Question
Write the method public String[][] getAll() given the information below. This is the getAll method specifications below (The rest of the class is given further
Write the method public String[][] getAll() given the information below.
This is the getAll method specifications below (The rest of the class is given further down):
/**
*
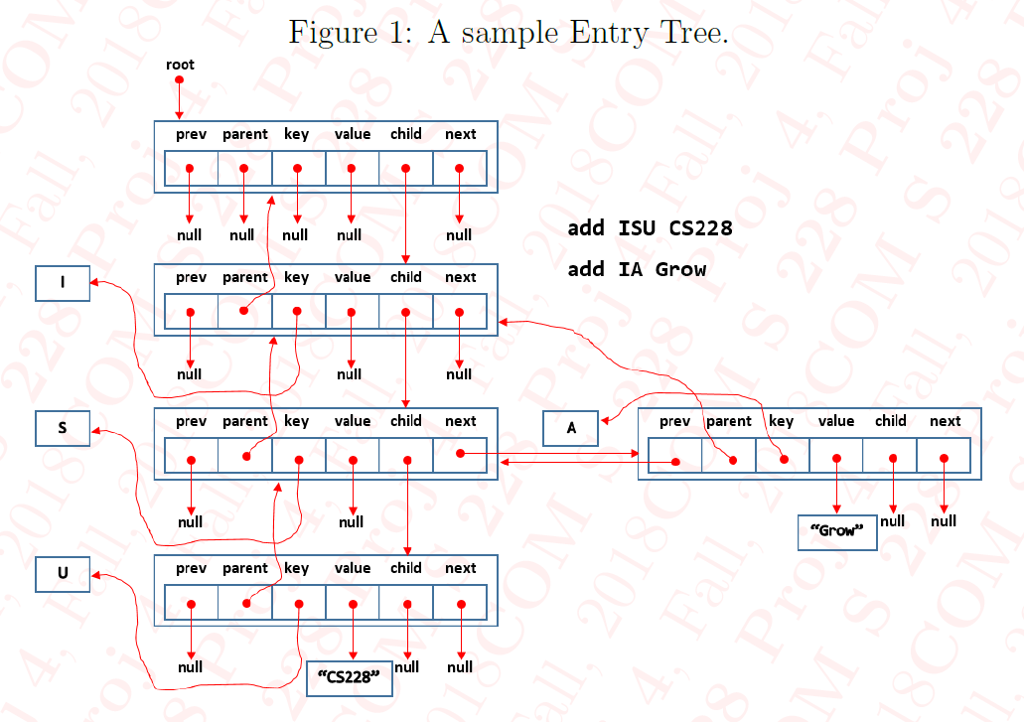
* Returns all values in this entry tree together with their keys.
* The order of outputs would be similar to level order traversal,
* i.e., first you would get all values together with their keys in
* first level from left to right, then second level, and so on.
* If tree has no values then it would return null.
*
* For the example image given in description, the
* returned String[][] would look as follows:
*
* {{"IA","Grow"}, {"ISU","CS228"}}
*
* NOTE: In this method you are allowed to use
* {@link java.util.LinkedList}.
*
*
*/
public String[][] getAll()
{
// TODO
}

THIS IS THE WHOLE CLASS (I only need help with getAll() so no need to implement the rest of the //TODO methods)
package edu.iastate.cs228.proj4;
/**
*
* @author
*
*
* An entry tree class.
*
*
*/
public class EntryTree
{
// Dummy root node.
// Made public for grading.
public Node root;
/**
*
* You are allowed to add at most TWO more data fields to
* EntryTree class of int type ONLY if you need to.
*
*/
// All made public for grading.
public class Node implements EntryNode
{
public Node child; // reference to the first child node
public Node parent; // reference to the parent node
public Node prev; // reference to the previous sibling
public Node next; // reference to the next sibling
public K key; // the key for this node
public V value; // the value at this node
public Node(K aKey, V aValue)
{
key = aKey;
value = aValue;
child = null;
parent = null;
prev = null;
next = null;
}
@Override
public EntryNode parent()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public EntryNode child()
package edu.iastate.cs228.proj4;
/**
*
* @author
*
*
* An entry tree class.
*
*
*/
public class EntryTree
{
// Dummy root node.
// Made public for grading.
public Node root;
/**
*
* You are allowed to add at most TWO more data fields to
* EntryTree class of int type ONLY if you need to.
*
*/
// All made public for grading.
public class Node implements EntryNode
{
public Node child; // reference to the first child node
public Node parent; // reference to the parent node
public Node prev; // reference to the previous sibling
public Node next; // reference to the next sibling
public K key; // the key for this node
public V value; // the value at this node
public Node(K aKey, V aValue)
{
key = aKey;
value = aValue;
child = null;
parent = null;
prev = null;
next = null;
}
@Override
public EntryNode parent()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public EntryNode child()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public EntryNode next()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public EntryNode prev()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public K key()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public V value()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
}
public EntryTree()
{
root = new Node(null, null);
}
/**
* Returns the value of the entry with a specified key sequence,
* or {@code null} if this tree contains no entry with this key
* sequence.
