The classical RK for a first-order ODE extends to second-order ODEs. If the ODE is y =
Question:
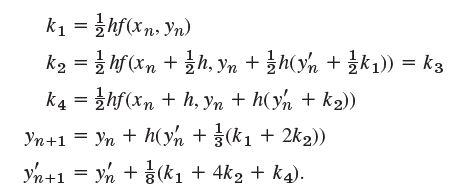
Apply this RKN (Runge€“Kutta€“Nyström) method to the Airy ODE in Example 2 with h = 0.2 as before, to obtain approximate values of Ai(x).
Transcribed Image Text:
k1 = }hf(xn, Yn) k2 = 3 hf (xn + }h, yn + h(yn + 3k1)) = k3 k4 = zhf(Xn + h, Yn + h( yn + k2)) %3D Yn+1 = yn + h(yn + (k1 + 2k2)) yn +1 = yn + (k1 + 4k2 + k4).
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Answer rating: 75% (8 reviews)
We obtain and the following numeric v...View the full answer

Answered By

Pushpinder Singh
Currently, I am PhD scholar with Indian Statistical problem, working in applied statistics and real life data problems. I have done several projects in Statistics especially Time Series data analysis, Regression Techniques.
I am Master in Statistics from Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
I have been teaching students for various University entrance exams and passing grades in Graduation and Post-Graduation.I have expertise in solving problems in Statistics for more than 2 years now.I am a subject expert in Statistics with Assignmentpedia.com.
4.40+
3+ Reviews
10+ Question Solved
Related Book For 

Question Posted:
Students also viewed these Mathematics questions
-
Solve by the classical RK. The system in Prob. 2 Data from Prob. 2 y' 1 = -y 1 + y 2 , y' 2 = -y 1 - y 2 , y 1 (0) = 0, y 2 (0) = 4, h = 0.2, 5 steps
-
Solve by the classical RK. The system in Prob. 4 Data from Prob. 4 Solve by the Eulers method. Graph the solution in the y 1 y 2 -plane. Calculate the errors. y' 1 = -3y 1 + y 2 , y' 2 = y 1 - 3y 2 ,...
-
Develop a user-friendly computer program for the classical fourth-order RK method. Test the program by duplicating Example 25.7.
-
Elevator Controller The block diagram for an elevator controller for a two-floorelevator follows. The inputs FB1 and FB2 are 1 when someone in the elevatorpresses the first and secondfloor buttons,...
-
What is the major difference between household accounting and business accounting?
-
You are an expert on GAAP and the quality of financial reporting, with extensive experience in rational investing. You determine the current quality of financial reporting as summarized in the...
-
A population of N 5 8 scores has a standard deviation of s 5
-
Lowery, Inc. purchased new plant equipment on January 1, 2011. The company paid $920,000 for the equipment, $62,000 for transportation of the equipment, and $10,000 for insurance on the equipment...
-
K At age 25, someone sets up an IRA (individual retirement account) with an APR of 8% At t contain when he retires at age 65? Compare that amount to the total deposits made over t After retirement...
-
BOOTS, Inc., recently completed work on a 1 year, $10 million contract for technical support services awarded by the US Army. The contract included a small business subcontracting plan, and it also...
-
One of Suzannes project engineers e-mailed her the screen-shot (below) of his spreadsheet analysis of the annual costs and savings for two equivalent systems considered for installation as a major...
-
What are the similarities between frequency hopping and TDMA?
-
What is the purpose of a subsidiary ledger?
-
Required information Use the following information for the Exercises below. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Ramirez Company installs a computerized...
-
Reproduced below from Farthington Supply s accounting records is the accounts receivable subledger along with selected general ledger accounts. General Ledger Accounts Receivable Dec. 3 1 / 2 2...
-
James A. and Ella R. Polk, ages 70 and 65, respectively, are retired physicians who live at 3319 Taylorcrest Street, Houston, Texas 77079. Their three adult children (Benjamin Polk, Michael Polk, and...
-
Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Shauna Coleman is single. She is employed as an architectural designer for Streamline Design (SD). Shauna...
-
The following are the ratings of men by women in an experiment involving speed dating. Use the given data to construct a boxplot and identify the 5-number summary. 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.5 5.5 6.5 6.5 6.5...
-
What would happen to the exchange value of euros in terms of U.S. dollars if incomes rose in both Europe and the U.S.?
-
r = 0.18 Find the coefficients of determination and non-determination and explain the meaning of each.
-
Evaluate the strength of evidence for the hypotheses in the previous question. a. Find the p-value for the hypotheses in the previous question using a simulation-based approach. b. Based on the...
-
The survey also asked participants to report the time the respondent spent reading or watching news coverage about the trial during the last three days. The poll found that, on average, respondents...
-
Among the sample, the information for three particular respondents is given here: (i) Respondent 1 reported spending 240 minutes in the last three days reading/watching news coverage about the trial...
-
When direct materials are issued from the storeroom, are any entries made in the subsidiary records? Question 2 options: Increase raw material item record Decrease raw material item record No entry...
-
Riverrun Co. provides medical care and insurance benefits to its retirees. In the current year, Riverrun agrees to pay $5,500 for medical insurance and contribute an additional $9,000 to a retirement...
-
DETAILS 1. [-/1 Points) SMITHNM13 11.2.025. MY NOTES Convert the credit card rate to the APR. Oregon, 2% per month % Need Help? ReadIt Watch

Study smarter with the SolutionInn App


