
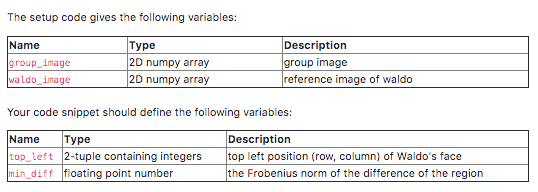
Where's Waldo? Waldo's gone missing again. Time to solve the problem once and for all with the power of norms. Norms provide a measure of 'length' for a vector or distance given the difference between two vectors. For vectors that represent images (as in this problem), a small distance indicates a high degree of similarity between images. x 2 assigns to every vector Here, we will be using the 2-norm (or Euclidean norm). A vector 2-norm XER" a nonnegative number by lellz=(E)" For a matrix, the vector 2-norm' corresponds to the Frobenius norm (and not the matrix 2-norm) = (C2x;)" The numpy function numpy, linalg.norm(x) will compute this norm by default. Your task: You are given a large image group_image containing Waldo somewhere and a smaller image waldo_image of Waldo's face. You can help search for Waldo by looking through each subimage (same dimensions as waldo_image) of group_image that has the minimum vector 2-norm of its difference with waldo_image. Each subimage can be uniquely identified by the position of its top-left-most pixel. . Once you've found Waldo's likeliest hiding spot, save that position in top_left. Also save the norm of the difference in min_diff. Lastly, highlight Waldo's face by multiplying all pixel values in group_image outside of waldo_image by 0.3 (this darkens the other portion of the image). Plot the resulting image. The plot isn't checked by the autograder, but it looks cool Hint: Both of the given images are grayscale, that means each pixel has a value between 0 (black) and 1 (white). To view them, use matplot lib.pyplot. imshowi..., cmap="gray"). (See this related matplotlib tutorial.) The setup code gives the following variables: Name group_image waldo image Type 2D numpy array 2D numpy array Description group image reference image of waldo Your code snippet should define the following variables: Name Type top_left 2-tuple containing integers min_diff floating point number Description top left position (row, column) of Waldo's face the Frobenius norm of the difference of the region Where's Waldo? Waldo's gone missing again. Time to solve the problem once and for all with the power of norms. Norms provide a measure of 'length' for a vector or distance given the difference between two vectors. For vectors that represent images (as in this problem), a small distance indicates a high degree of similarity between images. x 2 assigns to every vector Here, we will be using the 2-norm (or Euclidean norm). A vector 2-norm XER" a nonnegative number by lellz=(E)" For a matrix, the vector 2-norm' corresponds to the Frobenius norm (and not the matrix 2-norm) = (C2x;)" The numpy function numpy, linalg.norm(x) will compute this norm by default. Your task: You are given a large image group_image containing Waldo somewhere and a smaller image waldo_image of Waldo's face. You can help search for Waldo by looking through each subimage (same dimensions as waldo_image) of group_image that has the minimum vector 2-norm of its difference with waldo_image. Each subimage can be uniquely identified by the position of its top-left-most pixel. . Once you've found Waldo's likeliest hiding spot, save that position in top_left. Also save the norm of the difference in min_diff. Lastly, highlight Waldo's face by multiplying all pixel values in group_image outside of waldo_image by 0.3 (this darkens the other portion of the image). Plot the resulting image. The plot isn't checked by the autograder, but it looks cool Hint: Both of the given images are grayscale, that means each pixel has a value between 0 (black) and 1 (white). To view them, use matplot lib.pyplot. imshowi..., cmap="gray"). (See this related matplotlib tutorial.) The setup code gives the following variables: Name group_image waldo image Type 2D numpy array 2D numpy array Description group image reference image of waldo Your code snippet should define the following variables: Name Type top_left 2-tuple containing integers min_diff floating point number Description top left position (row, column) of Waldo's face the Frobenius norm of the difference of the region








