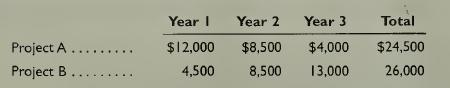
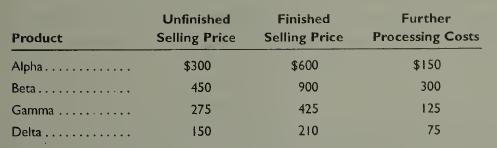
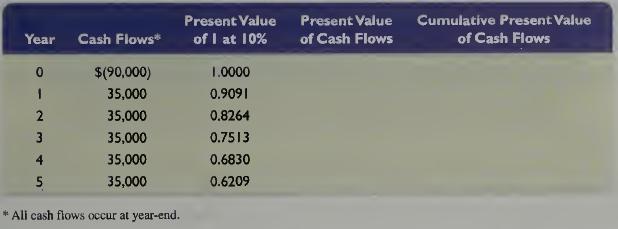
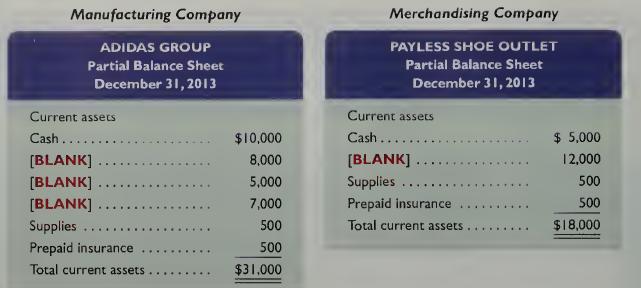
Fundamental Accounting Principles Volume 2 21st Edition John Wild, Ken Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta - Solutions
Unlock the full potential of "Fundamental Accounting Principles Volume 2 21st Edition" by John Wild, Ken Shaw, and Barbara Chiappetta with our comprehensive resources. Access the answers key and solution manual to explore detailed solutions in PDF format. Discover solved problems and step-by-step answers tailored for each chapter, ensuring a thorough understanding of the textbook material. Whether you're preparing for exams with the test bank or seeking instructor manual insights, our online platform offers reliable questions and answers. Enjoy the convenience of a free download, providing you with essential chapter solutions and a complete guide to mastering accounting principles.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()