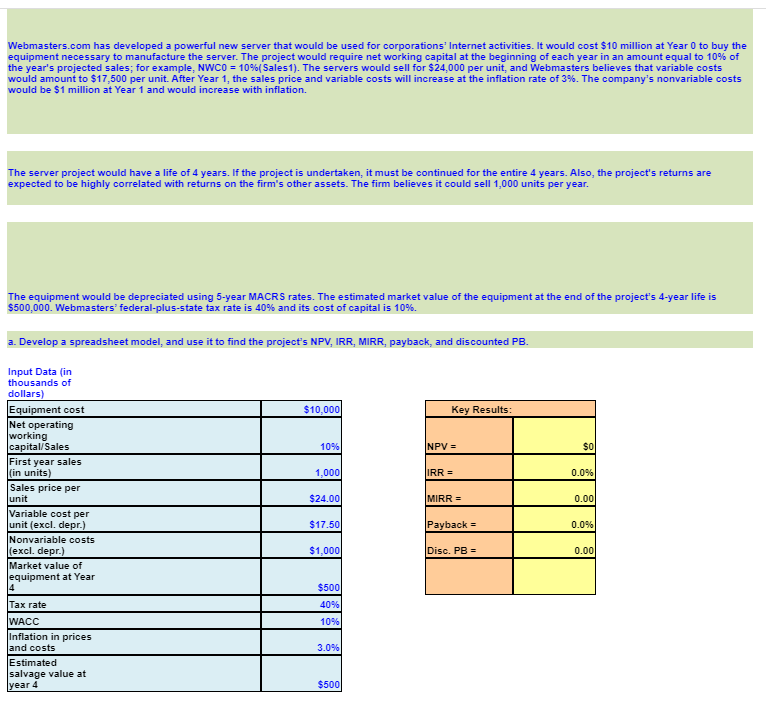
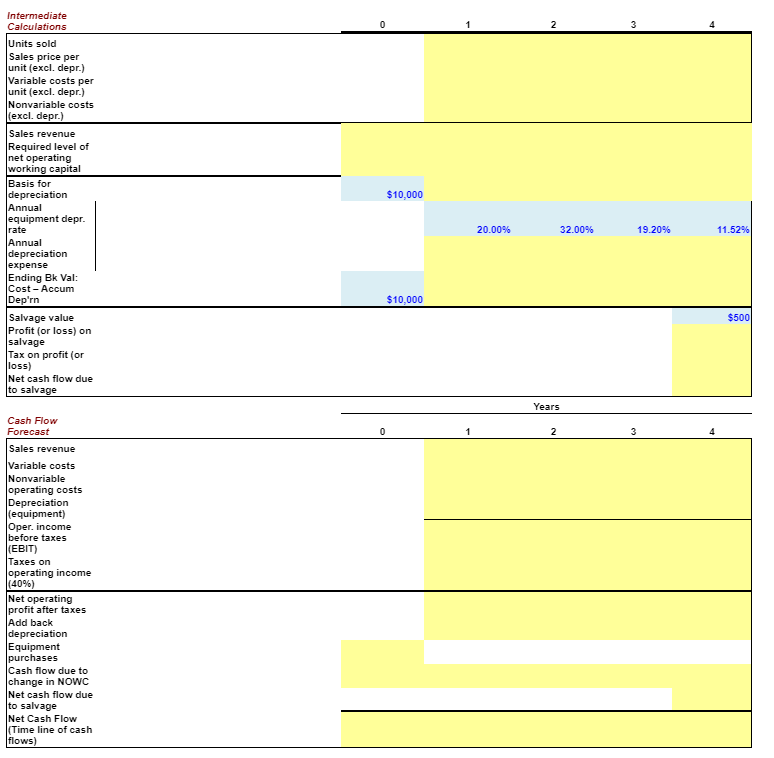
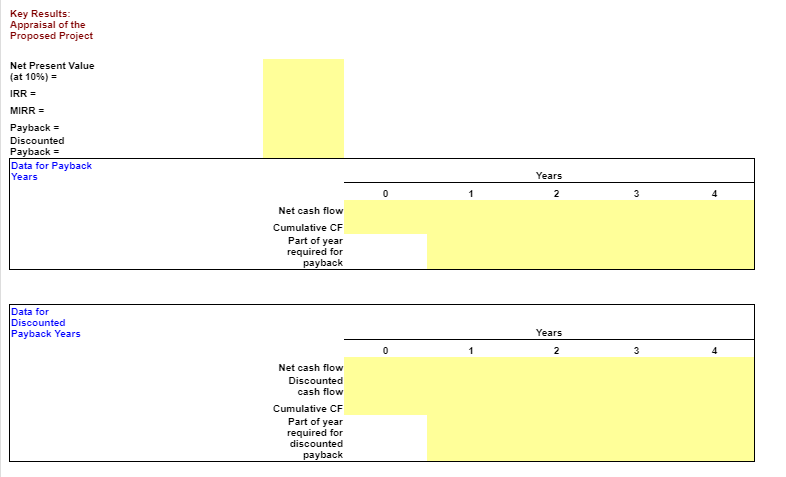
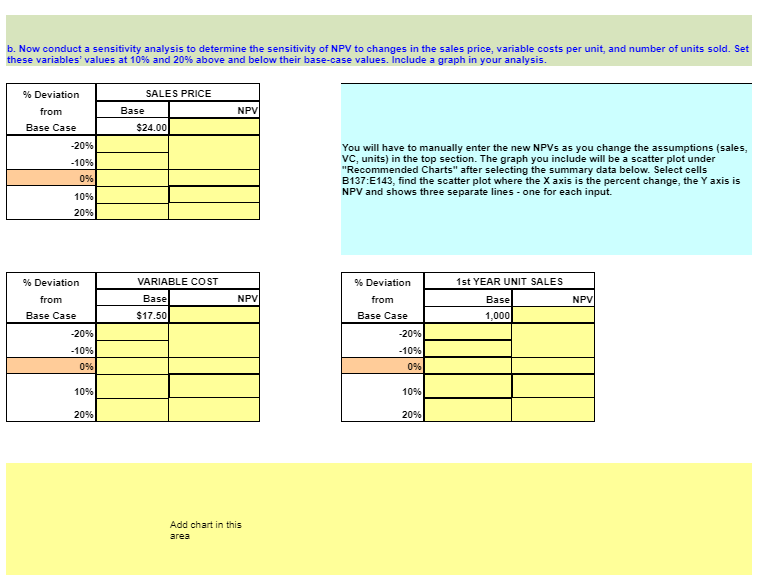
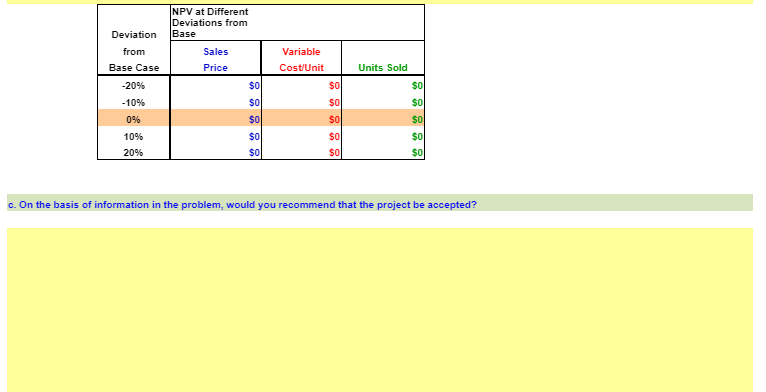
Webmasters.com has developed a powerful new server that would be used for corporations Internet activities. It would cost $10 million at Year 0 to buy the equipment necessary to manufacture the server. The project would require net working capital at the beginning of each year in an amount equal to 10% of the year's projected sales; for example, NWC0 = 10% ( Sales1). The servers would sell for $24,000 per unit, and Webmasters believes that variable costs would amount to $17,500 per unit. After Year 1, the sales price and variable costs will increase at the inflation rate of 3%. The company's nonvariable costs would be $1 million at Year 1 and would increase with inflation. The server project would have a life of 4 years. If the project is undertaken, it must be continued for the entire 4 years. Also, the project's returns are expected to be highly correlated with returns on the firm's other assets. The firm believes it could sell 1,000 units per year. The equipment would be depreciated using 5-year MACRS rates. The estimated market value of the equipment at the end of the project's 4-year life is $500,000. Webmasters' federal-plus-state tax rate is 40% and its cost of capital is 10%. Develop a spreadsheet model, and use it to