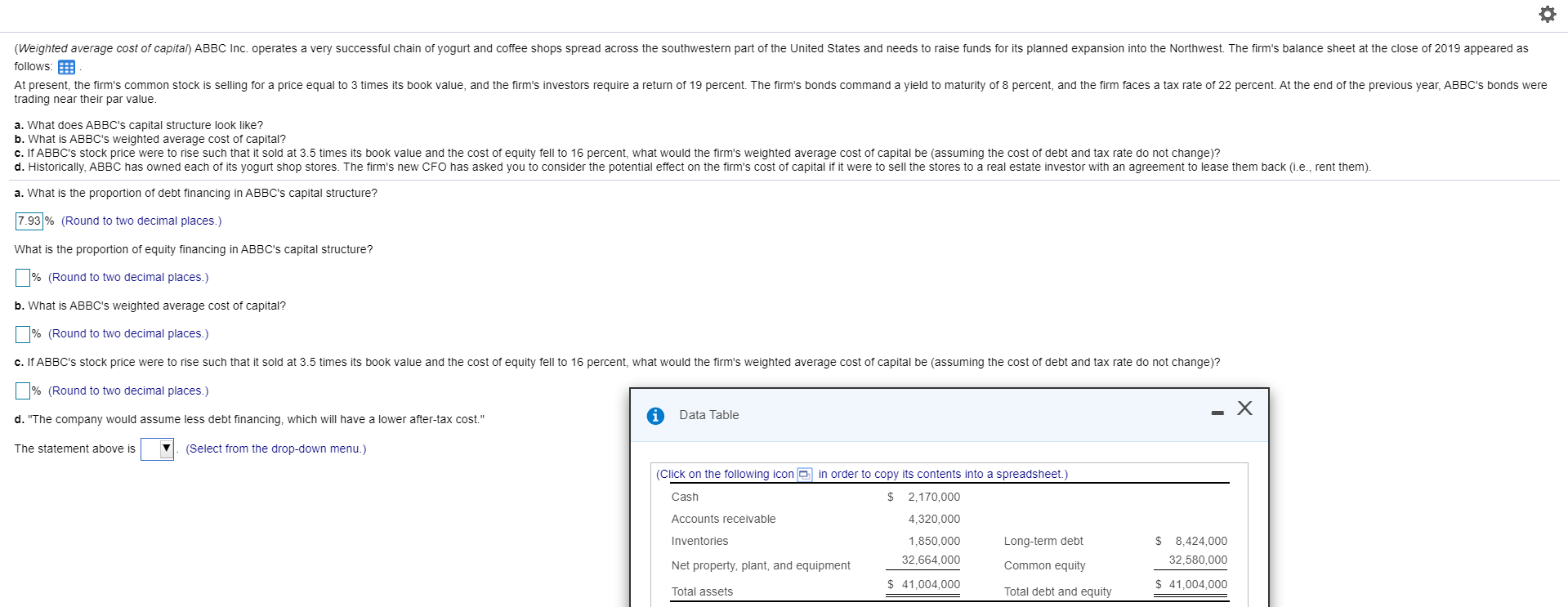
(Weighted average cost of capital) ABBC Inc. operates a very successful chain of yogurt and coffee shops spread across the southwestern part of the United States and needs to raise funds for its planned expansion into the Northwest. The firm's balance sheet at the close of 2019 appeared as follows: At present, the firm's common stock is selling for a price equal to 3 times its book value, and the firm's investors require a return of 19 percent. The firm's bonds command a yield to maturity of 8 percent, and the firm faces a tax rate of 22 percent. At the end of the previous year, ABBC's bonds were trading near their par value. a. What does ABBC's capital structure look like? b. What is ABBC's weighted average cost of capital? c. If ABBC's stock price were to rise such that it sold at 3.5 times its book value and the cost of equity fell to 16 percent, what would the firm's weighted average cost of capital be (assuming the cost of debt and tax rate do not change)? d. Historically, ABBC has owned each of its yogurt shop stores. The firm's new CFO has asked you to consider the potential effect on the firm's cost of capital if it were to sell the stores to a real estate investor with an agreement to lease them back (i.e., rent them). a. What is the proportion of debt financing in ABBC's capital structure? 7.93 % (Round to two decimal places.) What is the proportion of equity financing in ABBC's capital structure? % (Round to two decimal places.) b. What is ABBC's weighted average cost of capital? % (Round to two decimal places.) c. If ABBC's stock price were to rise such that it sold at 3.5 times its book value and the cost of equity fell to 16 percent, what would the firm's weighted average cost of capital be (assuming the cost of debt and tax rate do not change)? % (Round to two decimal places.) d. "The company would assume less debt financing, which will have a lower after-tax cost." A Data Table The statement above is V. (Select from the drop-down menu.) (Click on the following icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Cash $ Accounts receivable 2,170,000 4,320,000 1,850,000 32,664,000 Inventories Long-term debt $ 8,424,000 32,580,000 Net property, plant, and equipment Common equity $ 41,004,000 $ 41,004,000 Total assets Total debt and equity (Individual or component costs of capital) Compute the cost of the following: a. A bond that has $1,000 par value (face value) and a contract or coupon interest rate of 6 percent. A new issue would have a floatation cost of 9 percent of the $1,135 market value. The bonds mature in 5 years. The firm's average tax rate is 30 percent and its marginal tax rate is 21 percent. b. A new common stock issue that paid a $1.80 dividend last year. The par value of the stock is $15, and earnings per share have grown at a rate of 7 percent per year. This growth rate is expected to continue into the foreseeable future. The company maintains a constant dividend-earnings ratio of 30 percent. The price of this stock is now $26, but 8 percent flotation costs are anticipated. c. Internal common equity when the current market price of the common stock is $51. The expected dividend this coming year should be $3.50, increasing thereafter at an annual growth rate of 8 percent. The corporation's tax rate is 21 percent. d. A preferred stock paying a dividend of 12 percent on a $110 par value. If a new issue is offered, flotation costs will be 13 percent of the current price of $168. e. A bond selling to yield 9 percent after flotation costs, but before adjusting for the marginal corporate tax rate of 21 percent. In other words, 9 percent is the rate that equates the net proceeds from the bond with the present value of the future cash flows (principal and interest). a. What is the firm's after-tax cost of debt on the bond? % (Round to two decimal places.) b. What is the cost of external common equity? % (Round to two decimal places.) c. What is the cost of internal common equity? | % (Round to two decimal places.) d. What is the cost of capital for the preferred stock? % (Round to two decimal places.) e. What is the after-tax cost of debt on the bond? % (Round to two decimal places.) Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes








