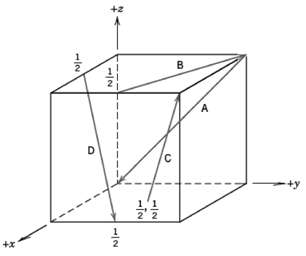
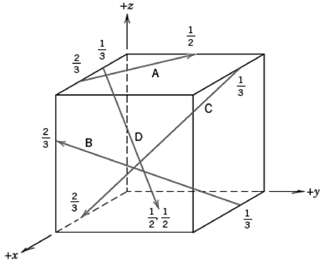
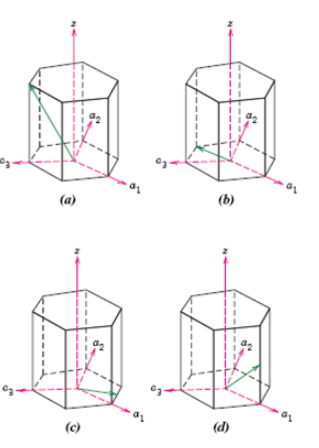
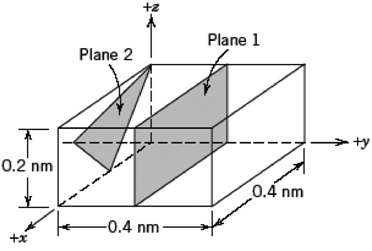
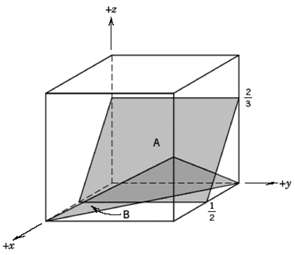
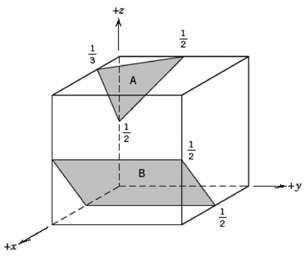
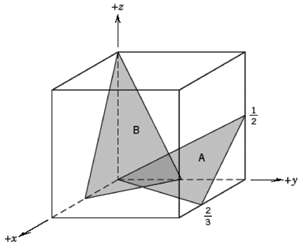
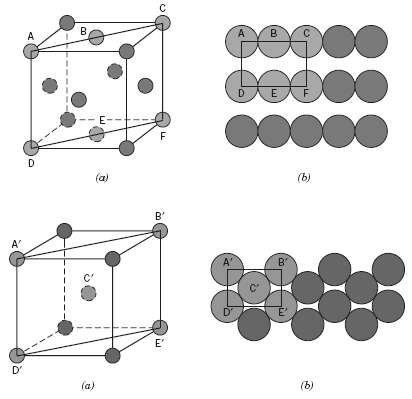
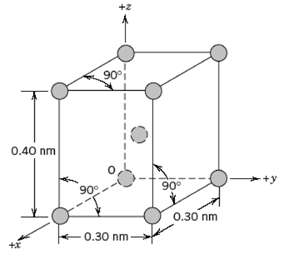
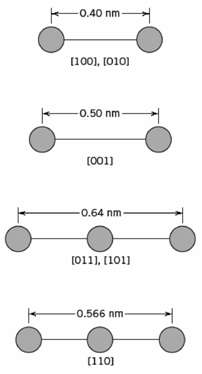
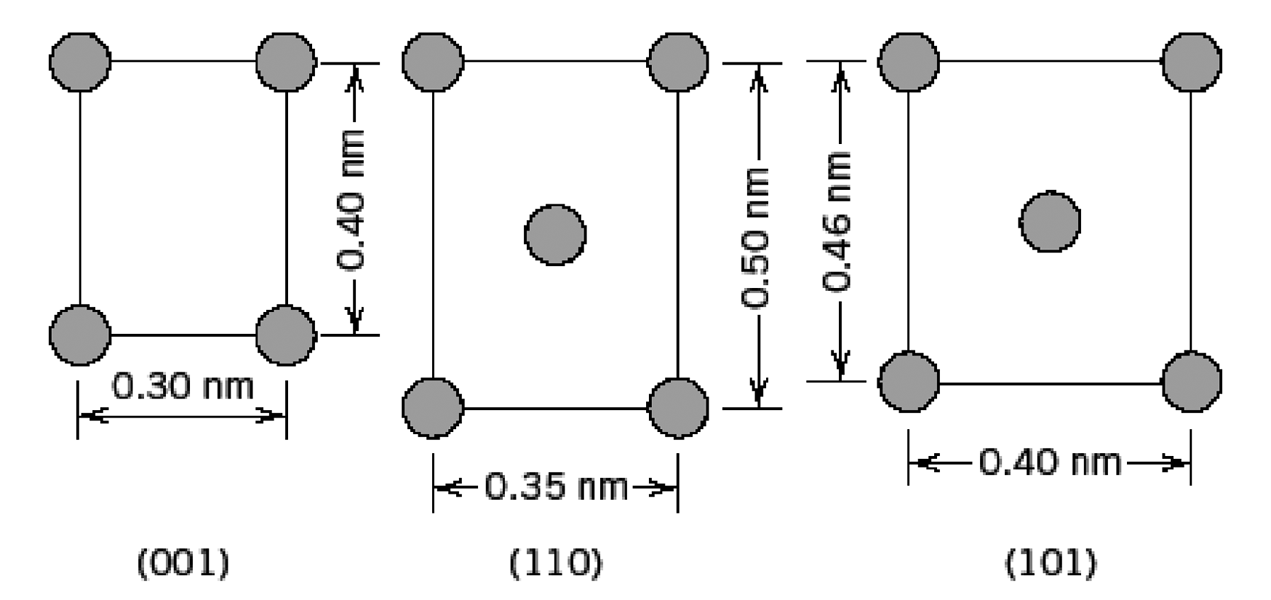
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering An Integrated Approach 4th Edition David G. Rethwisch - Solutions
Discover the ultimate resource for "Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering: An Integrated Approach, 4th Edition" by David G. Rethwisch. Our comprehensive online platform provides an extensive answers key and solutions manual, offering detailed step-by-step answers and solved problems for all chapters. Access the complete test bank, instructor manual, and textbook solutions in an easy-to-use solutions PDF format. Whether you're looking for chapter solutions or questions and answers, our free download ensures you have the tools you need for academic success. Dive into the world of materials science with confidence and ease.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()