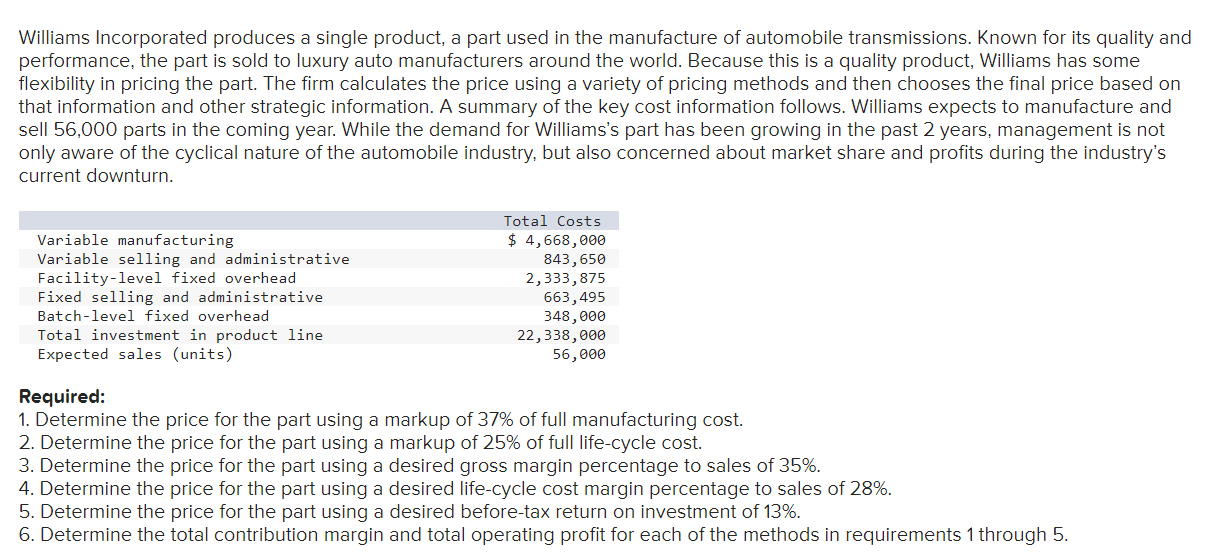
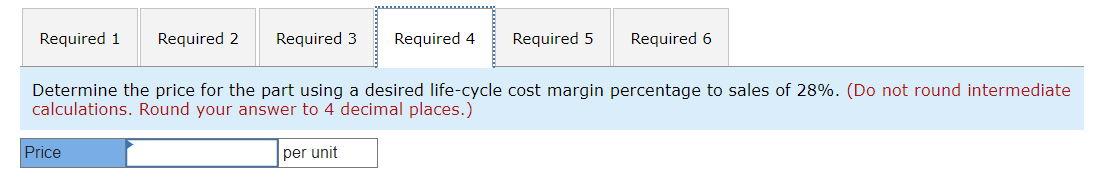
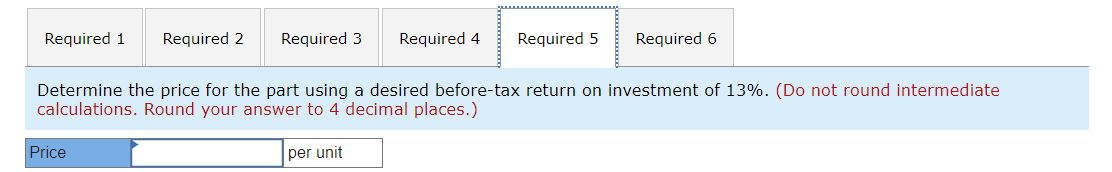
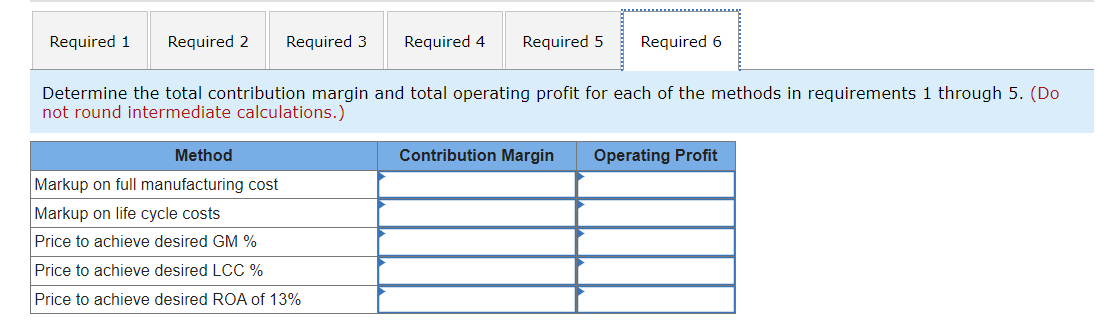
Williams Incorporated produces a single product, a part used in the manufacture of automobile transmissions. Known for its quality and performance, the part is sold to luxury auto manufacturers around the world. Because this is a quality product, Williams has some flexibility in pricing the part. The firm calculates the price using a variety of pricing methods and then chooses the final price based on that information and other strategic information. A summary of the key cost information follows. Williams expects to manufacture and sell 56,000 parts in the coming year. While the demand for Williams's part has been growing in the past 2 years, management is not only aware of the cyclical nature of the automobile industry, but also concerned about market share and profits during the industry's current downturn. Required: 1. Determine the price for the part using a markup of 37% of full manufacturing cost. 2. Determine the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost. 3. Determine the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 35%. 4. Determine the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost margin percentage to sales of 28%. 5. Determine the price for the part using a desired before-tax return on investment of 13%. 6. Determine the total contribution margin and total operating profit for each of the methods in requirements 1 through 5. Determine the price for the part using a markup of 37% of full manufacturing cost. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 35%. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost margin percentage to sales of 28%. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a desired before-tax return on investment of 13%. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the total contribution margin and total operating profit for each of the methods in requirements 1 through 5 . (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Williams Incorporated produces a single product, a part used in the manufacture of automobile transmissions. Known for its quality and performance, the part is sold to luxury auto manufacturers around the world. Because this is a quality product, Williams has some flexibility in pricing the part. The firm calculates the price using a variety of pricing methods and then chooses the final price based on that information and other strategic information. A summary of the key cost information follows. Williams expects to manufacture and sell 56,000 parts in the coming year. While the demand for Williams's part has been growing in the past 2 years, management is not only aware of the cyclical nature of the automobile industry, but also concerned about market share and profits during the industry's current downturn. Required: 1. Determine the price for the part using a markup of 37% of full manufacturing cost. 2. Determine the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost. 3. Determine the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 35%. 4. Determine the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost margin percentage to sales of 28%. 5. Determine the price for the part using a desired before-tax return on investment of 13%. 6. Determine the total contribution margin and total operating profit for each of the methods in requirements 1 through 5. Determine the price for the part using a markup of 37% of full manufacturing cost. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 35%. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost margin percentage to sales of 28%. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the price for the part using a desired before-tax return on investment of 13%. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) Determine the total contribution margin and total operating profit for each of the methods in requirements 1 through 5 . (Do not round intermediate calculations.)













