Major newspapers lose their credibility (and subscribers) when they are found to have published deceptive or misleading
Question:
Major newspapers lose their credibility (and subscribers) when they are found to have published deceptive or misleading news stories. In Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly (Summer 2007), University of Texas researchers investigated whether certain stereotypes (e.g., negative references to certain nationalities) occur more often in deceptive news stories than in authentic news stories. The researchers analyzed 183 news stories that were proven to be deceptive in nature and 128 news stories that were considered authentic. Specifically, the researchers determined whether each story was negative, neutral, or positive in tone. The accompanying table gives the number of news stories found in each tone category.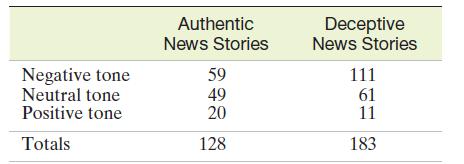
a. Find the sample proportion of negative tone news stories that are deceptive.
b. Find the sample proportion of neutral news stories that are deceptive.
c. Find the sample proportion of positive news stories that are deceptive.
d. Compare the sample proportions, parts a–c. Does it appear that the proportion of news stories that are deceptive depends on story tone?
e. Give the null hypothesis for testing whether the authenticity of a news story depends on tone.
f. Conduct the test, at α = .05.
Step by Step Answer:

Statistics For Business And Economics
ISBN: 9780136855354
14th Edition
Authors: James T. McClave, P. George Benson, Terry T Sincich