*
* This method returns {@code null} if {@code keyarr} is null or
* if its length is {@code 0}. If any element of {@code keyarr}
* is {@code null}, then the method throws a
* {@code NullPointerException}. The method returns the value of
* the entry with the key sequence in {@code keyarr} or {@code null}
* if this tree contains no entry with this key sequence. An example
* is given in provided sample input and output files to illustrate
* this method.
*
* @param keyarr Read description.
* @return Read description.
* @throws NullPointerException Read description.
*/
public V search(K[] keyarr)
{
// TODO
return null;
}
/**
*
* This method returns an array of type {@code K[]} with the longest
* prefix of the key sequence specified in {@code keyarr} such that
* the keys in the prefix label the nodes on the path from the root
* to a node. The length of the returned array is the length of the
* longest prefix.
*
* This method returns {@code null} if {@code keyarr} is {@code null},
* or if its length is {@code 0}. If any element of {@code keyarr} is
* {@code null}, then the method throws a {@code NullPointerException}.
* A prefix of the array {@code keyarr} is a key sequence in the
subarray
* of {@code keyarr} from index {@code 0} to any index {@code m>=0},
* i.e., greater than or equal to; the corresponding suffix is a key
* sequence in the subarray of {@code keyarr} from index {@code m+1} to
* index {@code keyarr.length-1}. The method returns an array of type
* {@code K[]} with the longest prefix of the key sequence specified in
* {@code keyarr} such that the keys in the prefix are, respectively,
* with the nodes on the path from the root to a node. The lngth of the
* returned array is the length of the longest prefix. Note that if the
* length of the longest prefix is {@code 0}, then the method returns
* {@code null}. This method can be used to select a shorted key
sequence
* for an {@code add} command to create a shorter path of nodes in the
* tree. An example is given in the attachment to illustrate how this
* method is used with the {@code #add(K[] keyarr, V aValue)} method.
*
* NOTE: In this method you are allowed to use
* {@link java.util.Arrays}'s {@code copyOf} method only.
*
* @param keyarr Read description.
* @return Read description.
* @throws NullPointerException Read description.
*/
public K[] prefix(K[] keyarr)
{
// TODO
return null;
}
/**
*
* This method returns {@code false} if {@code keyarr} is {@code null},
* its length is {@code 0}, or {@code aValue} is {@code null}. If any
* element of {@code keyarr} is {@code null}, then the method throws a
* {@code NullPointerException}.
*
* This method locates the node {@code P} corresponding to the longest
* prefix of the key sequence specified in {@code keyarr} such that the
* keys in the prefix label the nodes on the path from the root to the
node.
* If the length of the prefix is equal to the length of {@code keyarr},
* then the method places {@code aValue} at the node {@code P} (in place
of
* its old value) and returns {@code true}. Otherwise, the method
creates a
* new path of nodes (starting at a node {@code S}) labelled by the
* corresponding suffix for the prefix, connects the prefix path and
suffix
* path together by making the node {@code S} a child of the node {@code
P},
* and returns {@code true}. An example input and output files
illustrate
* this method's operation.
*
* NOTE: In this method you are allowed to use
* {@link java.util.Arrays}'s {@code copyOf} method only.
*
* @param keyarr Read description.
* @param Read description.
* @return Read description.
* @throws NullPointerException Read description.
*/
public boolean add(K[] keyarr, V aValue)
{
// TODO
return false;
}
/**
* Removes the entry for a key sequence from this tree and returns its
value
* if it is present. Otherwise, it makes no change to the tree and
returns
* {@code null}.
*
* This method returns {@code null} if {@code keyarr} is {@code null} or
its
* length is {@code 0}. If any element of {@code keyarr} is {@code
null}, then
* the method throws a {@code NullPointerException}. The method returns
* {@code null} if the tree contains no entry with the key sequence
specified
* in {@code keyarr}. Otherwise, the method finds the path with the key
sequence,
* saves the value field of the node at the end of the path, sets the
value field
* to {@code null}.
*
* The following rules are used to decide whether the current node and
higher
* nodes on the path need to be removed. The root cannot be removed. Any
node
* whose value is not {@code null} cannot be removed. Consider a non-
root node
* whose value is {@code null}. If the node is a leaf node (has no
children),
* then the node is removed. Otherwise, if the node is the parent of a
single
* child and the child node is removed, then the node is removed.
Finally, the
* method returns the saved old value.
*
*
* @param keyarr Read description.
* @return Read description.
* @throws NullPointerException Read description.
*
*/
public V remove(K[] keyarr)
{
// TODO
return null;
}
/**
*
* This method prints the tree on the console in the output format
* shown in provided sample output file. If the tree has no entry,
* then the method just prints out the line for the dummy root node.
*
*/
public void showTree()
{
// TODO
return;
}
/**
*
* Returns all values in this entry tree together with their keys.
* The order of outputs would be similar to level order traversal,
* i.e., first you would get all values together with their keys in
* first level from left to right, then second level, and so on.
* If tree has no values then it would return {@code null}.
