Write a client class (application) in which you:
a) Define an array (not an ArrayList) of 7 Vehicles, and fill it with 4 Cars and 3 Bicycles objects using values assigned by the programmer. Do not ask the user to enter the values.
b) Write a static method ArrayList getLocations(Vehicle[ ] vehicles, String location) that takes as parameter an array of vehicles and a String location. This method returns an array list containing the cars (in the array vehicles) checked in the location.
c) In the main method, use the getLocations method to display the cars checked in Beirut.
d) Display the information of the most expensive vehicle (the vehicle with the biggest price).
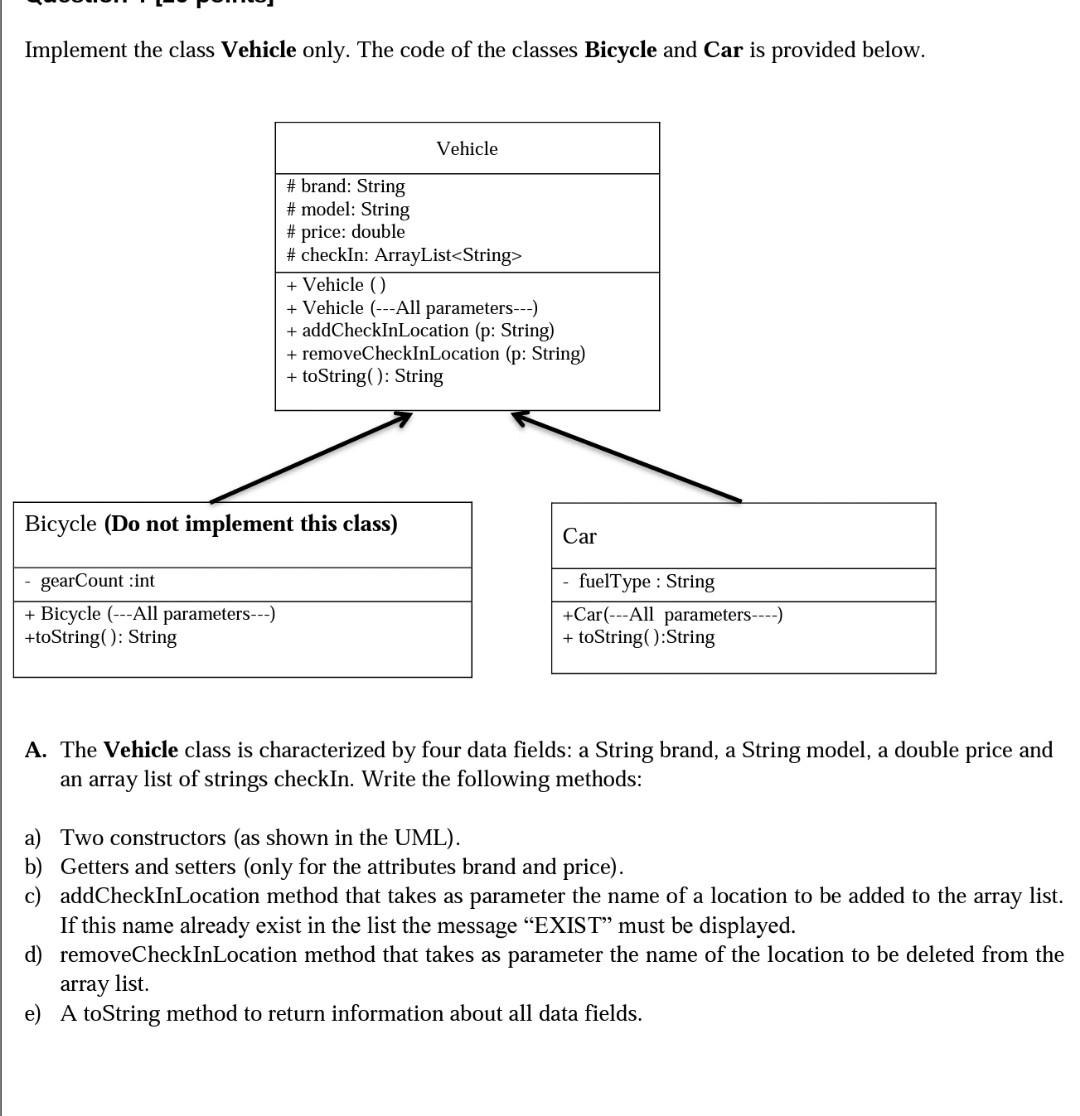
Below are the given classes:
Write a client class (application) in which you: a) Define an array (not an ArrayList) of 7 Vehicles, and fill it with 4 Cars and 3 Bicycles objects using values assigned by the programmer. Do not ask the user to enter the values. b) Write a static method ArrayList
getLocations (Vehicle[ ] vehicles, String location) that takes as parameter an array of vehicles and a String "location. This method returns an array list containing the cars (in the array vehicles) checked in the "location. c) In the main method, use the getLocations method to display the cars checked in Beirut. d) Display the information of the most expensive vehicle (the vehicle with the biggest price). Implement the class Vehicle only. The code of the classes Bicycle and Car is provided below. Vehicle # brand: String # model: String # price: double #checkIn: ArrayList + Vehicle + Vehicle (---All parameters---) + addCheckInLocation (p: String) + removeCheckInLocation (p: String) + toString(): String Bicycle (Do not implement this class) Car gearCount :int + Bicycle (---All parameters---) +toString(): String - fuelType : String +Car(---All parameters ----) + toString():String A. The Vehicle class is characterized by four data fields: a String brand, a String model, a double price and an array list of strings checkIn. Write the following methods: a) Two constructors (as shown in the UML). b) Getters and setters (only for the attributes brand and price). c) addCheckInLocation method that takes as parameter the name of a location to be added to the array list. If this name already exist in the list the message "EXIST must be displayed. d) removeCheckInLocation method that takes as parameter the name of the location to be deleted from the array list. e) A toString method to return information about all data fields. B. The Bicycle class inherits from the class Vehicle. The code is below: import java.util.ArrayList; public class Bicycle extends Vehicle { private int gearCount; public Bicycle(int gearCount, String brand, String model, double price, ArrayList checkin) { super (brand, model, price, checkin); this.gearCount gearCount; public String toString() { return super.toString() + ", the gear count is } + gearCount; C. The Car class inherits from the class Vehicle. The code is below: import java.util.ArrayList; public class Car extends Vehicle { private String fuelType; public Car (String fuelType, String brand, String model, double price, ArrayList checkIn) { super (brand, model, price, checkin); this.fuelType fuelType; } public String toString() { return super.toString() + ", the fuel type is " + fuelType; }