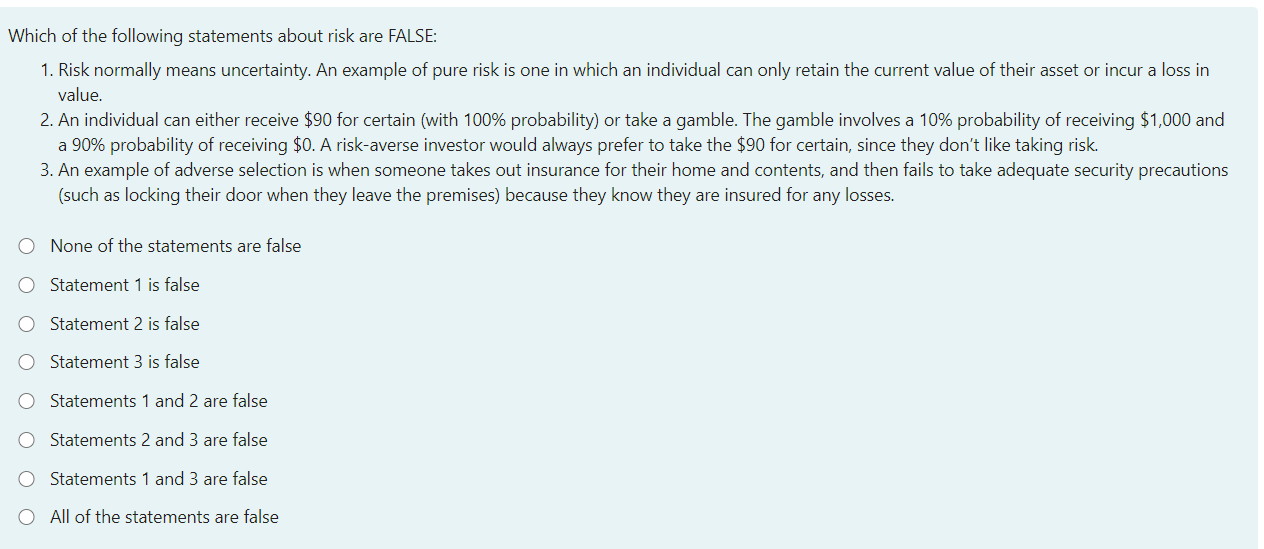
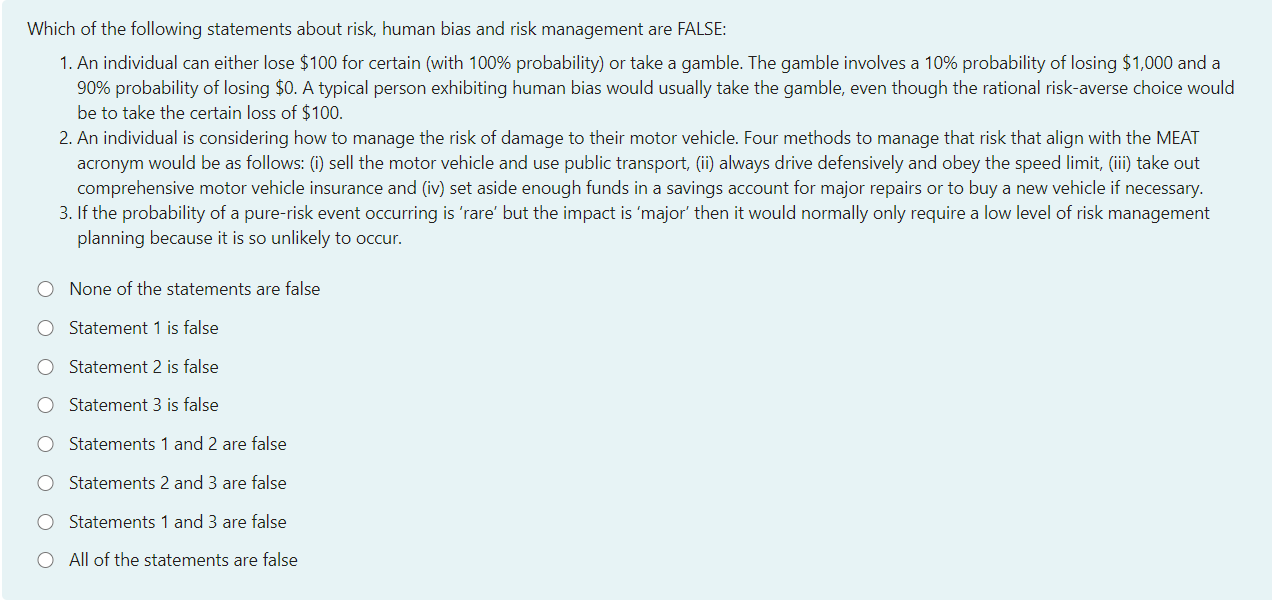

Which of the following statements about risk are FALSE: 1. Risk normally means uncertainty. An example of pure risk is one in which an individual can only retain the current value of their asset or incur a loss in value. 2. An individual can either receive $90 for certain (with 100% probability) or take a gamble. The gamble involves a 10% probability of receiving $1,000 and a 90% probability of receiving $0. A risk-averse investor would always prefer to take the $90 for certain, since they don't like taking risk. 3. An example of adverse selection is when someone takes out insurance for their home and contents, and then fails to take adequate security precautions (such as locking their door when they leave the premises) because they know they are insured for any losses. O None of the statements are false Statement 1 is false O Statement 2 is false O Statement 3 is false Statements 1 and 2 are false Statements 2 and 3 are false O Statements 1 and 3 are false O All of the statements are false Which of the following statements about risk, human bias and risk management are FALSE: 1. An individual can either lose $100 for certain (with 100% probability) or take a gamble. The gamble involves a 10% probability of losing $1,000 and a 90% probability of losing $0. A typical person exhibiting human bias would usually take the gamble, even though the rational risk-averse choice would be to take the certain loss of $100. 2. An individual is considering how to manage the risk of damage to their motor vehicle. Four methods to manage that risk that align with the MEAT acronym would be as follows: (i) sell the motor vehicle and use public transport, (ii) always drive defensively and obey the speed limit, (iii) take out comprehensive motor vehicle insurance and (iv) set aside enough funds in a savings account for major repairs or to buy a new vehicle if necessary. 3. If the probability of a pure-risk event occurring is 'rare' but the impact is 'major' then it would normally only require a low level of risk management planning because it is so unlikely to occur. O None of the statements are false O Statement 1 is false O Statement 2 is false O Statement 3 is false O Statements 1 and 2 are false O Statements 2 and 3 are false O Statements 1 and 3 are false O All of the statements are false Which of the following statements about life insurance are FALSE: 1. Death cover pays a lump-sum amount upon death. The amount of death cover that most people need should normally increase between the ages of 20 and 60 (with the most needed at age 60). 2. Income protection can replace a portion of a person's income if they have an accident or illness that prevents you from working. After the accident or illness occurs, the person can nominate whether to wait between 14 and 90 days until the benefit starts. They can also decide on a benefit period of between 2 years and all the way until age 65. 3. Trauma insurance pays a lump-sum amount upon diagnosis of a serious illness, such as cancer. This could be a useful form of insurance if someone has a history of a particular type of cancer in their family. O None of the statements are false O Statement 1 is false O Statement 2 is false O Statement 3 is false Statements 1 and 2 are false O Statements 2 and 3 are false Statements 1 and 3 are false O All of the statements are false Which of the following statements about risk are FALSE: 1. Risk normally means uncertainty. An example of pure risk is one in which an individual can only retain the current value of their asset or incur a loss in value. 