Question: According to its directional distribution, solar radiation incident on the earth's surface may be divided into two components. The direct component consists of parallel rays
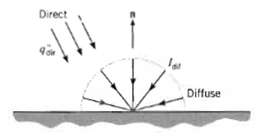
According to its directional distribution, solar radiation incident on the earth's surface may be divided into two components. The direct component consists of parallel rays incident at a fixed zenith angle ?, while the diffuse component consists of radiation that may be approximated as being diffusely distributed with ?. Consider clear sky conditions for which the direct radiation is incident at ? = 30?, with a total flux (based on an area that is normal to the rays) of q''dir = 1000 W/m2, and the total intensity of the diffuse radiation is 1 dif = 70 W/m2 ? sr. What is the total solar irradiation at the earth's surface?
Direct Diffuse
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (182 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Flux and intensity of direct and diffuse components respective... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (1089).docx
120 KBs Word File