find the project's NPV, IRR, MIRR, payback, and discounted PB. Input Data (in thousands of dollars) Equipment cost $10,000 Key Results: Net operating working capital/Sales 10% $0 First year sales (in units) 1,000 0.0% Sales price per unit $24.00 0.00 Variable cost per unit (excl. depr.) $17.50 0.0% Nonvariable costs (excl. depr.) $1,000 0.00 Market value of equipment at Year $500 Tax rate 40% WACC 10% Inflation in prices and costs 3.0% Estimated salvage value at year 4 $500 NPV = IRR = MIRR = Payback = Disc. PB = Intermediate Calculations Units sold Sales price per unit (excl. depr.) Variable costs per unit (excl. depr.) Nonvariable costs (excl. depr.) Sales revenue Required level of net operating working capital Basis for depreciation Annual equipment depr. rate Annual depreciation expense Ending Bk Val: Cost - Accum Dep'rn Salvage value Profit (or loss) on salvage Tax on profit (or loss) Net cash flow due to salvage Cash Flow Forecast Sales revenue Variable costs Nonvariable operating costs Depreciation (equipment) Oper. income before taxes (EBIT) Taxes on operating income (40%) Net operating profit after taxes Add back depreciation Equipment purchases Cash flow due to change in NOWC Net cash flow due to salvage Net Cash Flow (Time line of cash flows) 0 $10,000 $10,000 1 20.00% 2 Years 2 32.00% 3 3 19.20% 4 11.52% $500 Key Results: Appraisal of the Proposed Project Net Present Value (at 10%) = IRR = MIRR = Payback = Discounted