Treatment of a-terpineol (Chapter 10, Problem 60) with aqueous mercuric acetate followed by sodium borohydride reduction leads
Question:
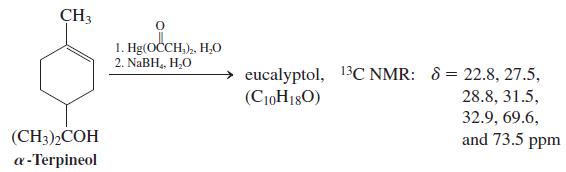
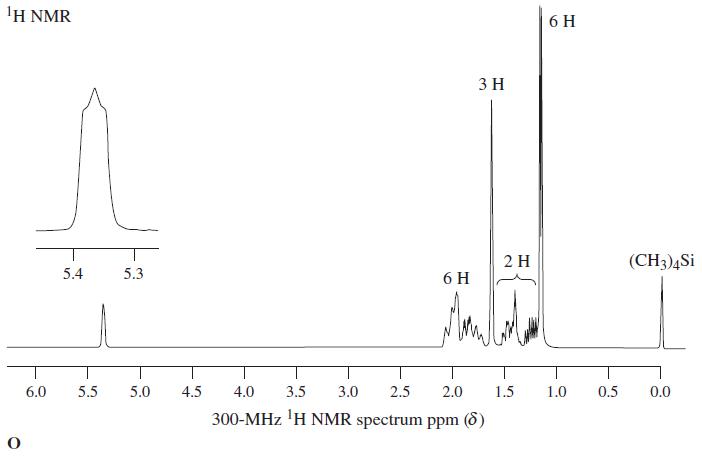
Treatment of a-terpineol (Chapter 10, Problem 60) with aqueous mercuric acetate followed by sodium borohydride reduction leads predominantly to an isomer of the starting compound (C10H18O) instead of a hydration product. This isomer is the chief component in oil of eucalyptus and, appropriately enough, is called eucalyptol. It is popularly used as a flavoring for otherwise foul-tasting medicines because of its pleasant spicy taste and aroma. Deduce a structure for eucalyptol on the basis of sensible mechanistic chemistry and the following proton-decoupled 13C NMR data.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Organic Chemistry structure and function
ISBN: 978-1429204941
6th edition
Authors: K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil E. Schore
Question Posted:




