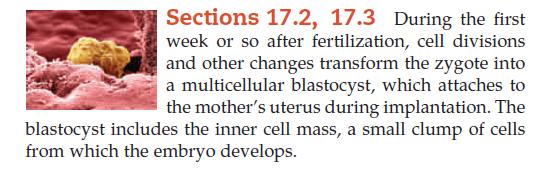
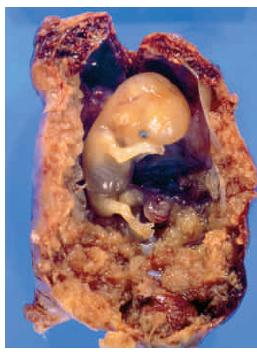
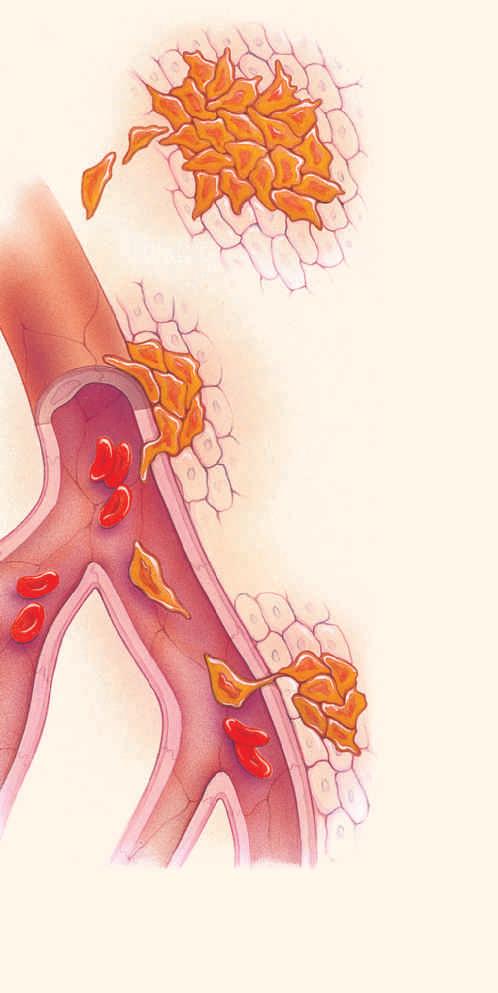
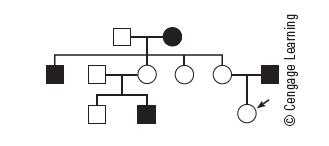
Human Biology 11th Edition Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan - Solutions
Discover the ultimate resource for mastering "Human Biology 11th Edition" by Cecie Starr and Beverly McMillan. Access our comprehensive solutions manual, featuring step-by-step answers and a detailed instructor manual. Our expertly crafted solutions PDF provides answers key to complex questions, ensuring a thorough understanding of each chapter. Explore the test bank, complete with solved problems and chapter solutions, tailored to enhance your learning experience. Benefit from free downloads of textbook solutions and online answers, all designed to assist in your academic journey. Unlock the potential of your studies with our online platform, offering unparalleled guidance and support.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()