*
* For the example image given in description, the
* returned String[][] would look as follows:
*
* {{"IA","Grow"}, {"ISU","CS228"}}
*
* NOTE: In this method you are allowed to use
* {@link java.util.LinkedList}.
*
*
*/
public String[][] getAll()
{
// TODO
return null;
}
}
Thank you very much for your answer and I will thumbs up!
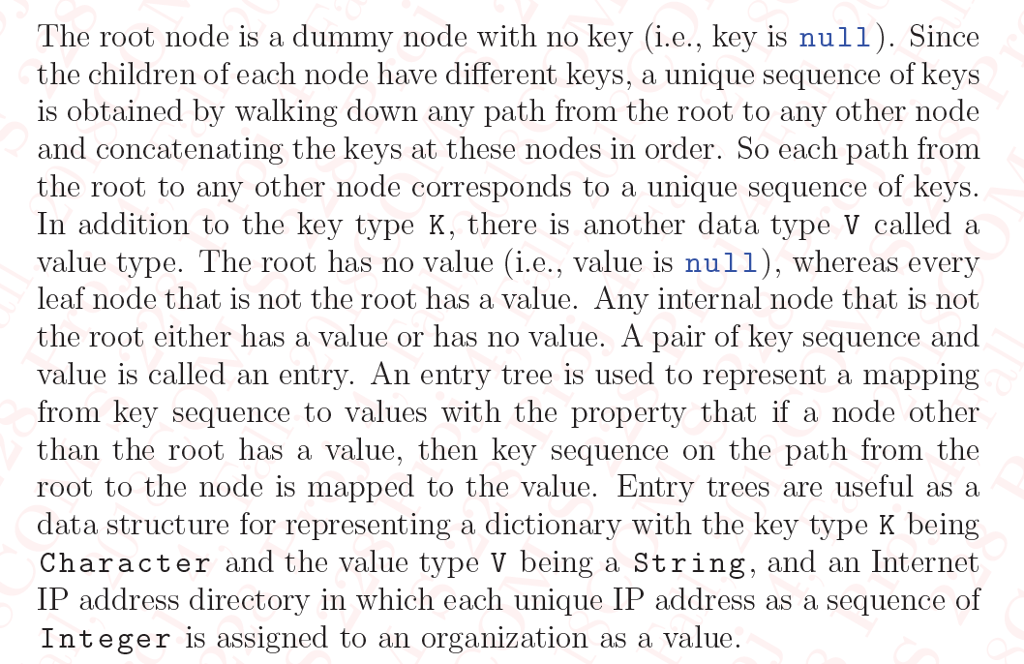
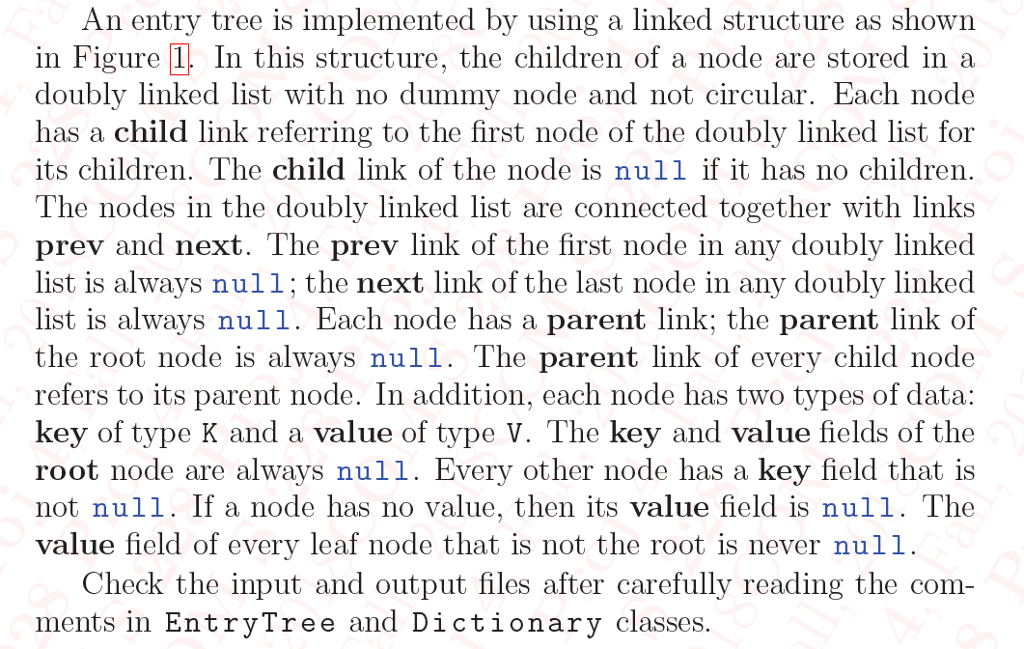
Project 4: Trees of Entries of Key Sequence and Value 1. Description An entry tree, Figure l is a rooted tree with each node having any number of unordered children that are each given a unique key of type K. Project 4: Trees of Entries of Key Sequence and Value 1. Description An entry tree, Figure l is a rooted tree with each node having any number of unordered children that are each given a unique key of type KStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


