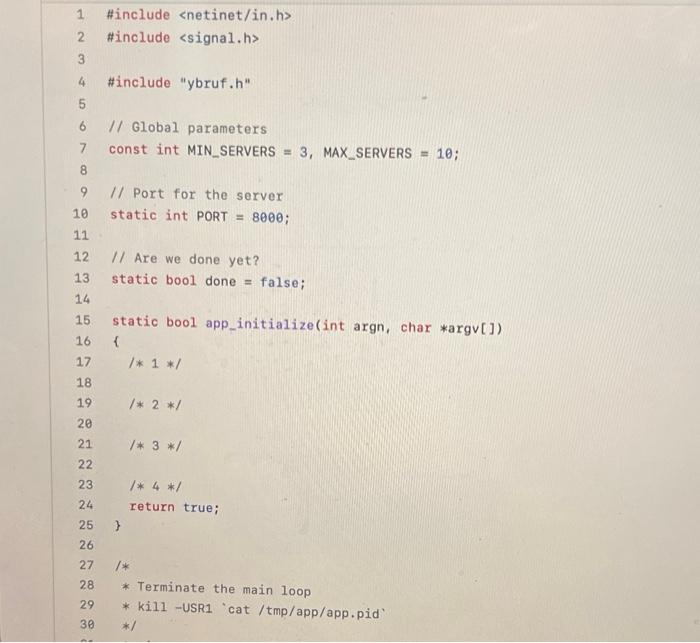
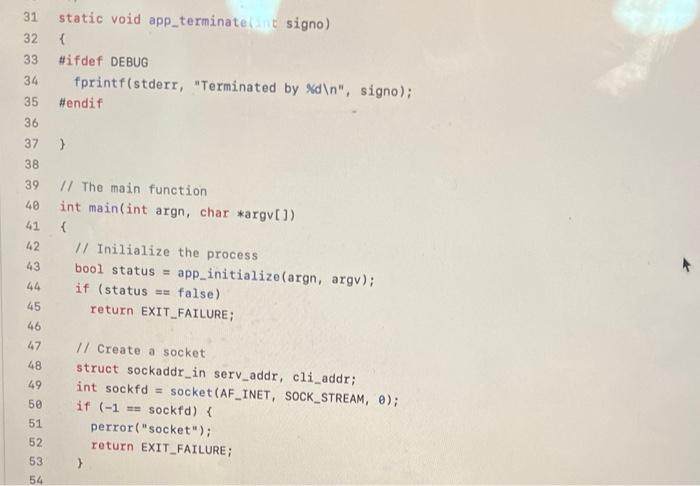
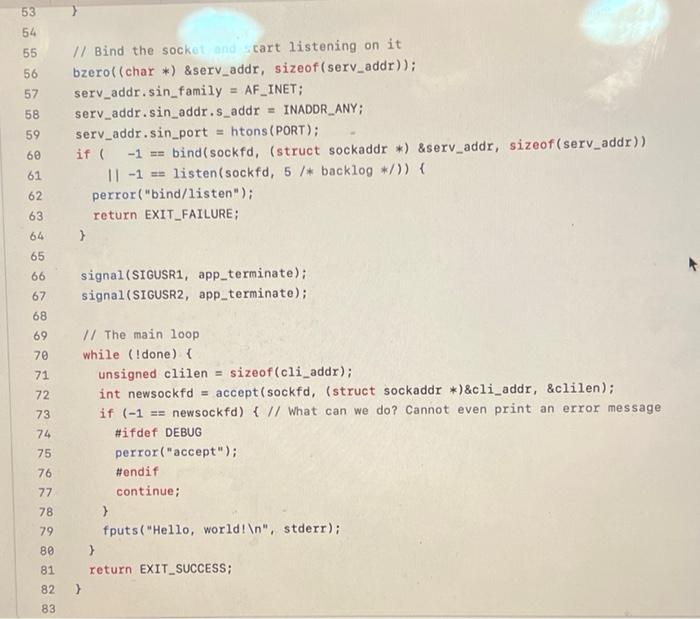
Question: what more info do you need ? it has to be written in C POSIX functions atoi(), chdir(), fopen(), fclose(), perror(), signal(), exit(), htons(); bind(),
what more info do you need ? it has to be written in C
POSIX functions atoi(), chdir(), fopen(), fclose(), perror(), signal(), exit(), htons(); bind(), listen(), and accept() before starting coding. Your program must compile without any warnings both in the debug mode and in the production mode (see ybruf.h:10). Function bool app_initialize(int argn, char *argull) shall initialize the server by executing the following tasks: Function bool app_initialize in argn, char *argull) shall initialize the server by executing the following tasks: 1. Check the number of command-line parameters. If there are more than two parameters, report an error to stderr and return false. If there are two parameters, check if the second parameter is a positive integer number with atoi(). If not, report a usage message to stderr with fprintf() and return false. If it is, assign it to the global variable PORT (provided; the default value is 8000). 1 2. Change the server's working directory to APP_WD (defined in ybruf.h) with chdir(). If the function fails, report the error with perror() and return false. 3. Create a new file called ybruf.pid, and write the server's process ID into that file as a decimal number. If the file exists, overwrite it. If the file cannot be created or in the case of a write error, report the error with perror() and return false. 4. On success, return true. Function void app_terminate(int signo) is a signal handler. It shall be invoked when the server receives the signals USR1 or USR2. If the signal is USR1 ("soft" termination), the server shall wait for the subsequent request and stop without accepting it (change the variable done). If the signal is USR2 ("hard" termination), the server shall exit at once with EXIT_SUCCESS. Additional action will be added to this scenario later. 1 2. 3 #include #include 4 #include "ybruf.h" 5 6 // Global parameters const int MIN_SERVERS = 3, MAX_SERVERS - 10; 7 8 // port for the server static int PORT = 8000; 10 11 12 11 Are we done yet? static bool done = false; 13 14 15 16 17 static bool app_initialize(int argn, char *argv[]) { 1* 1 */ 18 19 1* 2 */ 2e 21 1* 3 */ 22 23 24 return true; 25 } 26 27 28 /* * Terminate the main loop * kill -USR1 cat /tmp/app/app.pid */ 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 static void app_terminate signo) { #ifdef DEBUG fprintf(stderr, "Terminated by %d ", signo); i endif 36 > 37 38 39 40 41 42 // The main function int main(int argn, char *argv[]) { // Inilialize the process bool status = app_initialize(argn, argv); if (status == false) return EXIT_FAILURE; 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 // Create a socket struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, cli_addr; int sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (-1 == sockfd) { perror("socket"); return EXIT_FAILURE; 50 51 52 53 54 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 11 Bind the socket and cart listening on it bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)); serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; serv_addr.sin_port = htons (PORT); if ( -1 == bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) 11 -1 == listen (sockfd, 5 /* backlog */)) { perror("bind/listen"); return EXIT_FAILURE; } 61 62 63 64 65 66 signal(SIGUSR1, app_terminate); signal(SIGUSR2, app_terminate); 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 W/ The main loop while (!done) { unsigned clilen = sizeof(cli_addr); int newsockfd = accept (sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&cli_addr, &clilen); if (-1 -- newsockfd) { // What can we do? Cannot even print an error