Overoxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids is caused by the water present in the usual aqueous
Question:
Overoxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids is caused by the water present in the usual aqueous acidic Cr(VI) reagents. The water adds to the initial aldehyde product to form a hydrate, which is further oxidized. In view of these facts, explain the following two observations.
(a) Water adds to ketones to form hydrates, but no overoxidation follows the conversion of a secondary alcohol into a ketone.
(b) Successful oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes by the water-free PCC reagent requires that the alcohol be added slowly to the Cr(VI) reagent. If, instead, the PCC is added to the alcohol, a new side reaction forms an ester. This is illustrated for 1-butanol.
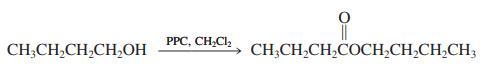
(c) Give the products expected from reaction of 3-phenyl-1-propanol and water-free CrO3 (1) when the alcohol is added to the oxidizing agent and (2) when the oxidant is added to the alcohol.
Step by Step Answer:

Organic Chemistry structure and function
ISBN: 978-1429204941
6th edition
Authors: K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil E. Schore





