Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
With the wider use of sensor and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, the fourth Industrial Revolution (IR4.0) has brought in a wave of data
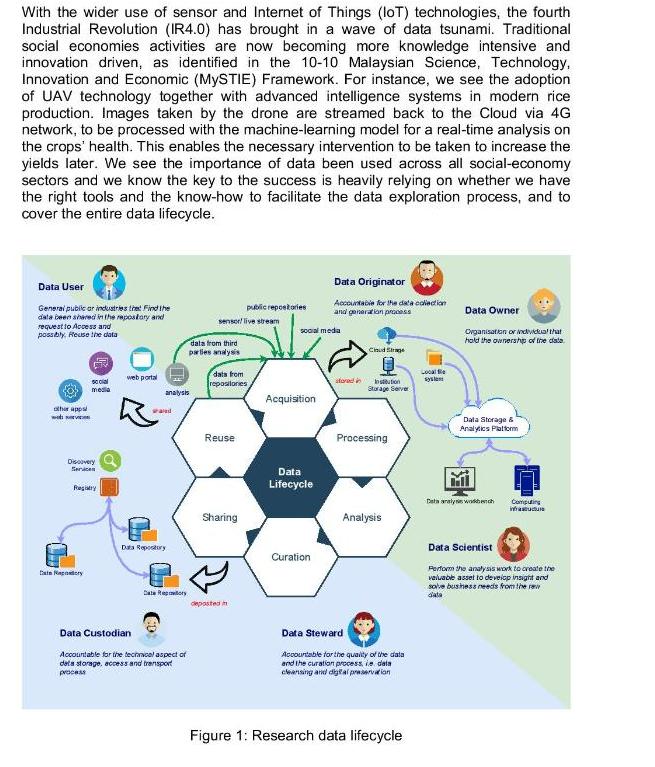

With the wider use of sensor and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, the fourth Industrial Revolution (IR4.0) has brought in a wave of data tsunami. Traditional social economies activities are now becoming more knowledge intensive and innovation driven, as identified in the 10-10 Malaysian Science, Technology, Innovation and Economic (MySTIE) Framework. For instance, we see the adoption of UAV technology together with advanced intelligence systems in modern rice production. Images taken by the drone are streamed back to the Cloud via 4G network, to be processed with the machine-learning model for a real-time analysis on the crops' health. This enables the necessary intervention to be taken to increase the yields later. We see the importance of data been used across all social-economy sectors and we know the key to the success is heavily relying on whether we have the right tools and the know-how to facilitate the data exploration process, and to cover the entire data lifecycle. Data User Data Originator Accountable for the data collection and generation process Data Owner General public or industries the Find the data been shared in the repository and request to Access and possibly, Reuse the data public repostories sensor live stream Organisation or individual that hold the ownership of the data Cloud Se G web portal social media Institution Storage Server other apps web serve Data Storage & Analytics Platform Discovery Services Registry Category analysis and Data Repository data from third parties analysis Category Data Custodian Accountable for the technical aspect of data storage, access and transport process data from repositories Reuse Sharing deposted in social media Acquisition Data Lifecycle Curation stored in Processing Analysis Data Steward Accountable for the quality of the data and the curation processi data cleansing and digital preservation Figure 1: Research data lifecycle Locat syste Data analysis wobench Computing instucture Data Scientist Perform the analysis work to create the valuable asset to develop insight and solve business needs from the re data WOC7017 As shown in Figure 1, the data lifecycle comprises six phases: acquisition, processing, analysis, curation, sharing and reuse. The data acquired from various sources needs to be organised in the data storage platform before it can be further processed. The processing of large volume requires a high-performance computing platform, especially when the machine-learning (ML) methods are used. A typical ML model training process requires the use of graphical processing unit (GPU) and the computational power that is beyond a normal laptop can provide. Once the data has been analysed and results been obtained, it is now entering the post-research phases. To extend the longevity and ensure the reusability of the data, we need to curate the data---adding useful metadata to describe it. The curated data is then deposited into organisational or community-driven repositories, for a long-term data preservation and storing. The data repositories are integrated with the national or domain data discovery services, such as the Malaysia Open Science Platform, to increase the visibilities and sharing of the data. Data can then be used to fuelled future research, and this completes the entire data lifecycle. This is in line with the international movement of democratising knowledge and reinforcing open scientific inquiry and integrity by making research data Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable (FAIR). Part 1: Case Study 1. Conduct desk research to understand the Open Science context in this big data era. You can cover (but not limited to) the aspects below: (a) The opportunities as well as the challenges for Open Science communities in this big data era. (b) The enabling technologies for handling the computing challenge incurred by the data deluge of Open Science. (c) The existing big data processing platforms that have been deployed world- wide in supporting Open Science initiatives. 2. Write a short report to discuss your finding. The report should comprise: (a) An introduction to set the scene. (b) The main discussion topics, with suitable facts to support your argument. (c) A conclusion to summarise your finding. (d) References used in your desk research. . Content: 7 marks o Development of arguments. o Evidence presented to support the arguments. Reference to the evidence. Structure: 3 marks o Organisation. o Sentencing. O Grammar & Spelling. Marking scheme: 3/5
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.50 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 The movement towards open science is a consequence of seemingly pervasive failures to replicate previous research This transition comes with great benefits but also significant challenges that are l...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