Payback = Data for Payback Years Data for Discounted Payback Years Net cash flow Cumulative CF Part of year required for payback Net cash flow Discounted cash flow Cumulative CF Part of year required for discounted payback 0 1 1 Years 2 Years 2 3 b. Now conduct a sensitivity analysis to determine the sensitivity of NPV to changes in the sales price, variable costs per unit, and number of units sold. Set these variables' values at 10% and 20% above and below their base-case values. Include a graph in your analysis. % Deviation SALES PRICE from Base NPV Base Case You will have to manually enter the new NPVs as you change the assumptions (sales, VC, units) in the top section. The graph you include will be a scatter plot under "Recommended Charts" after selecting the summary data below. Select cells B137:E143, find the scatter plot where the X axis is the percent change, the Y axis is NPV and shows three separate lines - one for each input. 1st YEAR UNIT SALES % Deviation from Base Base Case 1,000 -20% -10% 0% 10% 20% % Deviation from Base Case -20% -10% 0% 10% 20% $24.00 VARIABLE COST Base $17.50 NPV Add chart in this area -20% -10% 0% 10% 20% NPV NPV at Different Deviations from Sales Price Deviation Base from Base Case -20% $0 -10% $0 0% $0 10% $0 20% $0 $0 c. On the basis of information in the problem, would you recommend that the project be accepted? $0 88888 $0 $0 Variable Cost/Unit 50 50 50 50 50 $0 $0 Units Sold











