Question: You are valuing a organisation that has $2 hundred million in debt using probability-weighted-situation evaluation. You carefully version 3 situations, such that the resulting enterprise
You are valuing a organisation that has $2 hundred million in debt using probability-weighted-situation evaluation. You carefully version 3 situations, such that the resulting enterprise fee equals $three hundred million in state of affairs 1, $two hundred million in state of affairs 2, and $one hundred million in scenario 3. The probabilities of the scenarios are 25 percent, 50 percentage, and 25 percentage, respectively. What is the anticipated enterprise price? What is the predicted equity fee? Management pronounces a brand new plan that gets rid of the drawback state of affairs (state of affairs three), yielding a 75 percent possibility of situation 2. What occurs to corporation price and fairness price? Why does company price rise greater than fairness price? 5. You are valuing a era enterprise whose organization cost is $800 million. The agency has no debt however substantial employee alternatives, 10 million in total. Based on choice-pricing models, you cost every alternative at $6.67 in line with choice. Assume that the common strike fee equals $15. If the business enterprise has forty [10:57 AM, 10/11/2021] .: million stocks incredible, what is the organisation's fairness price and price in keeping with percentage the usage of (a) the option-pricing model and (b) the exercising price method? Why is the choice-pricing model the favored approach? 6. You are valuing an business company whose enterprise value is $10 billion. The organisation has no instantly debt but does have one hundred,000 convertible bonds amazing. The marketplace price of every bond is $1,one hundred fifty. If the enterprise has 500 million shares terrific, what is the corporation's equity value and fee per percentage using (a) the market value approach and (b) the conversion value approach?
question 1
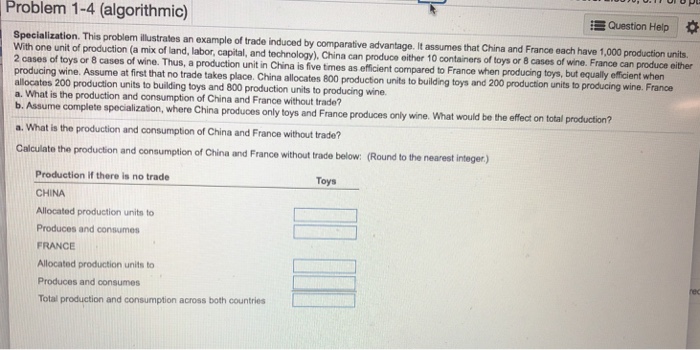

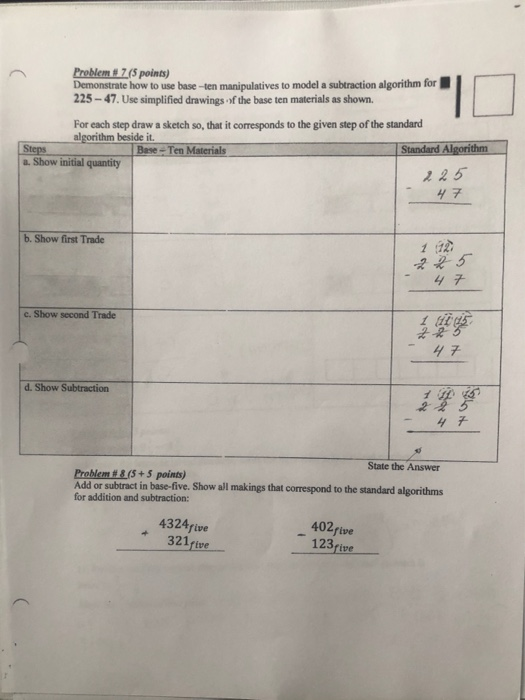
Problem 1-4 (algorithmic) Question Help Specialization. This problem illustrates an example of trade induced by comparative advantage. It assumes that China and France each have 1,000 production units. With one unit of production (a mix of land, labor, capital, and technology). China can produce either 10 containers of toys or B cases of wine. France can produce either 2 cases of toys or 8 cases of wine. Thus, a production unit in China is five times as efficient compared to France when producing toys, but equally efficient when producing wine. Assume at first that no trade takes place. China allocates 800 production units to building toys and 200 production units to producing wine. France allocates 200 production units to building toys and 800 production units to producing wine. a. What is the production and consumption of China and France without trade? b. Assume complete specialization, where China produces only toys and France produces only wine. What would be the effect on total production? a. What is the production and consumption of China and France without trade? Calculate the production and consumption of China and France without trade below: (Round to the nearest integer.) Production if there is no trade Toys CHINA Allocated production units to Produces and consumes FRANCE Allocated production units to Produces and consumes Total production and consumption across both countriesConsider the following pseudocode for a sorting algorithm: SORTING-ALG(X) n = X. length for a = 1 to n - 1 hold = a for b = a+1 to n if X[b] > X[hold] hold = b trade X[a] with X[hold] a) What is the O worst-case running time of this algorithm? b) What is the best-case running time of this algorithm? c) Can we assert a general running time of this algorithm? If so, what is it? If not, why not? d) In the first loop, why does it need to only loop for n-1 times? e) What is the result of this algorithm?Problem # 7 (5 points) Demonstrate how to use base -ten manipulatives to model a subtraction algorithm for 225- 47. Use simplified drawings of the base ten materials as shown. For each step draw a sketch so, that it corresponds to the given step of the standard algorithm beside it. Steps Base - Ten Materials Standard Algorithm a. Show initial quantity 225 4 7 b. Show first Trade c. Show second Trade d. Show Subtraction State the Answer Problem # 8 (5 + 5 points) Add or subtract in base-five. Show all makings that correspond to the standard algorithms for addition and subtraction: 4324five 402five 321 five 123five
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


