Question: Air at 320 K with a free stream velocity of 10 m/s is used to cool small electronic devices mounted on a printed circuit board
Air at 320 K with a free stream velocity of 10 m/s is used to cool small electronic devices mounted on a printed circuit board as shown in the sketch below. Each device is 5 mm × 5 mm square in plane-form and dissipates 60 milliwatts. A turbulator is located at the leading edge to trip the boundary layer so that it will become turbulent. Assuming that the lower surface of the electronic devices are insulated, estimate the surface temperature at the center of the fifth device on the circuit board.GIVENAir flows over small electronic devicesAir temperature (T??) = 320 KAir velocity (U?? = 10 m/sDimensions of each device = 5 mm × 5 mm = .005 m × .005 mPower dissipation per device (qG) = 60 milliwatts = 0.06 WThere is a turbulator at the leading edgeASSUMPTIONSSteady stateLower surface of the devices is insulated (negligible heat loss)The devices are placed edge-to-edge on the boardThe boundary layer is turbulent from the leading edge onThe bulk fluid temperature isconstant
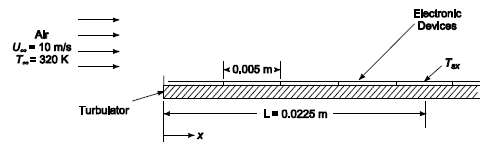
Electronic Al Devlces U.- 10 m/s T= 320 K k0.005 m> Tex L- 0.0225 m Turbulator
Step by Step Solution
3.29 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The center of the fifth chip is 00225 m from the leading edge The R... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
66-E-M-E-H-M-T (1654).docx
120 KBs Word File


