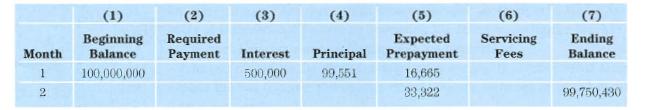
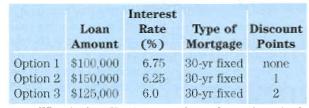
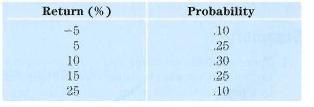
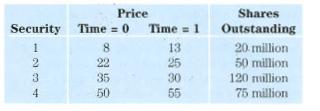Financial Markets and Institutions 5th edition Frederic S. Mishkin, Stanley G. Eakins - Solutions
Unlock the secrets of financial understanding with the "Financial Markets and Institutions 5th Edition" by Frederic S. Mishkin and Stanley G. Eakins. Access comprehensive solutions and answers key to all your questions in one convenient location. Whether you're searching for a solution manual, solutions PDF, or step-by-step answers, our resource has you covered. Explore solved problems and detailed chapter solutions to enhance your learning experience. Dive into the instructor manual and test bank for in-depth insights and textbook guidance. Best of all, enjoy the convenience of free download and online access to elevate your financial knowledge effortlessly.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()