message #ifdef DEBUG perror("accept"); # endif continue; > fputs("Hello, world! ", stderr); > return EXIT_SUCCESS; > 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 POSIX functions atoi(), chdir(), fopen(), fclose(), perror(), signal(), exit(), htons(); bind(), listen(), and accept() before starting coding. Your program must compile without any warnings both in the debug mode and in the production mode (see ybruf.h:10). Function bool app_initialize(int argn, char *argull) shall initialize the server by executing the following tasks: Function bool app_initialize in argn, char *argull) shall initialize the server by executing the following tasks: 1. Check the number of command-line parameters. If there are more than two parameters, report an error to stderr and return false. If there are two parameters, check if the second parameter is a positive integer number with atoi(). If not, report a usage message to stderr with fprintf() and return false. If it is, assign it to the global variable PORT (provided; the default value is 8000). 1 2. Change the server's working directory to APP_WD (defined in ybruf.h) with chdir(). If the function fails, report the error with perror() and return false. 3. Create a new file called ybruf.pid, and write the server's process ID into that file as a decimal number. If the file exists, overwrite it. If the file cannot be created or in the case of a write error, report the error with perror() and return false. 4. On success, return true. Function void app_terminate(int signo) is a signal handler. It shall be invoked when the server receives the signals USR1 or USR2. If the signal is USR1 ("soft" termination), the server shall wait for the subsequent request and stop without accepting it (change the variable done). If the signal is USR2 ("hard" termination), the server shall exit at once with EXIT_SUCCESS. Additional action will be added to this scenario later. 1 2. 3 #include #include 4 #include "ybruf.h" 5 6 // Global parameters const int MIN_SERVERS = 3, MAX_SERVERS - 10; 7 8 // port for the server static int PORT = 8000; 10 11 12 11 Are we done yet? static bool done = false; 13 14 15 16 17 static bool app_initialize(int argn, char *argv[]) { 1* 1 */ 18 19 1* 2 */ 2e 21 1* 3 */ 22 23 24 return true; 25 } 26 27 28 /* * Terminate the main loop * kill -USR1 cat /tmp/app/app.pid */ 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 static void app_terminate signo) { #ifdef DEBUG fprintf(stderr, "Terminated by %d ", signo); i endif 36 > 37 38 39 40 41 42 // The main function int main(int argn, char *argv[]) { // Inilialize the process bool status = app_initialize(argn, argv); if (status == false) return EXIT_FAILURE; 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 // Create a socket struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, cli_addr; int sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (-1 == sockfd) { perror("socket"); return EXIT_FAILURE; 50 51 52 53 54 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 11 Bind the socket and cart listening on it bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)); serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; serv_addr.sin_port = htons (PORT); if ( -1 == bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) 11 -1 == listen (sockfd, 5 /* backlog */)) { perror("bind/listen"); return EXIT_FAILURE; } 61 62 63 64 65 66 signal(SIGUSR1, app_terminate); signal(SIGUSR2, app_terminate); 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 W/ The main loop while (!done) { unsigned clilen = sizeof(cli_addr); int newsockfd = accept (sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&cli_addr, &clilen); if (-1 -- newsockfd) { // What can we do? Cannot even print an error message #ifdef DEBUG perror("accept"); # endif continue; > fputs("Hello, world! ", stderr); > return EXIT_SUCCESS; > 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83