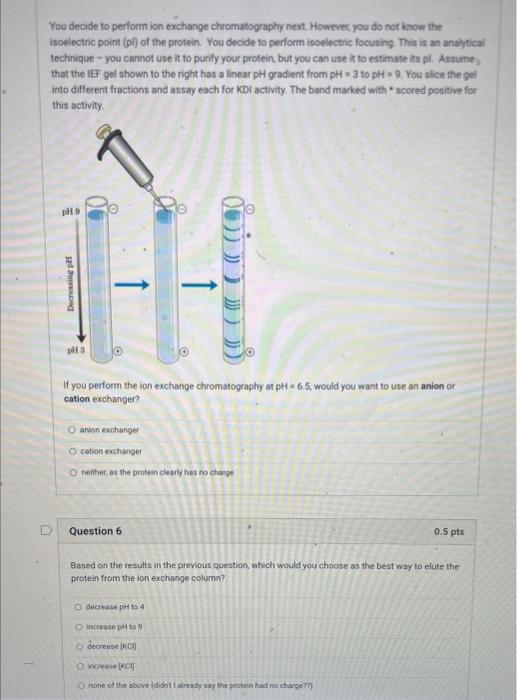
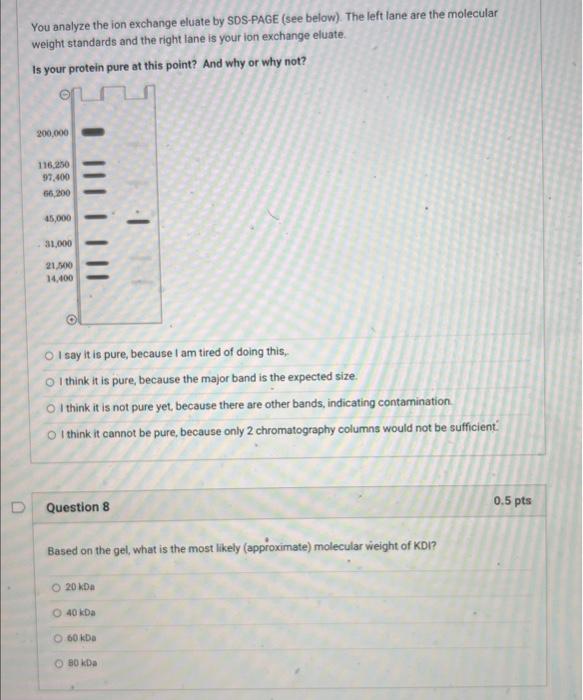
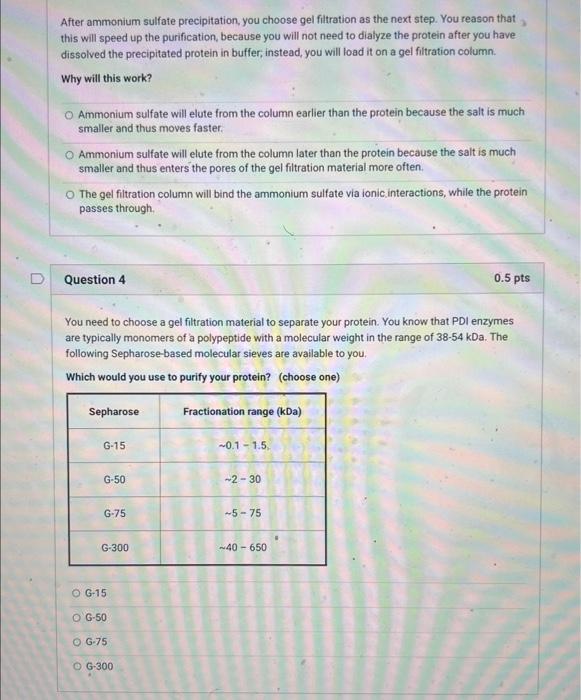
You decide to perform ion exchange chromatography next. Howevec, you do not know the isoelectric point (p) of the protein. You decide to perform isoelectric focuting. This is an anaytical technique - you cannot use in to purify your profein but you can use it to eatimate its pt. Assume, that the IEF gel shown to the night has a linear pH gradient from pH=3 to pH=9. You slice the gel into different fractions and assay each for KDI activity. The band marked with * scored positive for this activity. If you perform the ion exchange chromatography at pH=6.5, would you want to use an anion or cation exchanger? anvon exchanger cation exchanger neithet, as the protein cleably has no charge Question 6 0.5pts Based on the results in the previous question, which would you choose as the best way to elute the protein from the ion exchange column? decrease pht to 4 increase pH to 9 decrease ikgli wisewhe pocel none of the above (didoit I aliesdy say the peoten had no chargemy You analyze the ion exchange eluate by SDSPAGE (see below). The left lane are the molecular weight standards and the right lane is your ion exchange eluate. Is your protein pure at this point? And why or why not? I say it is pure, because I am tired of doing this, I think it is pure, because the major band is the expected size. I think it is not pure yet, because there are other bands, indicating contamination. I think it cannot be pure, because only 2 chromatography columns would not be sufficient. Question 8 0.5 pts Based on the gel, what is the most likely (approximate) molecular wieight of KDI? 20kDa 40kDa 60kDa 80kDa You turn to affinity purification for your last step. You make a column to which you attach hair keratin. You know that the PDI mechanism involves a transient intermediate in which the protein is covalently linked to its substrate via a disulfide linkage. (The protein has two thiols. After the first stage of the reaction, it has reduced a disulfide and its two thiols are oxidized to an internal disulfide. In the second stage, the oxidized enzyme oxidizes two thiols on a new substrate, regenerating its two thiols and making a new disulfide on the substrate.) You also know that the affinity of KDI for keratin is not very high. You reason that you can load the ion exchange eluate on the column, wash it with buffer, and then elute KDI with buffer containing DTT (dithiothreitol). Which of the following is NOT true about this strategy? Only proteins that bind to keratin in some way will be initially retained on the column. Proteins that do not bind keratin at all will pass through. DTT should cause KDI to elute because it will reduce all disulfides, including the ones between KDI and keratin that are generated as part of the enzyme mechanism. DTT should cause KDI to elute because KDI is expected to have affinity for DTT. Proteins that bind keratin non-covalently should not be eluted by DTT. After ammonium sulfate precipitation, you choose gel filtration as the next step. You reason that this will speed up the purification, because you will not need to dialyze the protein after you have dissolved the precipitated protein in buffer, instead, you will load it on a gel filtration column. Why will this work? Ammonium sulfate will elute from the column earlier than the protein because the salt is much smaller and thus moves faster. Ammonium sulfate will elute from the column later than the protein because the salt is much smaller and thus enters the pores of the gel filtration material more often. The gel filtration column will bind the ammonium sulfate via ionic. interactions, while the protein passes through. Question 4 0.5 pts You need to choose a gel filtration material to separate your protein. You know that PDI enzymes are typically monomers of a polypeptide with a molecular weight in the range of 3854kDa. The following Sepharose-based molecular sieves are available to you. Which would you use to purify your protein? (choose one) G-15