2. An individual can either receive $90 for certain (with 100% probability) or take a gamble. The gamble involves a 10% probability of receiving $1,000 and a 90% probability of receiving $0. A risk-averse investor would always prefer to take the $90 for certain, since they don't like taking risk. 3. An example of adverse selection is when someone takes out insurance for their home and contents, and then fails to take adequate security precautions (such as locking their door when they leave the premises) because they know they are insured for any losses. O None of the statements are false Statement 1 is false O Statement 2 is false O Statement 3 is false Statements 1 and 2 are false Statements 2 and 3 are false O Statements 1 and 3 are false O All of the statements are false Which of the following statements about risk, human bias and risk management are FALSE: 1. An individual can either lose $100 for certain (with 100% probability) or take a gamble. The gamble involves a 10% probability of losing $1,000 and a 90% probability of losing $0. A typical person exhibiting human bias would usually take the gamble, even though the rational risk-averse choice would be to take the certain loss of $100. 2. An individual is considering how to manage the risk of damage to their motor vehicle. Four methods to manage that risk that align with the MEAT acronym would be as follows: (i) sell the motor vehicle and use public transport, (ii) always drive defensively and obey the speed limit, (iii) take out comprehensive motor vehicle insurance and (iv) set aside enough funds in a savings account for major repairs or to buy a new vehicle if necessary. 3. If the probability of a pure-risk event occurring is 'rare' but the impact is 'major' then it would normally only require a low level of risk management planning because it is so unlikely to occur. O None of the statements are false O Statement 1 is false O Statement 2 is false O Statement 3 is false O Statements 1 and 2 are false O Statements 2 and 3 are false O Statements 1 and 3 are false O All of the statements are false Which of the following statements about life insurance are FALSE: 1. Death cover pays a lump-sum amount upon death. The amount of death cover that most people need should normally increase between the ages of 20 and 60 (with the most needed at age 60). 2. Income protection can replace a portion of a person's income if they have an accident or illness that prevents you from working. After the accident or illness occurs, the person can nominate whether to wait between 14 and 90 days until the benefit starts. They can also decide on a benefit period of between 2 years and all the way until age 65. 3. Trauma insurance pays a lump-sum amount upon diagnosis of a serious illness, such as cancer. This could be a useful form of insurance if someone has a history of a particular type of cancer in their family. O None of the statements are false O Statement 1 is false O Statement 2 is false O Statement 3 is false Statements 1 and 2 are false O Statements 2 and 3 are false Statements 1 and 3 are false O All of the statements are false









