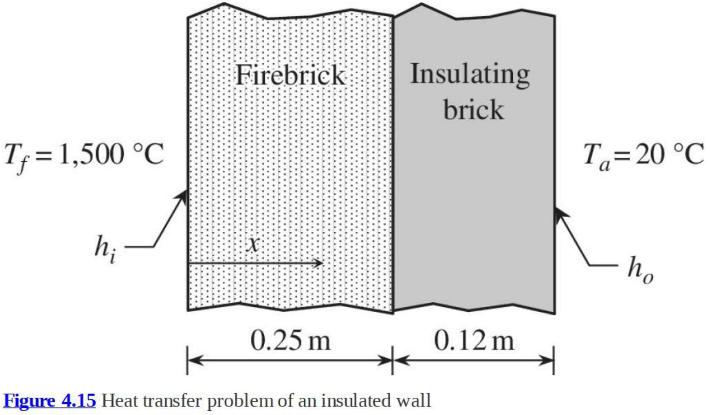
A furnace wall, as shown in figure 4.15, consists of two layers, firebrick inside and insulating brick
Question:
A furnace wall, as shown in figure 4.15, consists of two layers, firebrick inside and insulating brick on the outside. The thermal conductivities are \(k_{1}=1.2 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m} /{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) for the firebrick and \(k_{2}=0.2 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m} /{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) for the insulating brick. The temperature inside the furnace is \(T_{f}=1,500{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), and the convection coefficient at the inner surface is \(h_{i}=12 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m}^{2} /{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The ambient temperature is \(T_{a}=25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), and the convection coefficient at the outer surface is \(h_{o}=2.0 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m}^{2} /{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The thermal resistance of the interface between firebrick and insulating brick can be neglected. Using two finite elements (one for each brick), determine the rate of heat loss through the outer wall, the temperature \(T_{i}\) at the inner surface, and the temperature \(T_{o}\) at the outer surface.
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
ISBN: 9781119078722
2nd Edition
Authors: Nam H. Kim, Bhavani V. Sankar, Ashok V. Kumar





