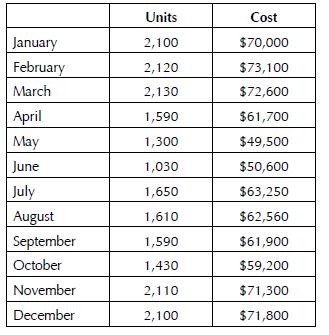
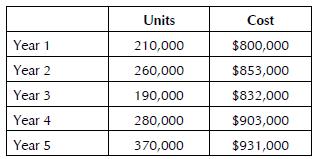
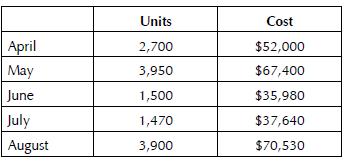
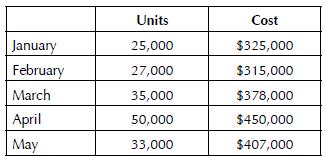
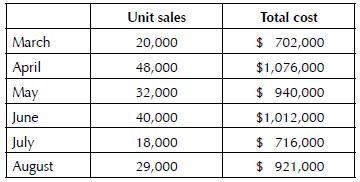
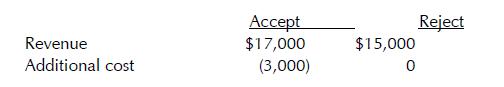Accounting 23rd Edition Carl S. Warren - Solutions
Unlock the potential of your studies with the "Accounting 23rd Edition" by Carl S. Warren. Dive into a comprehensive collection of solved problems and detailed questions and answers designed to enhance your understanding. Access the solution manual and answers key, providing step-by-step answers to streamline your learning process. Explore the test bank for thorough preparation and benefit from chapter solutions and the instructor manual, offering in-depth insights into textbook material. Experience seamless learning with solutions available in a convenient PDF format, available for free download, ensuring you have the necessary tools at your fingertips.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()