Question
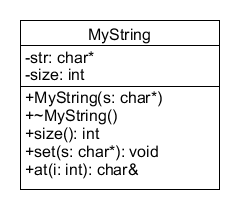
Write a class that implements your own string class, called MyString. Description of the class attributes: str: stores the memory address for a dynamically allocated
Write a class that implements your own string class, called MyString.
Description of the class attributes:
str: stores the memory address for a dynamically allocated array of characters. This stores a C-string. size: stores the number of characters in the c-string (not including the null terminator).
Constructor: accepts a C-String as it's only argument. Dynamically allocates an array long enough to store the argument and a null terminator. Sets size to the appropriate value. Copies the argument C-string into the new array.
Destructor: frees up the memory used by the dynamically allocated array.
size() - returns the number of characters in the string stored by MyString (excluding the null terminator).
set() - accepts a C-string as it's only argument. Replaces the current C-string held by the MyString object, resizing the array as needed.
at() - accepts an integer as it's only argument. Returns a reference to the element indicated by the argument. That is, if at is passed 1, then the second element is returned by reference. The method should throw the C-String exception "OUT OF BOUNDS!" if the argument passed would be an invalid subscript.
Place your complete class in it's own header file named MyString.h. Be sure to include preprocessor guards and mark accessors const.
UML diagram below:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


